Unit Number - Christopher Busuttil
advertisement

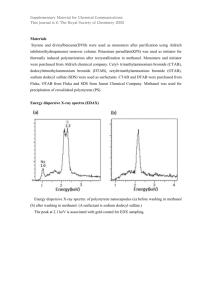
Unit Number: 8 Unit Title: Using Statistics for Science Unit Code: F/502/5547 Outcomes Covered: (1) Be able to use statistical techniques to investigate scientific problems Instructions: All necessary working must be shown. The use of scientific calculators is allowed. The use of electronic graph plotting tools is allowed. All questions must be read carefully before attempted. Question 1: This question covers grading criterion P1. P1.1 One of the European laws about the quality of food states that farmers should be equipped with the right machinery so that they can grade eggs produced in their farms. As part of the annual quality assurance program, the quality manager in a particular farm in the north of Malta sampled 20 fresh eggs directly from the line. The manager measured the diameter of each egg accurately, using a Vernier calliper.The following set of data represents the diameter of each egg in cm correct to one decimal place: 2.51, 2.55, 2.56, 2.58, 2.58, 2.59, 2.62, 2.75, 2.88, 2.98, 3.05, 3.04, 2.55, 2.55, 2.67, 2.78, 2.92, 2.95, 3.09, 3.10 Calculate the: (i) mean diameter of eggs, (ii) modal diameter of eggs, (iii) median diameter of eggs, (iv) standard error of the mean diameter, (v) 95% confidence limit. P1.2 The thickness of a newly produced fusing wire used in the circuit shown is recorded from a sample of newly produced reels of the same wire. A micrometer screw gauge in mm was used and the following results in mm were obtained: 0.66, 0.64, 0.61, 0.63, 0.62, 0.60 (i) Without using a calculator, calculate the standard deviation of the above set of data. (ii) Re-calculate your result with the aid of a calculator. Show all steps involved and compare the result with that obtained manually and justify any differences. Unit 8: Using Statistics for Science (F/502/5547) Page 2 P1.3 A box filled with bottles of chemicals was delivered to a laboratory. Upon delivery, the chemist who received the box wished to check his order. A bottle is picked at random from the box containing 2 methanol bottles, 3 hexane bottles and 5 formic acid bottles. Find the probability of picking: (i) a bottle of methanol, (ii) a bottle that is not hexane, (iii) a bottle that is either methanol or formic acid. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Question 2: This question covers grading criterion M1. M1.1 Recently, an industrial laboratory carried out a simple study to gather information about some of the chemical solutions used in the same laboratory. The study shows that methanol is used in 75% of the solutions, acetone is used in 15% of the solutions and 5% contain both chemicals. (i) Draw a fully labelled Venn diagram to represent the above information the chemical solutions used in this laboratory. about (ii) Calculate the probability that a solution chosen at random contains both methanol and acetone. (iii) Calculate the probability that a solution chosen at random contains either methanol or acetone. (iv) Calculate the probability that a solution chosen at random contains acetone given that it contains methanol. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit 8: Using Statistics for Science (F/502/5547) Page 3 Question 3: This question covers grading criterion D1. D1.1 As a physicist you are required to devise a simple physical experiment whereby you need to measure the time of fall of a simple object from a height of 2.5m. Devise a set-up for this experiment and record the time of fall for a chosen mass. Repeat the experiment for 100 times and record the time of fall in seconds correct to two decimal places. Tabulate your results and using Microsoft Excel plot a frequency plot for your data. Use the software to calculate the standard deviation for the set of data. Finally, identify and describe your distribution. D1.2 Sandra works for a private company as a quality manager. Currently, she is doing a quality assurance routine in a chemical production plant which manufactures 5 litre bottles of chemicals for industrial use. One particular bottlefilling machine fills bottles with hexane with volume normally distributed with a mean of 5.04 litres and a standard deviation of 0.05 litres. Sandra needs to find the probability that the volume of a randomly selected bottle will be less than 5.07 litres. Calculate this percentage probability. (Refer to the Appendix for the Standard Normal Table). D1.3 Suppose that you are an ecologist studying the abundance of food for a population of koalas in a forest located in the north west of Australia. The masses of a sample of male koalas taken from the same cluster of trees can be modelled by a normal distribution, with a mean of 70kg and standard deviation 5kg. Ten male koalas are chosen at random. Unit 8: Using Statistics for Science (F/502/5547) Page 4 (i) Find the probability that their mean mass is less than 65kg. (ii) Calculate the standard error of the mean. (iii) What are the 95% confidence limits? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit 8: Using Statistics for Science (F/502/5547) Page 5 Appendix Unit 8: Using Statistics for Science (F/502/5547) Page 6