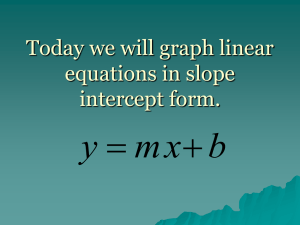Exercise * Receptor binding and the Hill plot
advertisement

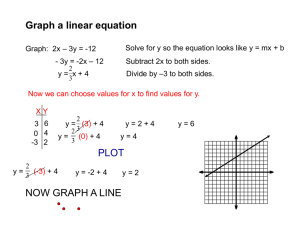
Martin Johnsson HT 2011 Exercise – Receptor binding and the Hill plot The aims of this exercise are to learn and familiarize your selves with a number of pharmacological terms and expressions. Also the exercise will point out some important features in Microsoft Excel. The data needed to complete this exercise can be found in the provided Excel-file. Important terms and expressions Concentration – Response curve Logarithmic (log) scales and log plots Mean values and standard deviation (SD) EC50 - value Hill plot / Hill slope 1) Calculate the logarithmic values of the concentrations administered (hint: use the command “=LOG(concentration)” in excel) This will help you to be able to construct log plots later on. 2) Calculate the mean % Response (hint: use the command “=MEDEL(first response:last response)” or “=AVERAGE(first response:last response)”in excel) 3) Calculate the standard deviation for the % Responses A-C. (hint: use the command “=STDAV(first response:last response)” or “=STDEV(first response:last response)”in excel). 4) Calculate Standard error mean deviation (SEM). 𝑆𝐸𝑀 = 𝑆𝑇𝐷𝐸𝑉 √𝑛 where n = amount of experiments run (A,B, and C) (hint: use command “=cell where you previously calculated the standard deviation/ROT(n)” or “=cell where you previously calculated the standard deviation/sqrt(n)” 1 Martin Johnsson HT 2011 5) Construct a Concentration – Response plot (with “mean % response” on the y-axis and “log(concentration)” on the x-axis). For all graphs in this exercise, use the XY-scatter option. Insert SEM error bars (Right click on a data point Format data series Y error bars. Then chose the double error bar and select custom input. Use your obtained SEM values as the source for the error bars). Describe in your own words what the graph looks like. 6) Graphically obtain the EC50-value. This is the concentration when you get 50% of the maximal response. Remember that you have a logarithmic x-axis! 7) Now make a Hill plot. This is a plot with “log(MeanValue%Response/100- MeanValue%Response)” on the y-axis and “log(concentration)” on the x-axis. This should give you an almost straight line. 8) The slope of the Hill plot tells you something about the ligand binding to the receptors. The Hill slope equals 1 when a ligand binds with no cooperativity to one site. When the slope is greater than 1 the receptor or ligand has multiple binding sites with positive cooperativity. The Hill slope is less than 1 when there are multiple binding sites with different affinities for ligand or when there is negative cooperativity. (hint: to get a straight trendline in your Hill plot, right click on a data point, chose add trendline, chose a linear trendline. To get the slope of the trendline, right click on the trendline and chose format trendline options display equation on chart. This equation is the standard straight line equation Y=kX+m; k being the slope.) How would you interpret the data in this case? Answer questions: Is the agonist acting on a homogenous receptor population or a heterogeneous receptor population? What is the exact EC50, which can be obtained from your Hill plot? 2