figure 1
advertisement

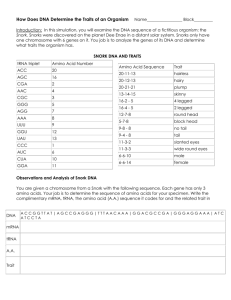
Build-a-Bug Workshop Introduction: DNA is the blueprint for protein synthesis. By controlling protein production, DNA controls all cellular functions. How does it do this? Protein is produced by ribosomes that are found in the cytoplasm. DNA is stored and protected in the nucleus. In order for DNA to transmit the required information to the ribosomes it must be copied into RNA. This process is called transcription. This mRNA can then move out into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes for protein production. In the ribosome, the mRNA is decoded to build a protein. This process is called translation. Translation occurs when tRNA molecules attach the proper amino acids to the mRNA codon. A chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. Your task is to transcribe and translate 11 gene sequences for a given bug. Once you know the bug’s traits, you are to draw and color it. No two bugs will be the same! Directions: 1. Start with gene 1. Transcribe the DNA sequence into mRNA. (*Remember- Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA.) 2. Next, use the 3 mRNA codons to determine the 3 tRNA anti-codons. 3. Use the 3 mRNA codons to determine the amino acid number in FIGURE 1. 4. Now you should have a sequence of 3 amino acid numbers. Look this sequence up in FIGURE 2 and write down the trait. 5. Repeat steps 1-4 for the remaining genes. Make sure to be careful on each step and record the proper information. An error will cause a mutation! 6. Once all 11 traits have been found, go to FIGURE 3 and determine insect parts for your bug. Note: genes 8-11 do not have parts… they are traits for color. 7. Use the back of the gene sequence worksheet to draw and color your bug. Practice Examples: Gene: DNA: 1 Gene: CCC ATC AGG DNA: 2 CGA mRNA: mRNA: tRNA: tRNA: Amino Acid Sequence: Amino Acid Sequence: Trait: Trait: TTT CTA GENES Gene 1 = body style Gene 5 = mouth parts Gene 9 = wing color Gene 2 = leg sytle Gene 6 = eye style Gene 10 = appendage color Gene 3 = wing style Gene 7 = tail style Gene 11 = eye color Gene 4 = antennae style Gene 8 = body color FIGURE 1 mRNA codon Amino Acid Number UGG……….………….…………….20 UCG…………….…………..………16 GCU……………………..…………...2 UUG………………………………….4 GCG………………………………….3 CCC…………………………………..5 UCC…………………………………..7 UUU…………………………………..8 AAA…………………………….…….9 CCA……………………………….…12 AUA………………………………….13 GGG……………………………..……1 UAG……………………….………….6 GAU…………………………………10 CCU…….…………………………....11 GAC………..…….…………………..14 UAU………………………….……...15 CCG…………………………………19 UGU…………………………………17 ACA…………………………………18 2 FIGURE 2 Amino Acid Sequence Trait 1-2-3 1-4-5 1-6-7 1-8-9 1-10-11 1-12-13 1-14-15 Body style 1 Body style 2 Body style 3 Body style 4 Body style 5 Body style 6 Body style 7 2-3-4 2-5-6 2-7-8 2-9-10 Leg style 1 Leg style 2 Leg style 3 Leg style 4 3-4-5 3-6-7 3-8-9 3-10-11 3-12-13 3-14-15 Wings 1 Wings 2 Wings 3 Wings 4 Wings 5 Wings 6 20-19-18 20-17-16 20-15-14 20-13-12 Antennae 1 Antennae 2 Antennae 3 Antennae 4 19-18-17 19-16-15 19-14-13 Mouth parts 1 Mouth parts 2 Mouth parts 3 18-17-16 18-15-14 18-13-12 Eyes 1 Eyes 2 Eyes 3 3 FIGURE 2 continued Amino Acid Sequence Trait 17-16-15 17-14-13 17-12-11 17-10-9 Tail 1 Tail 2 Tail 3 Tail 4 12-13-14 12-15-16 12-17-18 12-19-20 12-1-2 12-3-4 12-5-6 Body color – black Body color – yellow/black Body color – red/yellow Body color – blue Body color – green/yellow Body color – brown Body color – purple 13-14-15 13-16-17 13-18-19 13-20-1 13-2-3 13-4-5 Wing color – orange/black Wing color – red/yellow Wing color – blue/yellow Wing color – red/blue Wing color – yellow/black Wing color – green/yellow 20-15-10 All appendages black 13-10-5 13-9-4 13-8-3 13-7-2 Eye color – red Eye color – black Eye color – yellow Eye color – orange 4 5