key_3_u13_vocab
advertisement
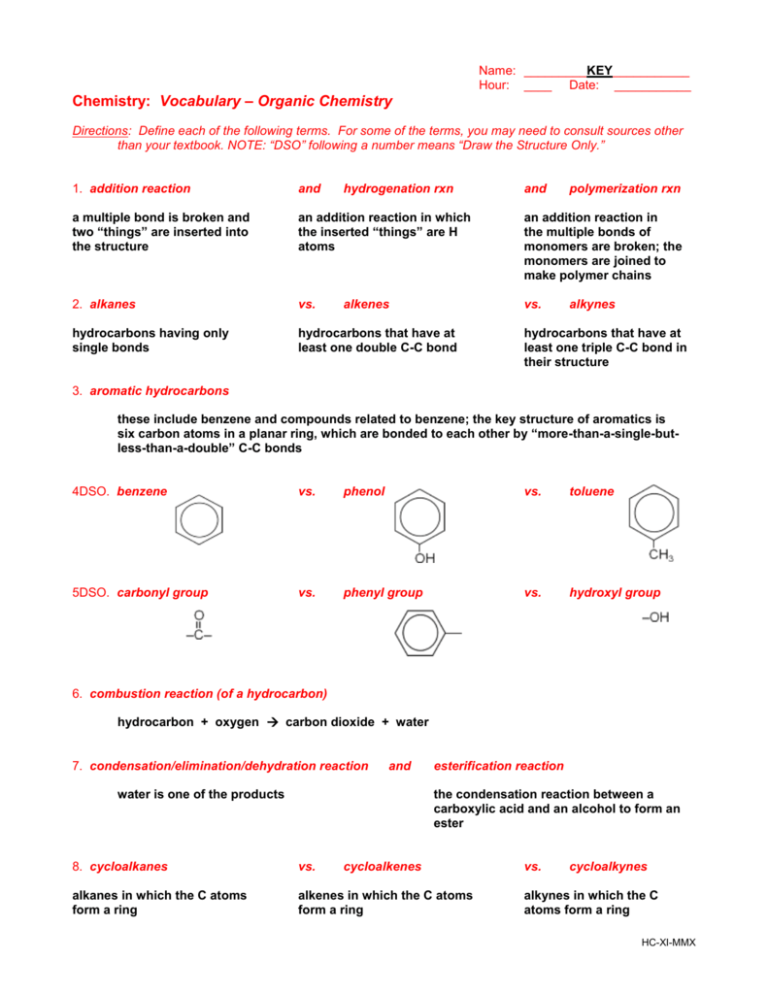
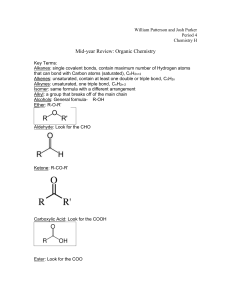
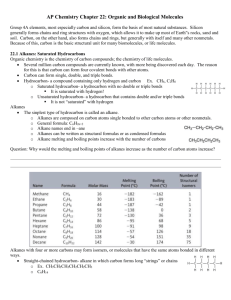
Name: _________KEY___________ Hour: ____ Date: ___________ Chemistry: Vocabulary – Organic Chemistry Directions: Define each of the following terms. For some of the terms, you may need to consult sources other than your textbook. NOTE: “DSO” following a number means “Draw the Structure Only.” 1. addition reaction and hydrogenation rxn a multiple bond is broken and two “things” are inserted into the structure an addition reaction in which the inserted “things” are H atoms an addition reaction in the multiple bonds of monomers are broken; the monomers are joined to make polymer chains 2. alkanes vs. vs. hydrocarbons having only single bonds hydrocarbons that have at least one double C-C bond alkenes and polymerization rxn alkynes hydrocarbons that have at least one triple C-C bond in their structure 3. aromatic hydrocarbons these include benzene and compounds related to benzene; the key structure of aromatics is six carbon atoms in a planar ring, which are bonded to each other by “more-than-a-single-butless-than-a-double” C-C bonds 4DSO. benzene vs. phenol vs. toluene 5DSO. carbonyl group vs. phenyl group vs. hydroxyl group 6. combustion reaction (of a hydrocarbon) hydrocarbon + oxygen carbon dioxide + water 7. condensation/elimination/dehydration reaction and water is one of the products esterification reaction the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form an ester 8. cycloalkanes vs. cycloalkenes alkanes in which the C atoms form a ring alkenes in which the C atoms form a ring vs. cycloalkynes alkynes in which the C atoms form a ring HC-XI-MMX 9. functional group a characteristic pattern that makes up a portion of a larger molecule 10 . hydrocarbon a compound containing only hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms 11. organic chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds 12. primary alcohol an alcohol having a single hydroxyl group (–OH) vs. secondary alcohol vs. an alcohol having two hydroxyl groups 13. saturated hydrocarbon vs. a hydrocarbon that has only single bonds; alkanes are saturated tertiary alcohol an alcohol having three hydroxyl groups unsaturated hydrocarbon a hydrocarbon that has one or more multiple bonds; alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic compounds are unsaturated 14. straight-chain compound vs. branched-chain compound these have a single C backbone a hydrocarbon in which a hydrocarbon substituent branches off from the main line of C atoms vs. substituted comp. a compound in which something other than H is in the place of where the H would normally be if the compound were a hydrocarbon 15. substituent “anything other than H” which takes the place of an H in a substituted compound 16. substitution reaction an H atom is removed and “something else” is put in its place and halogenation reaction a substitution reaction in which the “something else” is a halogen atom HC-XI-MMX