Critter Project Construct a Critter
advertisement

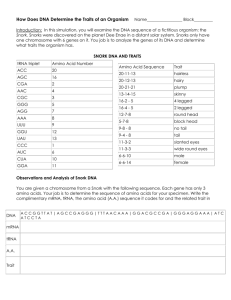
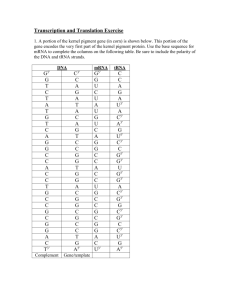
Critter Project Construct a Critter Proteins roles range from catalyzing chemical reactions to providing movement and support. Because of this proteins have a variety of structures. Differences among proteins are the result of their amino acid sequence. The amino acid sequences for proteins are coded for in each individual organism’s DNA in segments called genes. In a process known as transcription, the DNA code for a protein is copied by the messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus of the cell. The mRNA then carries the copy of the code to ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. The process of translation occurs when a second type of RNA, called transfer RNA (tRNA), brings the amino acids to the ribosomes in the order specified in the mRNA. The ribosomes function is to join the amino acids in the correct order to form the protein. In this activity, you will simulate protein synthesis and determine the traits of fictitious animals called critters. Critters have two chromosomes, each containing four genes. Each gene (A-H) is responsible for the proteins that create a certain trait. Procedure: Determine the trait for Gene A of your critter by completing the box labeled Gene A in the Data Table. Note the DNA sequence and then list the corresponding mRNA codons in the space provided. Determine the sequence of amino acids by matching the mRNA codons to the specific amino acids found in Table 1. List the amino acid abbreviations in the space provided in the data table, using a hyphen to separate each amino acid. Use Table 2 to identify the trait that matches the amino acid sequence. Record this information in the Data Table. Repeat steps 1 – 3 for the remaining traits. Using all 8 traits, sketch a diagram of your critter. Example Gene Z DNA CTC ACG TTC mRNA GAG UGC AAG amino acid sequence GLA CYS LYS trait female Observations Data Table Gene A DNA mRNA Gene B AAC TTA TAC GTT ______________________ DNA mRNA GGG CTC ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ trait ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ trait ______________________ Gene C DNA GGG AAG TGA mRNA ______________________ Gene D DNA GTG AAC GTT ATG mRNA ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ trait ______________________ trait ______________________ CAC ACG TCG ______________________ Gene F DNA mRNA CCC CGT ACC ACG ______________________ Gene E DNA mRNA amino acid sequence ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ trait trait ______________________ ______________________ Gene G DNA TAA GCG mRNA ______________________ Gene H DNA CTA TTC TTA mRNA ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ amino acid sequence ______________________ trait trait ______________________ ______________________ Table 1 mRNA codon GAU AUG UUG GAG UGG CAA AAG UAC AAU CCC UGC UUC ACU CAC AUU GCA CGC GUG AGC GGG Amino Acid aspartic acid methioine leucine glutamic acid tryptophan glutamine lysine tyrosine asparagine proline cysteine phenylalanine threonine histidine isoleucine alanine argentine valine serine glycine Table 2 Amino Acid Sequence PRO-PHE-THR PRO-LEU-THR ASP-LYS-ASP ASP-LEU-ASN PRO-GLU VAL-CYS-SER GLA-CYS-LYS ILE-ARG PRO-ALA-TRP-CYS GLY-ALA-TRP-CYS LEU-ASN-MET-GLU LEU-ASN-MET-ISO HIS-LEU-GLU-TYR VAL-PHE-GLU-TYR Amino Acid Abbreviation ASP MET LEU GLU TRP GLU LYS TYR ASN PRO CYS PHE THR HIS ILE ALA ARG VAL SER GLY Trait small nose big nose freckles no freckles four-legged male female four antennae blue fur orange fur plump skinny purple eyes yellow eyes Sketch: Questions: 1. Where in the cell: a. are the DNA instructions located? b. does transcription occur? c. does translation occur? 2. Describe three similarities and three differences between DNA and RNA. 3. Why is specific base pairing essential to the processes of transcription and translation? 4. How could the change in one DNA nucleotide alter the protein formed? 5. Suppose you knew the sequence of amino acids in a protein. How could you determine the DNA sequence for that gene? 6. Create two additional traits for your critter. Give their DNA sequences, the mRNA codons and the resulting amino acid sequences.