Unit 1B Review KEY
advertisement

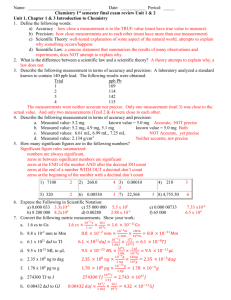
Conceptual Chem Name KEY KEY KEY 1B Review KEY! Unit 1 Section B - Looking at Water and Its Contaminants – A Review Physical Properties 1. Name two physical properties would allow you to distinguish between liquid water and rubbing alcohol. Odor, boiling point, freezing point, density Density 2. A graduated cylinder has a mass of 125 g. When a sample of an unknown liquid is placed in the cylinder, its new mass is 155 g. The volume of the liquid is 25 mL. What is the density of the liquid? 155 – 125 = 30. g of liquid 3. D = m/v D = 30.g/25 mL = 1.2 g/mL If the liquid in question 2 is insoluble in water, will it sink or float in the water? How do you know? Sink. It has a higher density. 4. A block has measurements of 6.00 cm, 17.0 cm, and 5.20 cm. The density of the block is 1.85 g/cm3. What is the mass of the block? V = L x W x H = 6.00 cm x 17.0 cm x 5.20 cm = 530. cm3 D = m/v so… 1.85 g/cm3 = m/ 530 cm3 so… m = 981 g Classification of Matter 5. What does the symbol (aq) following the formula for a compound mean? Would this substance be an element, a compound, a solution or a heterogeneous mixture? Aqueous (definition): mixed with water. This substance would be a solution. 6. Classify the following substances as homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homo a. Cl2 Hetero e. oil and water Homo b. potassium Homo f. air Homo c. KCl(aq) Hetero g. sedimentary rock Homo d. KNO3 Homo h. a solution 7. Classify the following substances as pure substances or mixtures. pure a. Cl2 mix e. oil and water pure b. potassium mix f. air mix KCl(aq) mix g. sedimentary rock KNO3 mix h. a solution c. pure d. 8. 9. Classify the following substances as an element, compound, homogeneous mixture or heterogeneous mixture. element a. Cl2 hetero mix e. oil and water element b. potassium homo mix f. air homo mix c. KCl(aq) hetero mix g. sedimentary rock compound d. KNO3 homo mix h. a solution Carbon tetrachloride, CCl4 is a liquid that can be used in dry cleaning. When 5.0 g of bromine is added to 75 g of clear colorless CCl4, the mixture has a reddish brown color. Over time, no settling out is observed. When the mixture is filtered, no residue is observed on the filter paper. When a light beam is directed at the mixture, its path through the mixture is not visible. Is the mixture a solution, colloid or suspension? Explain your answer. It is not an element and it is not a compound: it is a mixture. Since light doesn’t pass through the mixture, it shows the Tyndall effect (so it is not a solution). Since it doesn’t settle, it is not a suspension. The mixture is a colloid. Symbols, Formulas and Equations 10. Give the symbol for each element present in each molecule of Al2(SO4)3 and tell how many of atoms of each element are present. Al – 2 atoms S – 3 atoms O – 12 atoms Electrical Charges, Protons, Electrons, Atoms and Ions 11. Classify the following as anions, cations, or electrically neutral atoms. a. Rb+1 cation c. Se–2 anion b. CrO4–2 anion d. Sn neutral 12. 13. 14. Give the symbol and electrical charge for each of the following ions or atoms. Au+3 a. gold He b. F-1 c. 79 protons 76 electrons Helium 2 protons 2 electrons fluorine 9 protons 10 electrons For each of the atoms or ions, identify the number of protons and electrons. a. P–3 15 protons 18 electrons b. Zn 30 protons 30 electrons c. Ba+2 56 protons 54 electrons Give the symbol and charge for each of the following ions: Ca+2 a. calcium atom that lost 2 electrons N-3 b. nitrogen atom that gained 3 electrons 15. Were electrons gained or lost in order to form Be+1? Also explain what is wrong with the first part of this question. One electron was lost. This isn’t correct because Beryllium should lose 2 electrons according to the periodic table. 16. Complete the following table. Cation Anion Formula Mg 2+ O2– MgO Name Magnesium oxide Al3+ Cl– AlCl3 Aluminum chloride Mg2+ PO4–3 Mg3(PO4)2 Magnesium phosphate NH4+ CO32– (NH4)2CO3 Ammonium carbonate Fe+3 SO3-2 Fe2(SO3)3 Iron(III) sulfite Ca+2 Cl-1 CaCl2 Calcium chloride Cu+2 NO3-1 Cu(NO3)2 Copper (II) nitrate Al+3 OH-1 Al(OH)3 Aluminum hydroxide