File - Mrs. LeCompte
advertisement

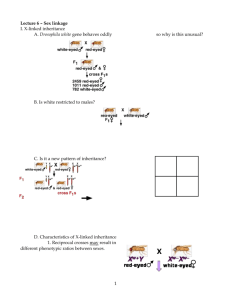
11-3 Notes: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Mendelian factors or genes are located on chromosomes Chromosomes separate and independently assort Genes = sections of a chromosome that code for a particular trait Thomas Hunt Morgan (1909) and the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster These are useful because they: 1. Are easily cultured in the lab 2. Are prolific breeders 3. Have a short generation time 4. Have only 4 pairs of chromosomes which are easily seen with a microscope - 3 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes For fruit flies, instead of using A or a to designate alleles, we use the following: Sex Chromosomes = chromosomes that determine the gender of the individual May carry other traits as well In most species, the females’ are identical (XX) = “homogametic” and the males’ differ (XY) = “heterogametic” o Some organisms, like grasshoppers have homogametic (XX) females, but males that are hemigametic = XO (Only have one sex chromosome) In humans, after meiosis, each haploid gamete has 22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome o Females can only give an X o Males can give either an X or a Y 50% chance of either determines the gender of the child Sex Linkage: Morgan’s Discovery Initial Cross: P Red-eyed female x White-eyed male F1 all red-eyed offspring F2 mostly red-eyed : some white-eyed EXPECTED 3:1 ratio, but GOT closer to 4:1!!!!! What happened? Breakdown of results: Red Females: 2459 White Females: 0 (huh?!?!) Red Males: 1011 White Males: 782 Is it possible to get a white-eyed female, or is it lethal to them? Crossed white-eyed male with F1 female and got an F1 generation with: Red Females: 129 White Females: 88 Expected a 1:1:1:1 ratio and was Red Males: 132 pretty close to these results White Males: 106 Morgan’s Hypothesis: Gene for eye color is carried only on the X chromosome and red is dominant over white That is, they are X-LINKED = carried on the X chromosome P Generation F1 Generation F2 Generation (do in class) When solving X-linked crosses, you must include the sex chromosomes and designate the genotype as a gene carried on each o Heterogametic sex (usually males) are said to be hemizygous for sex-linked traits (because they only have 1 allele instead of 2 for a that trait) Humans X-linked traits include: Red-Green Color-blindness, Menkes Syndrome, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Hemophilia, ALD (Lorenzo’s Oil), and Male Pattern Baldness LINKED GENES: Another problem with Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment… Ex. P BOTH DOMINANT BOTH RECESSIVE (purebreeding) tan & long x (purebreeding) black & short F1 All tan & long ↓ bred together F2 Two Possibilities: If unlinked: will get a 9:3:3:1 ratio If linked: will get a 3:1 ratio with ¾ (75%) tan & long and ¼ (25%) black & short Results: 95 tan & long (Like Parent #1) 31 black & short (Like Parent #2) 4 tan & short 6 black & long Close to the expectation for linked, but a few exceptions. WHY? Answer: CROSSING OVER - when crossing over occurs between positions of two different genes on the same homologous chromosomes, the genes may become “unlinked” Parental Type = Progeny that have the same phenotype as one or the other of the parents Recombinants = Progeny whose phenotypes differ from either parent - Arise from Genetic Recombination = the production of offspring with new combinations of traits different from those combinations found in the parents; results from the events of meiosis and random fertilization - Can be used to determine how far apart two genes are on a chromosome MAPPING CHROMOSOMES Loci (singular: Locus) = the particular position on a chromosome where a gene is located - same for all homologous chromosomes Sturtevandt (1913) – determined that the percentage of recombinants was probably related to the physical distance between two gene loci - Postulated: 1) genes are arranged in linear order on chromosomes 2) genes closer together separated by crossing over less frequently than those farther apart 3) should be possible to plot the sequence and relative distance of gene loci by determining the frequencies of recombination - defined 1 map unit = distance that would give one recombinant organism per 100 fertilized eggs - That is, 1 map unit = 1% recombination between genes EXAMPLE: Loci Recombination Frequencies Approximate Map Units b vg 17% 17 cn b 7% 7 cn vg 10% 10 So, if mapping on a chromosome: 7 10 │______________│_____________________│ b cn 17 vg