Common Network Terms 4.15
advertisement

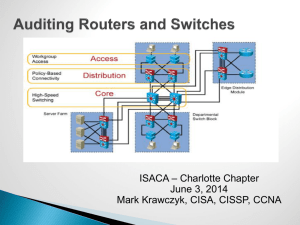
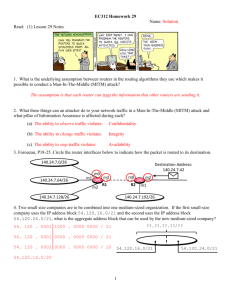
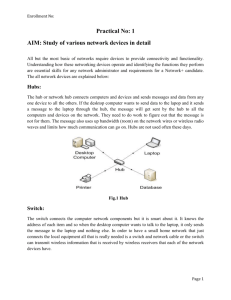
COMMON NETWORK TERMS Active Directory Active Directory serves as a central location for network administration and security. It is responsible for authenticating and authorizing all users and computers within a network of Windows domain type, assigning and enforcing security policies. Backbone a part of computer network infrastructure that interconnects various pieces of network, providing a path for the exchange of information between different Local Area Networks (LANs). A backbone can tie together diverse networks in the same building, in different buildings in a campus environment, or over wide areas. DNS Server A server connected to a network that resolves network names into network addresses. Domain Name System (DNS) is a database system that translates a computer's fully qualified domain name into an IP address. Dual Powered In essence, this is a power supply that actually includes two (or more) units within it, each of which is capable of powering the entire system by itself. If for some reason there is a failure in one of the units, the other one will seamlessly take over to prevent the loss of power. EPO Switch Short for emergency power off; also referred to as an EPO switch. A button or switch that shuts down the power in the data center. Typically used where there are large amounts of computers using large amounts of electricity, the EPO is meant to be activated by a human only in emergency situations when it is necessary to cut the power if human life is in jeopardy or if there is the potential for major damage to the building or equipment (e.g., in the case of a fire or electrocution). The sudden loss of power will inevitably lead to the loss of some data, and the EPO is not meant to be used under normal circumstances. Firewall A device or a software package that separates more secure network components from less secure components, protecting the more secure network from inappropriate access. Hot-Swappable Term used to describe the functions of replacing computer system components without shutting down the system.. I/O Input/Output. refers to the communication between an information processing system (such as a computer), and the outside world, possibly a human, or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system, and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. IOS – Internetworking Operating System IOS Cisco operating system software that runs the switches and routers. IP Internet Protocol. The network layer protocol in the TCP/IP stack offering a connectionless internetwork service. IP Address An address assigned to hosts using TCP/IP. It is used to speak to devices on other networks via the connecting router. KVM Switch Abbreviation for keyboard, video display unit, mouse. It is a hardware device that allows a user to control multiple computers from a single keyboard, video monitor and mouse. MAC address Media Access Control (MAC) address. A standardized address that is required for every device that connects to a LAN. It is used by the connecting switch to allow communication. MAC address is a unique value associated with a network adapter. MAC addresses are also known as hardware addresses or physical addresses. Multicast Multicast is a routing technique that allows IP traffic to be sent from one source or multiple sources and delivered to multiple destinations. Network A collection of computers, printers, routers, switches, and other devices that can communicate with each other over some transmission medium. Network Chassis AKA Blade Enclosure. Blade servers function well for specific purposes such as web hosting, virtualization, and cluster computing. Individual blades are typically hotswappable. They add more processing power, memory and I/O bandwidth to blade servers. OS Operating System. An operating system or OS, is a software program that enables the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software. For example Windows XP, Windows 7, etc…. Router A network device that forwards data packets between computer networks and switches Routing Protocol/OSPF OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), a protocol that accomplishes routing through the implementation of a specific routing algorithm. Security Patch A patch is a piece of software designed to fix problems with, or update a computer program or its supporting data. This includes fixing security vulnerabilities and other bugs, and improving the usability or performance.. Security Vulnerability Is a weakness which allows an attacker to reduce a system's information assurance. Vulnerability is the intersection of three elements: a system susceptibility or flaw, attacker access to the flaw, and attacker capability to exploit the flaw. Subnet Subnets are subdivisions of a Class A, B, or C network, as configured by a network administrator. Subnets allow a single Class A, B, or C network to be used instead of multiple networks, and still allow for a large number of groups of IP addresses, as is required for efficient IP routing. Switch A network device that joins multiple computers together TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol Is a common name for the suite of protocols developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s to support the construction of worldwide internetworks. TCP and IP are the two best-known protocols in the suite. These specific networking protocols enable computers to communicate over a network. UPS Uninterruptable Power Supply. This is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails. VLAN Virtual Local Area Network, A group of devices on one or more LANs (Local Area Networks) that are configured so that they can communicate as if they were attached to the same wire, when, in fact, they are located on a number of different LAN segments. WAN Wide Area Network is a telecommunication network that covers a broad area. Business and government entities utilize WANs to relay data among employees, clients, buyers, and suppliers from various geographical locations. In essence this mode of telecommunication allows a business to effectively carry out its daily function regardless of location. What is a Network Switch versus a Router? Switches create a network. Routers connect networks. A router links computers to the Internet, so users can share the connection. A router acts as a dispatcher, choosing the best path for information to travel so it's received quickly. Note: In our network, some switches also perform the routing capacity. WiFi A popular technology that allows an electronic device to exchange data wirelessly (using radio waves) over a computer network. Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances. Wireless Access Point (WAP or AP) A device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards. The WAP usually connects to a router (via a wired network), and can relay data between the wireless devices (such as computers or printers) and wired devices on the network.