The Processes
of the Cell
1
What has to happen to your cells in
order to grow from a baby into an
adult?
2
How do we know our cells
are working?
What do you think your
cells must do in order to
stay alive?
Your cells are constantly
working to perform many
activities such as getting
food, removing wastes,
growing, reproducing, and
making new materials
4
Your cells work to keep all of these
activities in balance, which is known
as homeostasis.
5
If your cells do not have the
materials necessary to conduct their
activities, they send out various
signals to let the rest of your body
know.
6
Homeostasis is also important because
if your cells are not balanced, chemical
reactions can not occur. This means
that your cells can not perform their job
correctly.
7
How are our cells able to do all of these
activities when they are surrounded by
a barrier, the cell membrane?
8
In our previous unit, we
learned that the job of the
cell membrane is to allow
materials in and out of the
cell.
9
The cell membrane is semi-permeable.
This means that it can let some
materials pass through while others
can not.
10
Since we now know that
materials can and must
move in and out of a cell
in order for it to survive,
let’s discuss the different
ways in which this occurs.
11
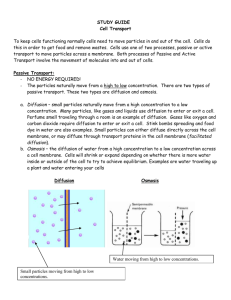
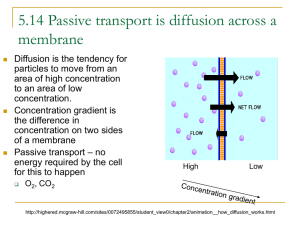
Some small particles can easily
move in and out of a cell, this
happens through diffusion.
Diffusion is when particles move
from an area where it is crowded
(high concentration) to an area
where it is less crowded (low
concentration)
Examples of Diffusion
Smell of food, perfume,
air freshener, and other
substances
13
Diffusion
http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/e
ducation/bitesize/standard/biolo
gy/investigating_cells/cells_and
_diffusion_rev3.shtml
14
Osmosis is the diffusion of water.
Water moving from where it is
crowded to where it is less
crowded.
15
Examples of Osmosis
Cooking rice, beans, and
macaroni
Watering a plant
16
Pure water diffuses more
than any other water
mixture because it is more
crowded (has a higher
concentration) than any
other water mixtures.
17
In this picture a red blood cell is put
in a glass of distilled water (pure
water with no salt or sugar in it).
Because there is a
higher concentration
of water outside the
cell, water enters the
cell by OSMOSIS.
The cell bursts and
dies
18
Osmosis
http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/e
ducation/bitesize/standard/biolo
gy/investigating_cells/cells_and
_diffusion_rev4.shtml
19
If your cell needs a
particle and the particle is
too big to diffuse into the
cell membrane, does your
cell just go without that
particle?
20
Although some particles
are too large to diffuse
into or out of a cell, they
can still get in or out of the
cell membrane.
How?
21
If a particle is too large to naturally go
through a cell membrane, it can enter or
exit in two ways:
Particles can move in and out of a
cell through protein doorways
If a particle is still too large to fit
through a protein doorway, it can
be engulfed (eaten) by the cell
22
Protein Doorways
23
Engulfing
24
Particles that have to go
through protein doorways can
enter one of two ways:
Passive transport -particles can
enter easily through the protein
doorway
Active transport -particles
require energy to move through
the protein doorway
25
26
Active transport is different from
passive transport because it
requires energy. Active transport is
necessary to make particles move
against their natural tendency. In
active transport, particles move
from less crowded (low
concentration) to more crowded
(high concentration).
27
Active Transport
28
Active transport is
important in organs such
as the kidneys when
harmful particles are
made to stay in the organ
when they naturally want
to diffuse
29
If a particle is too large to
fit through a protein
doorway, then it can enter
the cell by being engulfed,
endocytosis, or it can be
released from the cell by
exocytosis
30
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
31
Endocytosis
and
Exocytosis
32
Do cells need
energy?
33
Cells need energy to carry
out the activities which
allow them to live, grow,
and reproduce
34
Cells get energy from
food. Plant cells make
their own food while
animal cells must get their
food by eating other
things.
35
Plant cells make their own
food through the process
of photosynthesis. In this
process, plant cells take in
light energy and change it
into a food called glucose.
36
Photosynthesis
Sunlight + Water + Carbon
Dioxide = C6H12O6 (Glucose)
and Oxygen
37
Photosynthesis
38
Once food is obtained or
made in animal cells and
plant cells, it must be
broken down to release
energy. This process is
called cellular respiration.
39
Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 (Glucose) + Oxygen =
Carbon Dioxide, Water, and
Energy (ATP)
40
Cellular Respiration
41
Photosynthesis and
Cellular Respiration are
the opposite of one
another
42
We have discussed all of the
ways in which cells live and
grow by getting the nutrients
they need, but living
organisms would not exist
over long periods of time if
cells did not reproduce.
43
Living organisms can
reproduce sexually
and/or asexually.
44
Sexual reproduction
requires two parents to
make an offspring that
has characteristics of
both parents
45
Organisms that reproduce
sexually
Animals
Plants
Fungi
46
Asexual reproduction
requires one parent to
produce an identical
offspring
47
Organisms that reproduce
asexually
Bacteria
Plants
Fungi
48
Bacteria reproduces
asexually through a
process called binary
fission
49
Cells reproduce by
making more cells
or dividing through
a process called
mitosis (one cell
makes two)
This is a form of
asexual
reproduction.
50
Cells make sex cells to
help in the reproduction of
multi-cellular organisms
through a process called
meiosis (one makes four)
51
Meiosis
This is a form of
sexual
reproduction
52
Meiosis
53