GN 7-3 Physiology of Osseous Tissue/ Bone disorders and fractures
advertisement
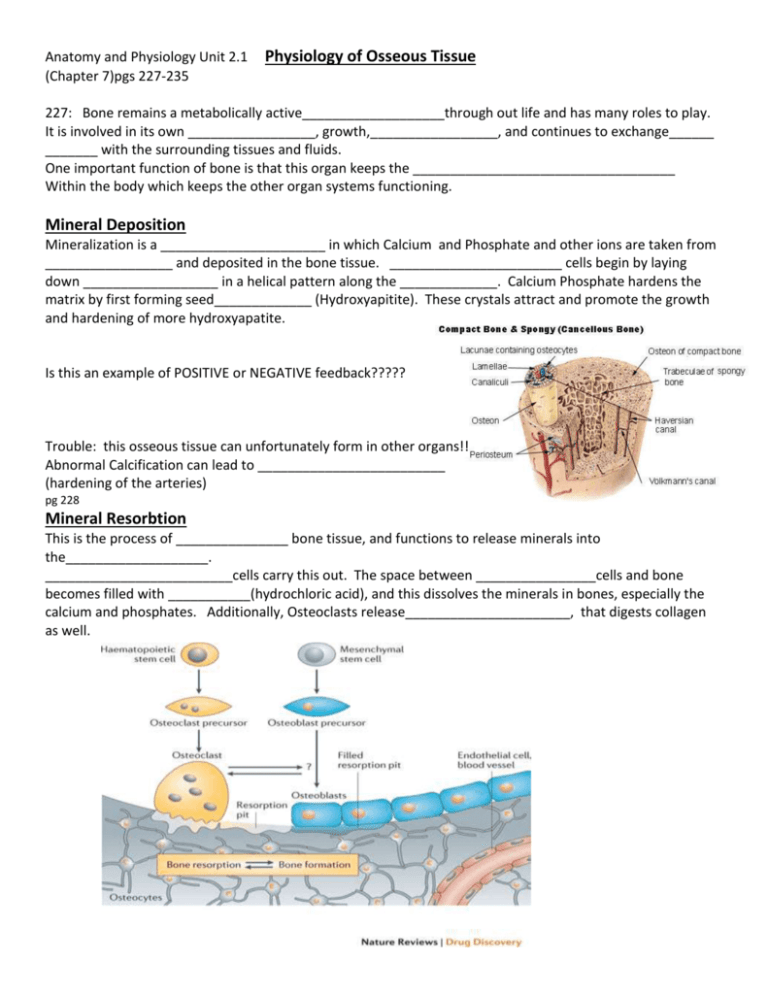
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 2.1 (Chapter 7)pgs 227-235 Physiology of Osseous Tissue 227: Bone remains a metabolically active___________________through out life and has many roles to play. It is involved in its own _________________, growth,_________________, and continues to exchange______ _______ with the surrounding tissues and fluids. One important function of bone is that this organ keeps the ___________________________________ Within the body which keeps the other organ systems functioning. Mineral Deposition Mineralization is a ______________________ in which Calcium and Phosphate and other ions are taken from _________________ and deposited in the bone tissue. _______________________ cells begin by laying down __________________ in a helical pattern along the _____________. Calcium Phosphate hardens the matrix by first forming seed_____________ (Hydroxyapitite). These crystals attract and promote the growth and hardening of more hydroxyapatite. Is this an example of POSITIVE or NEGATIVE feedback????? Trouble: this osseous tissue can unfortunately form in other organs!! Abnormal Calcification can lead to _________________________ (hardening of the arteries) pg 228 Mineral Resorbtion This is the process of _______________ bone tissue, and functions to release minerals into the___________________. _________________________cells carry this out. The space between ________________cells and bone becomes filled with ___________(hydrochloric acid), and this dissolves the minerals in bones, especially the calcium and phosphates. Additionally, Osteoclasts release______________________, that digests collagen as well. How do Bones Help Keep Ca2+ and P04 in Balance?? P04 groups are important in the formation of _____________, ________________, _______________, and phospholipids and they also help in correcting __________________ imbalances. Calcium plays roles in _______________communication, __________________contraction, formation of _____________________, exocytosis, cell signaling, and is also an important _____________________ for Enzyme function. Normal [Ca2+] in blood plasma is ____________________ ~45% is ionized Ca2+ that can diffuse through__________________________ and affect neighboring cells. ~55% is bound to blood plasma proteins which is not_________________________ but serves as a reserve. Normal [H2P04- ] and [HP042-]is found in concentrations of about 500-800g, almost all in the bone. Changes in the conc. of phosphates have little effect on the body. Changes in the conc. of calcium have SERIOUS effects on the body. Examples: HYPOCALCEMIA: Calcium conc. is too LOW Effects: excessive_______________ stimulation ___________________ spasms __________________ muscles can’t relax At about 4mg/dL muscles in larynx contract can lead to____________________. Hypocalcemia can result from 1. Vitamin _______________deficiency 2. _______________________________ 3. _______________________________ 4.________________________________ HYPERCALCEMIA: Calcium conc. is too HIGH Effects: Calcium binds to ____________________ inhibiting the Na channels from functioning Reduced or _________________nervous system Emotional ___________________________ This is Sluggish_________________________ RARE!!! Muscle___________________________, even cardiac arrest! Calcium and Phosphate homeostasis depends on a balance of_____________________, ______________and ___________________________ and exchanges with Osseous Tissue. This homeostasis is regulated by three hormones: 1.___________________ 2.________________________ 3._________________________ A) Calcitriol is the active form of ____________________________. It is a hormone that is a _____________________________from organ to another. Functions: To ____________________blood Calcium. How does it do this?? 1. It stimulates the increased absorption of Calcium in the ____________________________. 2. Increases resorption of CA in bone by binding to ______________________which stimulate stem cells to _______________________into more ____________________________. These then liberate ___________ And _________________from bone. 3. It promotes reabsorption of calcium by the kidneys so _______________is excreted. B) Calcitonin is released by C cells of the ________________________. Functions : to _____________________blood calcium. How does it do this??? 1. It is secreted when blood Ca is too high and this reduces ________________________ activity. (Osteoclast inhibition) 2. This increases the numbers of _______________________ which deposit Calcium into the bone. (Osteoblast Stimulation) Very important in children. C) Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) is secreted by the parathyroid gland. Functions: To Raise blood _____________levels. How does it do this??? 1. PTH binds to ____________________on Osteoclasts, promoting resorption, __________________Ca Into the blood stream. 2. PTH promotes kidneys to reabsorb Calcium so less is excreted. 3. Promotes last step in ______________synthesis so you have high conc. of ___________________ 4. Inhibits the formation of ____________________ thus inhibiting bone deposition. Additionally there are some 20 plus other hormones that play a small role in the homeostasis of calcium and phosphate concentrations in bone and blood. YIKES!!! BONE FRACTURES BASICALLY 2 TYPES: Pg 232 1. Stress Fracture________________________________________ 2. Pathological Fracture____________________________________ Bone breaks are categorized by: 1. direction of fracture 2._________________________ 3.________________________________ know the types of fractures listed in 7.19 Pg 233 Stages of Healing 1. 0-48 hrs Hematoma and Granulation Tissue:____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Formation of Soft Callus_______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. 4-6 wks Conversion to Hard Callus_______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. 3-4 mo. Remodeling___________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Medical Treatment of setting Fractures: Describe Closed Reduction:________________________________________________________________ Describe Open Reduction: __________________________________________________________________ Bone Disorders: Describe what happens when Osteoporosis occurs:_____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ What can one do to prevent this from occurring? What age is it best to start prevention measures? _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Pick one other bone disease and explain:_______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Illustrate the NEGATIVE Feedback loops for a. correction of hypercalcemia b. correction of hypocalcemia


![2012 [1] Rajika L Dewasurendra, Prapat Suriyaphol, Sumadhya D](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619083_1-f93216c6817d37213cca750ca3003423-300x300.png)