Covalent Bonding & Molecular Shapes: Chemistry Study Guide
advertisement

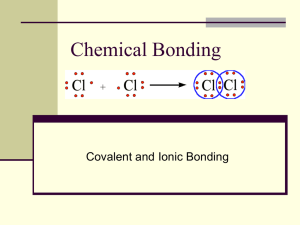
Thursday Oct 8 Naming acids Fri Oct 9 Naming Covalent compounds Mon Oct 12 Ionic vs. covalent lab Venn Ionic vs. Cov. Tues Oct 13 Quiz over acids & covalent compounds / Dot diagrams Wed Oct 14 PSAT for all 10th grade (11th grade report to Mrs Jones) VSEPR theory minilab Thurs Oct 15 continue Minilab – polar vs. nonpolar / Work time Fri Oct 16 workday Monday Oct 19 Review Tuesday Oct 20 TEST – NB check Georgia Performance Standard: SC1 d – Name and write formulas for covalent compounds and acids. SC3 e – Compare and contrast types of chemical bonds. (Ionic & covalent) Why are valence electrons related to the nature of the chemical bond? KQ - How does an ionic bond compare to a covalent bond? KQ - How do you use electronegativity values to determine polarity? Notebook check: Vocabulary Covalent / Acid handout Venn diagram Notes on VSEPR Model Minilab (chart) Virtual minilab Answer Learning targets Vocabulary you should know: Chemical Bond Valence electron (trend) Ionic bond Covalent bond Nonpolar covalent bond Polar covalent bond VSEPR theory electronegativity single, double & triple bond formula unit molecule Study Guide (Learning targets) At the end of this unit, you should be able to… BONDING 1) Explain what chemical bonds are and why they form. 2) Define electronegativity and use electronegativity values to determine bond types. 3) Compare and contrast ionic, polar covalent and nonpolar covalent bonds in terms of their electronegativity differences, properties, behaviors, etc. 4) Identify the typical characteristics of substances containing ionic, covalent and metallic bonds (melting point, structure, physical properties, etc.) 5) Identify the number of valence electrons in an atom based on its location on the periodic table. Draw a dot diagram for an element to illustrate the number of valence electrons it has. 6) Create Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions containing single, double, and triple bonds. 7) Predict the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions using VSEPR theory. Great video review for ionic bonding: (6 min) http://www.nbclearn.com/chemistrynow/cuecard/56354 Tutorial on covalent bonding: http://www.brightstorm.com/science/chemistry/chemical-bonds/covalent-bonds/ Naming acids tutorial: http://www.brightstorm.com/science/chemistry/acids-and-bases/naming-acids/ Acid nomenclature: Acids formulas begin with _________________ . Acids are usually covalent compounds but are treated as cation/anion combinations. Name them as an ionic compound and then apply the acid rules. Acid rules: ________________ ________________ ________________ Name 1) H2SO4 _____________________ 2) HBr ________________________ 3) HNO2 _______________________ 4) HI __________________________ 5) H2S _________________________ 6) H2CO3 ______________________ 7) HClO2 _______________________ 8) HClO3 _______________________ 9) H2Cr2O7 ____________________ 10) H3PO3 ______________________ 11) Hydrofluoric acid ______________ 12) Hydrochloric acid ______________ 13) Hydronitric acid _______________ 14) Sulfurous acid _________________ 15) Nitric acid ____________________ 16) Acetic acid ___________________ 17) Phosphoric acid _______________ 18) Hydrocyanic acid ______________ 19) Chromic acid __________________ 20) Perchloric acid _________________ Covalent compounds: Electrons are ________________ so no _________ result. Form between 2 __________________. Use _________________ to tell the number of _______ in the compound. Greek Prefixes: _______, _________,________,_______, _________, _______,_________,_________,_______,_________ Naming Covalent Compounds Practice Write the formulas for the following covalent compounds: 1) Nigrogen tribromide __________________________________ 2) hexaboron selenide __________________________________ 3) chlorine dioxide __________________________________ 4) hydrogen iodide __________________________________ 5) iodine pentafluoride __________________________________ 6) dinitrogen trioxide __________________________________ 7) Nitrogen trihydride__________________________________ 8) phosphorus triiodide __________________________________ 9) carbon monoxide ___________________________________ Write the names for the following covalent compounds: 10) P4S5 __________________________________ 11) CO2 __________________________________ 12) SeF6 __________________________________ 13) Si2Br6 __________________________________ 14) SCl4 __________________________________ 15) CF4 __________________________________ 16) SiO2__________________________________ 17) NF3 __________________________________ Unit 6: Predicting Shapes of Covalent Compounds Now that you know how to draw the Lewis dot structures of covalent compounds, you can now use these structures to determine the three dimensional shapes of molecules. VSEPR Theory: (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory) 1. Electrons all have a ____________ charge and like charges _________________. 2. In molecules, bonding pairs and non-bonding pairs (called __________ pairs) repel each other to the greatest possible extent. 3. The repulsion of the like charges gives the molecule a 3-D ________________ that depends on the numbers of _______________ and ___________ pairs. 4. Even though double and triple bonds have more than 1 __________ of electrons in the same region, they will respond to the repulsive effects as a ______________ unit (just like a single bond). 5 Shapes obtained for molecules with: 1) 4 bonding regions: 2) 3 bonding regions + 1 lone pair: 3) 3 bonding regions, 0 lone pair: 4) 2 bonding regions, 2 lone pair: 5) 2 bonding regions, 2 lone pair: Formula Lewis Diagram HCl HBr H2O CH4 CO2 H2CO NH3 Hard ones to try: HCOOH, CH3NH2, C2H4 Structural Formula Shape Polarity Building and Naming Molecules Learning Targets: I can name a covalent compound, given its formula. I can write the formula of a covalent compound, given its name. Open the http://phet.colorado.edu/ Click the “Play with Sims”. Click the “Chemistry” link on the left hand side of the page, then “General Chemistry”. Click the “Build a Molecule” simulation. Press “Download” hard disk or “Run” for on-line interaction. Stay in the “Make Molecule” Tab Explore how to make bonds by dragging the atoms and placing them together. Once the bond is formed, you can break the bond by placing the cursor between the atoms. Once you build a structure, you can break all bonds (atomize the particle) by clicking on the blue square, next to the green “3d” toggle. Kit #1 Draw the Lewis (electron-dot) structure of the hydrogen atom ______ and the oxygen atom ___________. Two possible molecules can be built with Kit #1. Build both molecules, and view the space-filling and ball and stick models by clicking the green “3D” toggle . The element ______________ , whose molecular formula is _______ and Lewis structure is _______; and, the compound ____________, whose molecular formula is _______ and Lewis structure is ____________. Once you have built both molecules, place one of the molecules on the right column by dragging it into the black space and move to the next kit. Click on “Reset Kit” to replace the original set of atoms in the bins, build the second molecule, and drag it to the correct black space in the right column. Go to Kit #2 by pressing on the Kit #1 “Next” yellow arrowhead. Kit #2 Four molecules can be built with Kit #2. Two of the molecules are elements, while the other two are compounds. Build the four molecules. Any molecule that is required in the right column may be dragged there. You might need to “Reset Kit” if you make a required molecule to complete the exercise. Make sure you view the space-filling and ball and stick models. Fill the following table: Name Formula Elements Lewis Structure Name Compounds Molecular Lewis Formula Structure Go to Kit #3 by pressing on the Kit #3 “Next” yellow, right-hand arrowhead. Kit #3 Draw the Lewis (electron-dot) structure of the carbon atom __________ , the nitrogen atom __________, and the oxygen atom ____________. More than ten (10) molecules can be built with this kit: Two (2) elements and at least eight (8) compounds. Two of the molecules are required in the right hand tray: carbon dioxide (CO 2) and nitrogen (N2). You should do CO2 and N2 as your ninth and tenth molecules. Build at least ten (10) different molecules, including CO2 and N2. List the names and formulas on the following table. Don’t forget to view the space-filling and ball-and-stick models for each molecule. If the molecule contains a double or a triple bond, check (√) the appropriate column. Substance Name Molecular Formula Double Bond Triple Bond Substance Name Molecular Formula Double Bond Triple Bond Finish the exercise by building CO2 and N2 and viewing their “3D” models. Draw the Lewis structure, below, and fill their data on the table. Once you finish your analysis, drag these molecules to the right-hand column. Lewis structures: CO2 N2 Second, Third, and Fourth Collections Complete the following collections, build the fifteen (15) required molecules, and fill the following table with the compound name, formula, and the types of bonds found in the molecule Name Formula Types of Bonds Single Double Triple Close the simulation. Name Formula Types of Bonds Single Double Triple