4.1 & 4.2 Plate Tectonics
advertisement
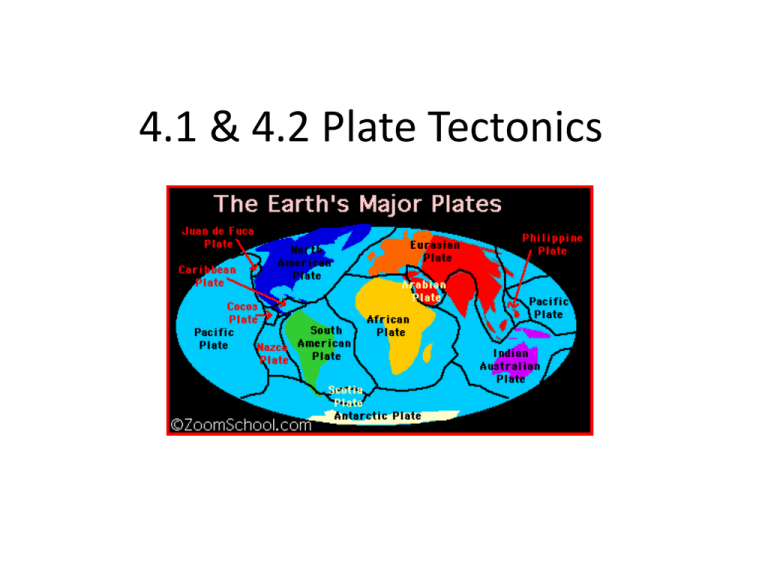
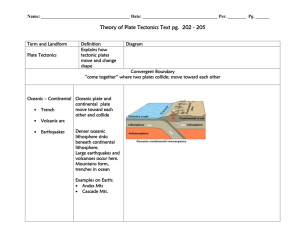
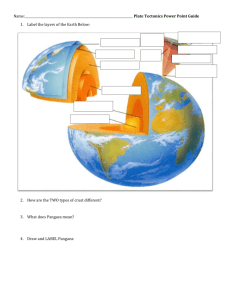
4.1 & 4.2 Plate Tectonics As explorers began bringing back information about the world, map makers began to notice the coastlines of continents could possibly be matched up…… • Where the continents once touching???? • This led to the formation of a hypothesis. Continental Drift • Hypothesis that continents had moved. – Pangaea: single landmass – Panthalassa: all seas Evidence for Continental Drift 1) Fossils of plants and animals in areas that would have been joined in Pangaea 2) Similar age and types of rocks • South America (Brazil) and Africa Evidence of Continental Drift 3) Sea floor Spreading • Mid Ocean Ridges 4) Paleomagnetism 3) Seafloor spreading • Newest rock is found at mid ocean ridges • The mid ocean ridges are breaks where magma flows up from with in the earth forming new rock. • Ocean floor is moving away from these rifts Journal: Seafloor spreading • Where is the newest (youngest) oceanic rock found in the diagram? • Where is the oldest oceanic rock found in the diagram? A B C Journal • In your own words, describe seafloor spreading: 4) Paleomagnetism • As magma solidifies, the iron in it aligns with earth’s magnetic field. • As earth’s poles switched, the iron bands polarity switched as well. • There is a pattern on each side of a mid ocean ridge which shows that the sides where formed at the same time and then spread out! The Theory of Plate Tectonics • Describes continental movement and proposes an explanation – 2 types of Crust Oceanic & Continental which make up the lithosphere – Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere which had the ability to flow. The Theory of Plate Tectonics • The pieces of lithosphere float on top of the asthenosphere What causes plate motion??? • Convection Currents: warm material rising, cool material sinking – Based on density differences – Less dense materials rise (warm magma) – More dense materials sink (cool magma) What causes plate motion??? In plate tectonics, - cycle of warm magma rising up to the lithosphere where it cools and solidifies - The new lithosphere moves away from the mid ocean ridges - It cools and becomes more dense - It eventually is subducted into the asthenosphere 3 main types of Plate Boundaries • Divergent • Convergent • Transform/ Transverse Journal – What does the word diverge mean? – What does the word converge mean? Journal: Boundaries Divergent Convergent Transform/ Transverse Divergent Boundaries • Two plates moving away from each other • Forms: – Rift Valley (Continental/Continental) – Mid Ocean Ridges (Oceanic/Oceanic) Convergent Boundaries • The direct collision of two plates – Oceanic-Continental • Form subduction zones and volcanoes – Continental-Continental • Form mountains – Oceanic-Oceanic • Form Island arcs Transform/Transverse Boundaries • When two plates move past each other – Form Faults – Can you name a famous local fault??? Microplate Terranes • Continents are a patchwork of terranes • Terranes: pieces of lithosphere – Own geological history – Separated by faults at its boundaries – Own magnetic properties On a separate piece of paper…. Quiz yourself: 1. Name and describe the 3 types of plate boundaries. 2. At what type of boundary would island arcs be found? 3. What is the evidence for continental drift?