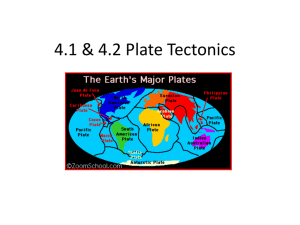
Plate Tectonics Fall 2015
advertisement

READING QUESTIONS: Plate Tectonics NAME________________________ PSCI 131 DUE: Monday, December 14th Fall 2015 52 pts Continental Drift: An Idea Before Its Time (p. 71-74) 1. List Alfred Wegener’s four lines of evidence for continental drift: (4 pts) a. _______________________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________________ c. _______________________________________________________ d. _______________________________________________________ 2. In the early 20th century, before continental drift, what were the three prevailing explanations for how land animals migrated across large oceans? (3 pts) a. ___________________________________________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________________________________________ c. ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. Fill in the blanks: Wegener suggested that a plausible explanation for the late Paleozoic ________________ was provided by the supercontinent of ___________________. In this configuration, the southern ________________________ are joined together and located near the ________________________. This would account for the conditions necessary to generate extensive expanses of _______________________ over much of these landmasses. At the same time, this geography would place today’s _________________________ continents nearer the ________________________ and account for the tropical _________________ that generated the vast __________________________. (5 pts) The Great Debate (p. 75-76) 4. What mechanism did Wegener propose for continental drift, and what objection did physicist Harold Jeffreys have to this mechanism? (4 pts) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________(more space on next page) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Fill in the blanks: Wegener incorrectly suggested that the larger, sturdier continents ________________________ the thinner oceanic crust, much as ____________________________ cut through ice. No evidence existed to suggest that the ocean floor was _____________ enough to permit passage of the continents without the continents being appreciably _____________________ in the process. (2 pts) The Theory of Plate Tectonics (p. 76-78) 6. What major ocean floor feature did oceanographers discover the extent of after World War II? _____________________________________ 7. Next to each characteristic below, indicate whether it applies to continental lithosphere, oceanic lithosphere, both kinds of lithosphere, or the asthenosphere. Indicate your choice by writing “C”, “O”, “CO”, or “A” next to each characteristic. (3 pts) a. Cool _____ b. Warm _____ c. Flows _____ d. Bends or breaks _____ e. Mafic in composition _____ f. Felsic in composition _____ 8. Match the name of each type of plate boundary with the arrows that show the kind of motion that occurs there. (3 pts) a. Transform ___ A. b. Divergent ___ B. c. Convergent___ C. Divergent Plate Boundaries and Seafloor Spreading (p. 78-81) 9. What is the average rate of seafloor spreading in modern oceans? _______ cm/year 10. Fill in the blanks: The primary reason for the ___________________ position of the oceanic ridge is that newly created lithosphere is ______, which means it is ________________ than cooler rocks found away from the ridge axis. (3 pts) 11. Examine figure 15 and fill in the blanks: Continental rifting occurs where plate motions produce __________________ forces that ________ the lithosphere and promote upwelling in the mantle. Stretching causes the brittle crust to ____________ into large ____________ that sink, generating a ________________. Continued spreading generates a long, narrow _______ similar to the presentday Red Sea. Eventually, an expansive _____________________ containing a centrally located _________________ is formed by continued seafloor spreading. (4 pts) Convergent Plate Boundaries and Subduction (p. 81-84) 12. Why does the global rate of lithosphere creation roughly balance with the rate of lithosphere destruction? (2 pts) _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Fill in the blanks: The angle at which an oceanic plate subducts depends largely on its _____ and therefore its ________________. (2 pts) 14. List the three possible combinations of lithosphere types that can occur at a convergent boundary. (3 pts) a. _______________________________ b. _______________________________ c. _______________________________ 15. EXTRA CREDIT: List one geographic example of a modern volcanic island arc, and one example of a continental volcanic arc. (2 pts) a. Volcanic island arc: _______________________________ b. Continental volcanic arc: ______________________________ 16. On page 81, the textbook refers to deep-ocean trenches as “surface manifestations” of subduction zones. Why does the book use the word “surface” even though these trenches are located in the deepest parts of the oceans? (2 pts) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 17. Oceanic lithosphere subducts because it is ____________________ than the asthenosphere beneath it. 18. Give a brief description of how the Himalayas formed, with reference to the buoyancy of continental lithosphere. (3 pts) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Transform Plate Boundaries (p. 85-86) 19. On this diagram of a fracture zone along an oceanic ridge, label the segment of the zone that is an active transform boundary by marking a “T” on one of the three blanks. 20. EXTRA CREDIT: List two examples of transform boundaries that cut through continental crust instead of through ocean basins. (2 pts) a. ________________________________________ b. ________________________________________ Testing the Plate Tectonics Model (p. 89-94) 21. What is the age of the oldest sediments recovered by deep-sea drilling? ______________________ 22. Continental rocks have been discovered that are older than _____________________ years. 23. Fill in the blanks: Drill cores have revealed that sediments are almost entirely ___________ on the crests of oceanic ____________, and that sediment thickness ______________ with increasing distance from the ridge. This suggests that the age of the ocean crust _______________ the further it is from an oceanic ridge. (2 pts) 24. Examine figure 32A on page 93. The white stripes indicate oceanic crust exhibiting normal magnetic polarity, and the red stripes indicate reversed polarity. How many time intervals of reversed polarity are represented by the oceanic crust in this figure? (Remember that, during each time interval of reversed or normal polarity, two stripes of crust with that polarity are created along divergent boundaries.) Number of time intervals of reversed polarity: ________