Module 18- Complex Arthroplasty curriculum map final
advertisement
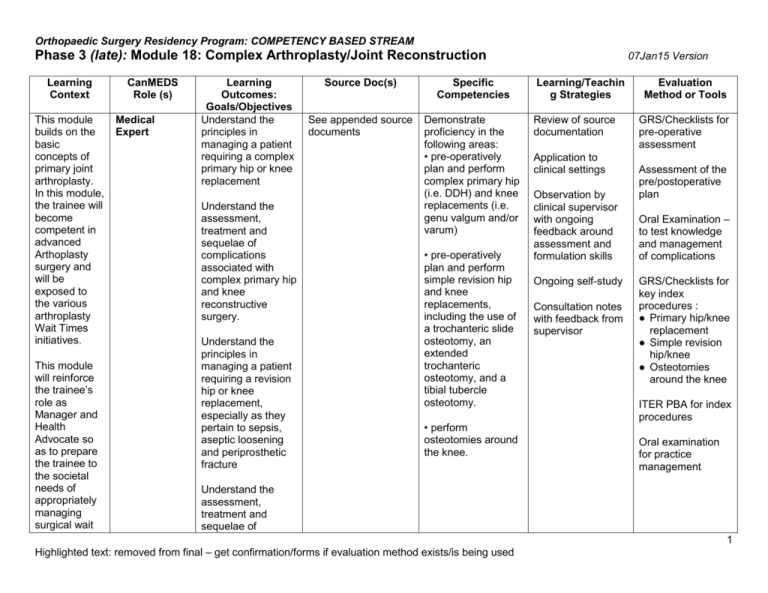
Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 3 (late): Module 18: Complex Arthroplasty/Joint Reconstruction Learning Context This module builds on the basic concepts of primary joint arthroplasty. In this module, the trainee will become competent in advanced Arthoplasty surgery and will be exposed to the various arthroplasty Wait Times initiatives. This module will reinforce the trainee’s role as Manager and Health Advocate so as to prepare the trainee to the societal needs of appropriately managing surgical wait CanMEDS Role (s) Medical Expert Learning Outcomes: Goals/Objectives Understand the principles in managing a patient requiring a complex primary hip or knee replacement Understand the assessment, treatment and sequelae of complications associated with complex primary hip and knee reconstructive surgery. Understand the principles in managing a patient requiring a revision hip or knee replacement, especially as they pertain to sepsis, aseptic loosening and periprosthetic fracture Source Doc(s) Specific Competencies See appended source documents Demonstrate proficiency in the following areas: • pre-operatively plan and perform complex primary hip (i.e. DDH) and knee replacements (i.e. genu valgum and/or varum) • pre-operatively plan and perform simple revision hip and knee replacements, including the use of a trochanteric slide osteotomy, an extended trochanteric osteotomy, and a tibial tubercle osteotomy. • perform osteotomies around the knee. 07Jan15 Version Learning/Teachin g Strategies Review of source documentation Application to clinical settings Observation by clinical supervisor with ongoing feedback around assessment and formulation skills Ongoing self-study Consultation notes with feedback from supervisor Evaluation Method or Tools GRS/Checklists for pre-operative assessment Assessment of the pre/postoperative plan Oral Examination – to test knowledge and management of complications GRS/Checklists for key index procedures : ● Primary hip/knee replacement ● Simple revision hip/knee ● Osteotomies around the knee ITER PBA for index procedures Oral examination for practice management Understand the assessment, treatment and sequelae of 1 Highlighted text: removed from final – get confirmation/forms if evaluation method exists/is being used Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 3 (late): Module 18: Complex Arthroplasty/Joint Reconstruction times. 07Jan15 Version complications associated with revision hip and knee reconstructive surgery. Medical Expert � Medical Expert Manager See appended source documentation See appended source documentation KNOW � Understand population-based Understand the indications for and perform a hip or knee osteotomy, arthrodesis, and/or joint replacement For complex primary joint arthroplasty and revision hip and knee replacement surgery, the resident should be able to comprehensively discuss the: • selection of appropriate implants • the factors affecting implant survivorship and function, including design, biomaterials, fixation and wear properties Be competent in: -triaging surgical cases Oral examination for choice of implant to use Review of documentation re: how to organize Structured Oral method using simulated 2 Highlighted text: removed from final – get confirmation/forms if evaluation method exists/is being used Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 3 (late): Module 18: Complex Arthroplasty/Joint Reconstruction approaches to health care services and understand the management of an arthroplasty practice including triage/priorities of patients. Be conscious and knowledgeable of human resources and finances as they relate to implants. -setting priorities in surgical bookings -be able to work with vendors in re: preoperative planning Be able to use appropriate, costeffective implants in surgeries dealing with: ● bone loss ● deformity ● periprosthetic fractures Resident will be responsible for preoperative planning and working with staff surgeon in the ordering of implants Health Advocate KNOW: � Understand the possibility of conflict of interest in performing the role as health advocate for a patient or community with that of being a manager or gate keeper Identify the health needs in the populations served through the various orthopedic outpatient settings, and promote its growth through ongoing communication with community organizations, etc. 07Jan15 Version sample list Resident observation of a staff performing all of the specific competencies, with the opportunity for questions and discussion Resident observation of taped simulated scenarios with opportunity for questions Direct observation of modeling competencies Regular supervision time with supervising surgeons, with opportunity to discuss social determinants of orthopaedic health and community scenarios/patient s and expert, faculty examiners around practice management Oral examination of implant selection including factors which affect implant survivorship Pre-operative plan – assessed by GRS Structured Oral Simulated scenarios with simulated patients. Residents will be assessed on their knowledge and communication of providing information around access to 3 Highlighted text: removed from final – get confirmation/forms if evaluation method exists/is being used Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 3 (late): Module 18: Complex Arthroplasty/Joint Reconstruction Learn about the orthopaedic, rehabilitation resources available to patients/families through community/intra/inte r professional setting Be able to identify and communicate risk medication and management 07Jan15 Version resources available to families Attending multidisciplinary team rounds in order to gain broader understanding of resources rehab services and post operative follow up procedures for the patient. Knee James H. MacDonald, et al Knee Arthrodesis. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., March 2006; 14: 154 - 163. Mark H. Gonzalez and Anis O. Mekhail. The Failed Total Knee Arthroplasty: Evaluation and Etiology. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., November/December 2004; 12: 436 – 446 Edward T. Su, Hargovind DeWal, and Paul E. Di Cesare. Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Above Total Knee Replacements J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., January/February 2004; 12: 12 – 20 Scuderi GR, Tenholder M, Capeci C. Surgical approaches in mini-incision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004 Nov;(428):61-7. Management of bone loss in revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006 Nov;452:186-92 Backstein D, Safir O, Gross A. Management of bone loss: structural grafts in revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006 May;446:104-12. Hip Paul E. Beaulé, Joel M. Matta, and Jeffrey W. Mast. Hip Arthrodesis: Current Indications and Techniques. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., July/August 2002; 10: 249 - 258. 4 Highlighted text: removed from final – get confirmation/forms if evaluation method exists/is being used Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program: COMPETENCY BASED STREAM Phase 3 (late): Module 18: Complex Arthroplasty/Joint Reconstruction 07Jan15 Version RA Brand. Hip Osteotomies: A Biomechanical Consideration. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., Oct 1997; 5: 282 - 291. Thomas P. Vail and John J. Callaghan. Minimal Incision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., December 2007; 15: 707 – 715 EL Masterson, BA Masri, and CP Duncan. Surgical approaches in revision hip replacement. J. Am. Acad. Ortho. Surg., Mar 1998; 6: 84 - 92. Howell JR, Garbuz DS, Duncan CP. Minimally invasive hip replacement: rationale, applied anatomy, and instrumentation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004 Apr;35(2):107-18 Gross AE, Goodman S. The current role of structural grafts and cages in revision arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004 Dec;(429):193-200 Harris WH. An integrated solution to acetabular revision surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006 Dec;453:178-82. Cui Q, Mihalko WM, Shields JS, Ries M, Saleh KJ. Antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the treatment of infection associated with total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007 Apr;89(4):871-82 Huo MH, Gilbert NF, Parvizi J. What's new in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007 Aug; 89(8):1874-85 5 Highlighted text: removed from final – get confirmation/forms if evaluation method exists/is being used