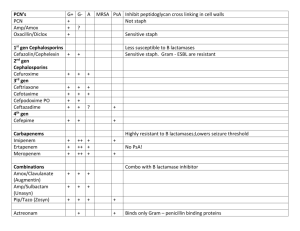
Question 1 Drugs that are likely to cause photosensitising reactions
advertisement

Question 2 Which of the following statements is FALSE A. In a Type I reaction, a free radical undergoes a reaction with singlet oxygen. B. Ground state oxygen exists in the triplet state. C. In a Type II reaction singlet oxygen reacts with a drug molecule resulting in a peroxide. D. Molecules in a singlet excited state may return to the ground state via fluorescence or internal conversion. E. All of the above are false. Question 3 Ibuprofen (I) is less likely to cause phototoxic reactions than many other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) because CH3 CH COOH C4H9 (I) Question 1 Drugs that are likely to cause photosensitising reactions commonly have the following structural features A. B. C. D. E. Planar, polycyclic stabilised resonance structures. Absorb UV radiation below 290 nm. Low molecular weight. A and C are correct. A, B and C are all correct. A. It does not contain a branched propionic acid group. B. Its maximal UV absorbance occurs at 265 nm. C. Its maximal UV absorbance occurs at 310 nm. D. It has an internal conversion mechanism allowing it to dissipate energy. E. None of the above are correct. Question 4 Which of the following answers is INCORRECT. An ideal sunscreen has which of the following properties A. B. C. D. E. Large molar absorbtivity Absorption at greater wavelengths between 280-360 nm Photochemically reactive Water insoluble B and C are both correct Question 5 Treatment of jaundiced babies with UV radiation causes a drop in bilirubin serum levels because A. the trans form of bilirubin absorbs UV radiation at 450 nm and isomerizes to the more soluble cis form which is able to form intermolecular Hbonds with water. B. the cis form of bilirubin absorbs UV radiation at 400 nm and isomerizes to the more soluble trans form which is not able to form intermolecular H-bonds with water. C. the cis form of bilirubin absorbs UV radiation at 450 nm and isomerises to the more soluble trans form which is able to form intermolecular Hbonds with water. D. the cis form of bilirubin absorbs UV radiation at 400 nm and isomerises to the more soluble trans form which is not able to form intermolecular Hbonds with water. E. None of the above are correct. Question 6 An ideal drug used in photodynamic therapy has which of the following characteristics A. B. C. D. E. Absorb Radiation between 650-800 nm. Have selective uptake in to tumour cells over healthy cells. Consist of a mixture of isomers. Rapidly undergo photobleaching. A, B and D are all correct. Question 9 In relation to the scheme below O O OH -thujone 7-hydroxy- -thujone Metabolism of -thujone in the brain to give 7-hydroxy--thujone results in A. B. C. D. E. toxification a less toxic metabolite a phase 2 metabolite hydroxyl conjugation a non-toxic metabolite Question 9 The cell cycle consists of the following phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Mitosis occurs during: A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M E. Both G1 and G2 Question 10 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP): A. is an antimetabolite that starves the cell of pyrimidine bases B. is an antimetabolite that starves the cell of purine bases C. inhibits thymidylate synthetase D. converted in vivo by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase to 6-MPMP E. Both B. and D. Question 11 Which of the following statements is incorrect? Cisplatin: A. was discovered by accident - released from platinum electrode during electrolysis induced inhibition of E. coli proliferation B. is a platinum complex containing two ammonia molecules and two chloride atoms in a cis configuration C. is a platinum complex containing two ammonia molecules and two chloride atoms in a trans configuration D. readily forms guanine-adenine cross-links on DNA E. reacts with nucleophilic sites such as nucleic acids and proteins Question 12 Which of the following statements is incorrect? Gram-positive bacteria: A. have an internal pressure of 6 atmospheres B. have an internal pressure of 20 atmospheres C. excrete β-lactamases D. display more β-lactamase-mediated resistance than the Gram-negative species E. Both A. and D. Question 13 Question 17 Vancomycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by: A. preventing the binding of the amino-acid containing end of the aminoacyl tRNA to the acceptor site on the 50 S in an irreversible manner B. preventing the binding of the amino-acid containing end of the aminoacyl tRNA to the acceptor site on the 50 S in a reversible manner C. binding to the D-ala-D-ala residues via five hydrogen bonds D. reversibly binding to the 30 S bacterial ribosome to prevent access of aminoacyl tRNA to the acceptor site E. irreversibly binding to the 30 S bacterial ribosome to prevent access of aminoacyl tRNA to the acceptor site Question 14 Antimicrobial effects can be achieved with the use of agents that affect nucleic acids, such as: A. the rifamycins, which inhibit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase B. the aminoglycosides, which inhibit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase C. the rifamycins, which inhibit gyrases D. the sulphonamides, which inhibit gyrases E. the quinolones, which inhibit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase Question 15 p53: A. B. C. D. E. is a tumour suppressor gene – absence can lead to cancer inhibits apoptosis in cells that have undergone DNA damage is an oncogene – presence can lead to cancer is a tumour suppressor gene – presence can lead to cancer p53 acts as a “checkpoint" to promote cell growth if damage is detected Question 16 Amantadine is effective against: A. Influenza A B. Influenza B C. Influenza C D. A. and B are correct E. A, B and C are correct What endogenous compound is the structure of Lamivudine (3TC) most similar to? A. Deoxycytidine B. Deoxythymidine C. Deoxyadenosine D. Deoxyguanosine E. Deoxyinosine Question 18 A functional group required for Indinavir’s activity is: A. 4-Amino B. Proline C. Acetoamido D. Phenylalanine E. Azide Question 19 Which of the following statements is correct? Stavudine (D4T) directly: A. Inhibits the synthesis of viral DNA B. Inhibits the penetration of the virus into the host cell C. Inhibits the viral translation process D. Interferes with the assembly of viral proteins E. Inhibits the spread of the viral infection from the host cell Question 20 Which of the following statements is correct? Oseltamivir phosphate: A. prevents the virus from exiting the host cell by blocking the cleavage of the terminal sialic acid from the virus B. prevents the virus from exiting the host cell by blocking the cleavage of the terminal sialic acid from the host cell C. is orally in-active, and has a 5-membered ring structure D. is orally in-active, and has a 6-membered ring structure E. is not specific for viral neuraminidase Question 21 Which of the following statements is correct? Cidofovir: A. B. C. D. E. is selective for viral thymidine kinase is a prodrug converted to cidofovir monophosphate is an oral prodrug requiring metabolic conversion to its active form preferentially inhibits viral DNA polymerase is a guanosine analogue