Moles and Stoichiometry Worksheet
advertisement

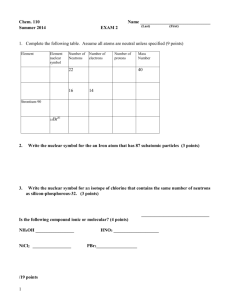
Moles and Stoichiometry By Noah Balla, Justin Panzarino, and Derek Prestera Key Terms: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● mole(mol): the amount of a substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12.00 grams of 12C ○ used to convert atomic mass units to grams molar mass: sum of the atomic masses (in grams) in a molecule ○ unit: g/mol 23 Avogadro’s number: 6.02 x 10 ○ number of particles in exactly one mole of a pure substance 22.4 L: This constant is used to convert from moles to volume or volume to moles. Empirical Formula: A chemical formula that gives the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in the formula. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula that gives the actual number of the elements in the molecular compound. Percent composition: The mass of each element in a compound compared to the entire mass of the compound and multiplied by 100 percent. ○ Percent composition of an element in a compound = n x molar mass of element molar mass of compound x 100% n = the number of moles of the element in 1 mole of the compound Mole ratio Molar mass A Molar mass A Mole ratio Mole ratio Molar mass B 1. 56.25 g Kr=_____________________ mol Kr 2. 3.67 x 1023 atoms Ag =_________________ mol Ag 3. 243 L O2 = __________________ mol O2 4. 0.035 mol magnesium phosphate = _______________ g magnesium phosphate 5. 1.01 grams Fe= _________ atoms Fe 6. 2KCl + 3O2 → 2KClO3 How many grams of oxygen are necessary to react completely with 63.0 g of KCl in the above reaction? 7. 2NH3 + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4 How many kilograms of NH3 are needed to produce 1.00 ✕ 105 kg of (NH4)2SO4? 8. MgO + CO2 MgCO3 6 CaO + P4O10 CaO + SO3 2 Ca3(PO4)2 CaSO4 (a) What mass of CO2 is needed to react with 124.6 g MgO? (b) What mass of magnesium carbonate is produced? (c) When 47.5 g P4O10 is reacted with an excess of calcium oxide, what mass of calcium phosphate is produced? 9. How many grams of sulfur (S) are needed to react completely with 519 g of Mercury (Hg) to form HgS? 10. How many moles of Fe are present in 39.4 g of the compound Fe2O3? 11. C6H12O6 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2 Starting with 500.4 g of glucose, what is the maximum amount of ethanol in liters that can be obtained by this process? (Density of ethanol = 0.789 g/mL.) 12. A compound is 64.9% carbon, 13.5% hydrogen, and 21.6% oxygen. Its molecular mass is 74 g/mol. What is its empirical and molecular formula? 13. How many liters of hydrogen must used to fully react 7.224x1024 atoms of carbon and create octane? 14. Tin (Sn) exists in Earth’s crust as SnO2. Calculate the percent composition by mass of Sn and I in SnO2. 15. There was an unknown compound with these percent compositions: 47.0% potassium, 14.5% carbon, and 38.5% oxygen. What is the empirical formula? If the true molar mass of the compound is 166.22 g/mol, what is its molecular formula? 16. If a manufacturer wanted to make 235 L of N2O, commonly known as laughing gas, how many grams of nitrogen are needed if there is an excess of oxygen? Answer Key 1. 0.6712 mol Kr 2. 0.610 mol Ag 3. 10.8 mol O2 4. 9.20 g magnesium phosphate 5. 1.08 x 10 22 atoms Fe 6. 24.7 g O2 7. 2.58 x 10 4 kg 8. a) b) c) 9. 83.0 g 10. 0.493 mol 11. 0.324 L 12. empirical: C4H10O Molecular: C4H10O 13. 537.6 L 14. Sn O 15. empirical: KCO2 molecular: K2C2O4 16. 231 g 136.1 g 260.7 g 104 g 78.77% 21.23%