Supplementary Methods Establishment of human TNBC The breast
advertisement

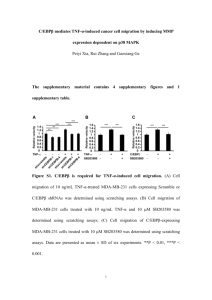
Supplementary Methods Establishment of human TNBC The breast cancer parental cells including MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Life Technologies) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution (Sigma) 37 °C, 5% CO2. Subconfluent parental cells were harvested and a single cell suspension with >95% viability (1×106) was injected subcutaneously into the mammary fat pads of female nude mice (5-8 weeks). Tumours were established (~30 mm3) approximately 4 weeks after tumour cell injection. By approximately 8 weeks post-tumour cell inoculation when the tumour volumes were allowed to reach ~700 mm3 (1.2 cm of diameter is the maximum size that the tumours are allowed to attain under institutional guideline of the University of Florida), tumours were excised, grown in culture and inoculated into the mammary fat pads of female nude mice. This procedure was repeated several times until similar tumour volumes (~700 mm3) were obtained with fewer cells (1×105) for shorter time (2 weeks). MDA-MB-231Br (brain metastatic) was a generous gift from Dr Patricia Steeg (National Cancer Institute, USA). Determination of maximum tolerated dose of NCI-41356 A single athymic female nude mice (nu/nu) was given a singly IP injection of 0.8g/kg of NCI41356 (equivalent to 100μM), while a second mouse received a dose of 0.4g/kg and a third mouse received a single dose of 0.2g/kg. Their weights were observed and recorded every two days for two weeks. Immunohsitochemistry detection and histological morphometric analysis The breast cancer xenograft tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Three serial frozen sections from each treatment of the breast cancer xenograft tissues were incubated with antibodies against CRYAB (Abcam), VEGF (Abcam) and von Willbebrand factor (Millipore), respectively, for 1 hour. Detection was done with an avidin-biotin complex method-based system. The secondary biotinylated antibodies were from Dako, Inc., and avidin biotin complex were from Vector laboratories. The sections were counterstained with Gill’s hematoxylin. At ×200, we used an eyepiece systematic point sampling grid with 100 points and 50 lines to count the fraction of points overlaying the positive stained structures of the 10 most vascular areas within the chosen sections. We average this over 10 microscopic fields to obtain a final result as a percentage of staining. Supplementary figure legend Supplementary Figure 1. a. Concentration response curves to the decoy peptides in the U2OS cells (20k/well) expressing the PathHunter™ cell-based CRYAB/VEGF165 interaction assay. Relative RUL is expressed as the percentage of the vehicle treatment. b. Synthetic decoy 1 peptides corresponded to the five sequences of VEGF165 interacting regions of human CRYAB. A control “scrambled” (*scr) peptide with the amino acid composition of *157/164.c. All decoy peptides exhibit similar internalization efficiencies in U2OS cells. Supplementary Figure 2. a. Schematic of the customized PathHunter™ cell-based CRYAB/VEGF165 interaction assay. b. Concentration response curves to the three leading compounds as indicated in the two cell densities (5k/well or 20k/well) of U2OS cells expressing PathHunter™ cell-based CRYAB/VEGF165 interaction assays. Supplementary Figure 3. a. The tumour volumes of different in vivo passages of breast cancer cells. The broken line indicated the maximum size that the tumours are allowed to attain under institutional guideline of the University of Florida. b. The percentage change of body weight of normal mice treated with different doses of NCI-41356 for two weeks. c. Western blot analysis of total protein levels of CRYAB in breast cancer cell lines. Supplementary Figure 4. a. Annexin V-propidium iodide-positive cells were shown by flow cytometric analysis (top right, late stage apoptosis; bottom right, early apoptosis). b. Phasecontrast of photographs of third in vivo passaged MDA-MB-231 cells show that NCI-43156 treatment leads to the cells less stellate with lower proportions of lamellipodia, filopodia and trailing compared with those of vehicle treatment. c. Vimentin mmunostaining was detected in MDA-MB-231 cells. d. Western blot analysis of total protein levels of vimentin in the MDAMB-231 cells normalized to GAPHD loading control. e. Survival assay of breast cancer cells were determined by crystal violet staining. f. VEGF165 protein levels in both supernatant and cell lysates of MCF-7 were measured by ELISA. Supplementary Figure 5. a. Western blot analysis the effect of NCI-41356 treatment on CRYAB expression in breast cancer cell lines. b. showing no detectable inhibitory effect on endothelial cells proliferation in the absence of MDA-MB-231 cell-stimulation. c. IHC staining for CRYAB, VEGF and von Willebrand factor. d. Three plots demonstrated the relationships between NCI-43156 treatment and the staining of CRYAB, VEGF or VWF (% of points). Supplementary Table NCI# IC50±SD (μM) Maximal inhibition at 100μM (%±SD) MDA-MB-231 MDA-MB-436 MDA-MB-231 MDA-MB-436 41356 24.5±1.4 30.8±3.2 97.6±1.9 90.1±2.2 525117 86.3±2.5 96.5±5.7 75.8±7.2 55.0±9.6 24681 61.9±7.7 77.4±1.1 81.0±0.5 59.2±1.3 52296 93.8±5.2 92.5±2.1 51.5±3.1 49.1±2.8 Supplementary table 1. IC50 of the four SMIs for MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 cells 2