Cells Ch 4 PPT W-S
advertisement

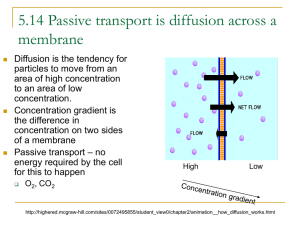
Chapter 4: Cells in Action Cells in Action A cell is a factory: an organism must obtain energy, raw materials, and eliminate waste. These functions keep cells healthy so they can grow through cell division. Cell growth allows cells to divide, therefore growing and repairing tissue as needed. Diffusion Particles naturally travel from crowded areas (dense) to less dense places. Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. When the particles are even throughout a space - it is called EQUILIBRIUM Diffusion Molecules move from areas of High concentration to areas of Low concentration. Osmosis Cells are surrounded by and filled with mostly water. Diffusion of water is so important that it was given a special name – Osmosis. Pure water has the highest concentration of water molecules Osmosis – Diffusion Chapter 4: Cells in Action Red Blood Cells Pure Water would rush into a Red Blood Cell Plasma – would maintain the Red Blood Cells Isotonic: Cells maintain normal shape. Hypertonic Solution: Cells shrink because water departs the cell Hypotonic Solution: Cells swell as they take in more water and rupture. \ Chapter 4: Cells in Action Passive Transport – Small Particles: Particles move through channels (protein cells). Diffusion and Osmosis are examples of Passive Transport - Thus no Energy is used for particles to move (High- Low) through a membrane. Active Transport - Energy: Active Transport usually involves the movement of small particles from an area of low concentration to an area of High concentration. Thus using Energy to perform this process. Large Particles: Large Particles use Active Transport to move in and out of cells to move in and out of cells Reverse Osmosis is a process that forces water across semipermeable membranes under Chapter 4: Cells in Action Reverse Osmosis: Reverse Osmosis is a process that forces water across semipermeable membranes under high pressure. The high pressure reverses the natural tendency of the solutes to travel from high to low concentration areas – this is how water is purified. Endocytosis Cell comes in contact with particle Cell membrane begin to wrap around particle The particle is completely surrounded – vesicles pinch off. Endocytosis means “within the cell” Chapter 4: Cells in Action Endocytosis Three Types: Phagocytosis, Receptor-Mediated and Pinocytosis. Phagocytosis – captures large particles by sending out pseudopods (false feet) Receptor Mediated – receptors on the membrane captures specific substances before endocytotic process begins. Pinocytosis– the cell membrane usually surrounds a substance – forming a vesicle to carry it into the cell. Exocytosis Large particles are packaged in vesicles to leave the cell Vesicle travels to membrane wall and fuses. Cell releases the Vesicle Exocytosis means “Outside the Cell” Materials discharged from cell (vacuole passes plasma membrane to dump contents out of cell). Photosynthesis: Plants use the energy captured by chlorophyll to change carbon dioxide and water into food. Glucose is a carbohydrate used by plants to convert sunlight into stored sugars (Energy). Chapter 4: Cells in Action Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration uses oxygen to breakdown food. Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration: Photosynthesis: Uses Sunlight Energy and CO to make Glucose and releasing O 2 Cellular Respiration: Cells use O to breakdown glucose and Releases CO . 2 2 2 Chapter 4: Cells in Action Cells in Action: A cell is a _____________: an organism must obtain ____________, raw ______________, and eliminate _____________. These functions keep cells healthy so they can grow through cell division. Cell growth allows cells to ______________, therefore _________________ and repairing _______________ as needed. Diffusion: Particles naturally travel from crowded areas (dense) to less dense places. Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from areas of ___________ concentration, to areas of ________ concentration. When the particles are even throughout a space - it is called ____________________. Chapter 4: Cells in Action Diffusion Molecules move from areas of _________ ____________________ to areas of ________________ ________________________. Osmosis Cells are ______________________ by and ________________ with mostly water. ___________________ of water is so important that it was given a special name – Osmosis. Pure water has the highest concentration of water molecules Osmosis – Diffusion Chapter 4: Cells in Action Red Blood Cells Pure Water would ________ into a Red Blood Cell Plasma – would maintain the Red Blood Cells Isotonic:_______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ Cells maintain normal shape. Hypertonic Solution: ____________________________________ Cells shrink because water departs the cell Hypotonic Solution: _____________________________________ ______________________________________________________ Cells swell as they take in more water and rupture. \ Chapter 4: Cells in Action Passive Transport – Small Particles: Particles move through channels (_______________ cells). Diffusion and _________________ are examples of Passive Transport - Thus no ________________ is used for particles to move (_________- ________) through a membrane. Active Transport - Energy: Active Transport usually involves the movement of small particles from an area of _______ concentration to an area of _______ concentration. Thus using Energy to perform this process. Large Particles: Large Particles use Active Transport to move in and out of cells Chapter 4: Cells in Action to move in and out of cells Reverse Osmosis: Reverse Osmosis is a process that forces water across ______________________ membranes under _______ pressure. The high pressure reverses the natural tendency of the solutes to travel from high to low concentration areas – this is how water is purified. Chapter 4: Cells in Action Endocytosis Cell comes in contact with particle Cell membrane begin to __________ around particle The particle is completely surrounded – vesicles _____________ off. Endocytosis means “_____________ ______ _________” Endocytosis ____________Types: Phagocytosis, Receptor-Mediated and Pinocytosis. Phagocytosis – captures large particles by sending out pseudopods (________ _________) Receptor Mediated – receptors on the membrane captures _________________ substances before endocytotic process begins. Pinocytosis– the cell membrane usually surrounds a substance – forming a _______________ to carry it into the cell. Chapter 4: Cells in Action Exocytosis __________ particles are packaged in vesicles to leave the cell ____________ travels to membrane wall and fuses. Cell releases the Vesicle Exocytosis means “________________ _______ __________” Materials discharged from cell (vacuole passes ______________ _______________________ to dump contents out of cell). Photosynthesis: Plants use the energy captured by ______________________ to change ____________ _____________ and water into food. Glucose is a ______________________ used by plants to convert sunlight into stored sugars (Energy). Chapter 4: Cells in Action Cellular Respiration: Cellular Respiration uses oxygen to breakdown food. Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration: Photosynthesis: Uses Sunlight Energy and CO to make Glucose and releasing O 2 Cellular Respiration: Cells use O to breakdown glucose and Releases CO . 2 2 2 Chapter 4: Cells in Action