Chapter 16 Section 2 Notes
advertisement

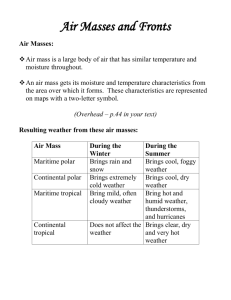
Chapter 16 Section 2 Notes AIR MASSES 1. The moisture content and temperature of an air mass are determined by the area over which the air mass forms. These areas are called ______________________. 2. The characteristics of these air masses are represented on maps by a two- letter symbol. The ____________ letter indicates the moisture content that is characteristic of the sir mass. The ________________ letter represents the temperature that is characteristic of the air mass. SYMBOLS WHERE IT IS FORMING maritime (m) Forms over water; wet continental (c) Forms over land; dry polar (P) Forms over the polar regions; cold tropical (T) Develops over the Tropics; warm COLD AIR MASSES 3. A continental polar (________) air mass forms over northern Canada, which bring extremely cold winter weather to the United States. 4. A maritime polar (_________) air mass that forms over the North Pacific Ocean is cool and very wet. This air mass brings rain and snow to the Pacific Coast in the winter and cool, foggy weather in the summer. WARM AIR MASSES 5. A maritime tropical (_____________) air mass that develops over warm areas in the Pacific Ocean is not as wet as the Maritime polar air mass that forms over the Pacific Ocean. 6. Other maritime tropical air masses develop over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. In the __________________, they bring hot and humid weather, hurricanes, and thunderstorms. In the _________________, they bring mild, often cloudy weather. 7. A continental tropical (_________) air mass forms over the deserts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. This air mass moves northward and brings clear, dry, and hot weather in the summer. FRONTS 8. The 4 kinds of fronts- ____________ fronts, _____________fronts, ______________ fronts, and ____________________ fronts. COLD FRONT 9. A ___________ front forms where cold air moves under warm air, which is less dense, and pushes the warm air up. A cold front usually brings ______________ weather. WARM FRONT 10. A ____________front forms where warm air moves over cold, denser air. Most likely produces hot, humid weather after a period of rain. OCCLUDED FRONT 11. An __________________ front forms when a warm air mass is caught between 2 colder air masses. This front produces cool temperatures and large amounts of rain and snow. STATIONARY FRONT 12. A ____________________ front forms when a cold air mass meets a warm air mass. This front brings many days of cloudy, wet weather. CYCLONES 13. In a cyclone winds spiral toward the __________. ANTICYCLONES 14. They are areas that have ___________________ pressure. 15. The sinking air in an anticyclone brings _________, ___________ weather.