Project Plan
advertisement
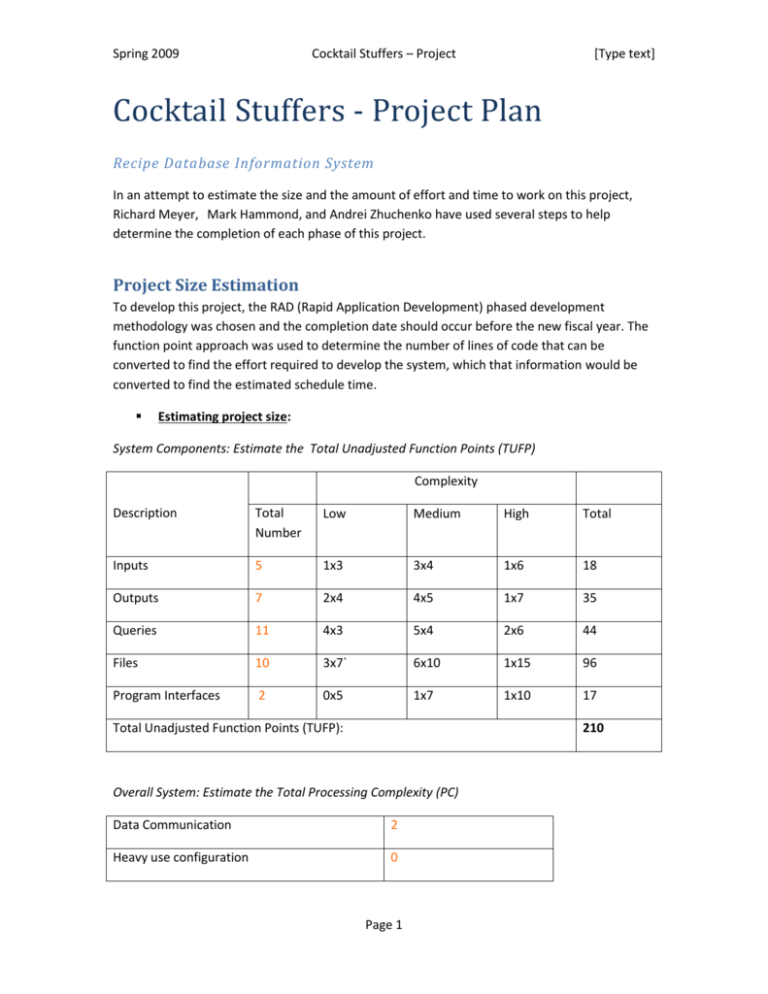
Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project [Type text] Cocktail Stuffers - Project Plan Recipe Database Information System In an attempt to estimate the size and the amount of effort and time to work on this project, Richard Meyer, Mark Hammond, and Andrei Zhuchenko have used several steps to help determine the completion of each phase of this project. Project Size Estimation To develop this project, the RAD (Rapid Application Development) phased development methodology was chosen and the completion date should occur before the new fiscal year. The function point approach was used to determine the number of lines of code that can be converted to find the effort required to develop the system, which that information would be converted to find the estimated schedule time. Estimating project size: System Components: Estimate the Total Unadjusted Function Points (TUFP) Complexity Description Total Number Low Medium High Total Inputs 5 1x3 3x4 1x6 18 Outputs 7 2x4 4x5 1x7 35 Queries 11 4x3 5x4 2x6 44 Files 10 3x7` 6x10 1x15 96 Program Interfaces 2 0x5 1x7 1x10 17 Total Unadjusted Function Points (TUFP): 210 Overall System: Estimate the Total Processing Complexity (PC) Data Communication 2 Heavy use configuration 0 Page 1 Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project Transaction rate 1 End-user efficiency 3 Complex processing 1 Installation ease 0 Multiple sites 0 Performance 0 Distributed functions 0 Online data entry 2 Online update 0 Reusability 0 Operational ease 2 Extensibility 0 Total Processing Complexity (PC): 11 [Type text] (0=no effect on processing complexity; 3=great effect on processing complexity) Adjusted Project Complexity (APC): .90 + (0.01 x 11) = 1 .01 Total adjusted Function Points (TAFP) = .1.01 (APC) x 210 (TAFP): 212.1 The development of this system will use the following: 60% Java, 30%XML, 8% SQL, 1% JavaScript, and 1% HTML Total Lines of code: [(.60x 212.1 x55) + (.30 x 212.1 x 15) + (.08 x 212.1 x 15) + (.01 x 212.1 x 15) + (.01 x 212.1 x 15)] = 8240.1 Estimating the effort: Page 2 Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project [Type text] The next step is to covert the lines of code using the COCOMO model which will determine the estimation of effort to complete this project in person-months. Effort (in person-month) = 1.4 X (8240.1/1000) = 11.536 person-months Estimating the time required: The total time that may be required to complete this project is determined by: Schedule time (months) = 3.0 x 11.5361/3 = 6.78 months Estimating the number of staff: For this project, the number of staff members are determined by: Number of staff = 11.536 / 6.78 = 1.70 ~ 2 staff members. Work Breakdown Structure Task Number Duration (In Days) Task Name Dependency Status 1 Project Initiation 2 2 Identify Problems 1 1 Complete 3 System Request 2 2 Complete 4 Feasibility Analysis 3 4.1 Technical Feasibility 1 3 Complete 4.2 Economic Feasibility 1 4.1 Complete 4.3 Organizational Feasibility 1 4.2 Complete Project Plan 6 5 Page 3 Complete Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project [Type text] 5.1 Size Estimation 1 4 5.2 Work Breakdown Structure 1 5.1 5.3 Work Plan 1 5.2 5.4 Staffing Plan 1 5.3 Complete 5.5 Standards List 1 6.4 Complete 5.6 Risk Assessment 1 6.5 Complete 6 Requirement Gathering 5 5 7 Data Flow Diagram 1 6 8 Data Dictionary 5 7 9 Database Design (E-R Diagram) 1 7 10 Document/Design Input Screens 2 9 11 Document/Design Output Report 2 9 12 Document/Design Menu System 3 9 13 Program Design 5 14 Program Test Design 5 15 System Architecture 15 16 Database Development 15 15 17 Program Codes 60 16 18 User Interface 30 17 19 Program Testing Results 30 18 Work Plan Insert Work Plan Diagram Here Page 4 13 Complete Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project Staffing Plan Mohammad Rob, Project Manager [Type text] Creates the work plan, staffs the project, and applies techniques to control and direct the project through the SDLC. Richard Meyer, System Analyst Analyzes and design the infrastructure and business process model while focusing on interfaces for the system and to ensure proper performance. , Business Analyst Analyzes the business process and documents the data flows , Programmer Codes System Richard Meyer, Implementation Install, maintain, and perform postimplementation audits. Standards To better organize the activities of this project, certain standards were created to promote efficiency and accountability among the project members and to avoid ambiguous documentation. Coding Standards All modules should include headers that identifies the programmer, last update information, and description of the code W3C web standards compliance Use Coding standards Use SQL standards Ensure cross platform compatibility (Windows, Mac, Unix) with different web browsers (Internet Explorer, Firefox/Nestsape, Safari, etc..) Page 5 Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project Documentation Standards All margins should be set to 1 inch. All deliverables should be added to the project binder and recorded in its table of contents, keeping the chronology in order. Project name and date should appear as a header on all documentation. Record task progress in the work plan every Friday, 10am. Mandatory meeting attendance for every Monday morning, 10am. E-mail notifications will be sent for canceled meetings. Any changes to the requirements must be submitted as a written format request and to be approved by the project manager. Name of program to be created Description of the program’s purpose Identify special calculations Apply business rules that should be incorporated into the Pseudo-code Include due date Procedural Standards Specifications Requirement Standards Page 6 [Type text] Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project [Type text] User Interface Design Standards Labels will appear in boldface text, left justified. Company Logo/Name must appear on top left of entry screen The tab order of the screen will move from top left to bottom right. Risk Assessment Potential risks that could be associated with this project are: Poor design---Medium Risk o Implemented system does not work on current infrastructure Scope creep—Medium Risk o Will delay entire process and will offset the project Solution: Analysis and requirements gathering should be thorough. Solution: Avoid changes if possible. Include the modifications to system after the completion of the project. Inadequate personnel—Low Risk o May extend time to complete project Solution: Include additional personnel Solution: Provide training Page 7 Spring 2009 Cocktail Stuffers – Project [Type text] Over estimating the project plans—Low Risk o Will require additional resources (size, effort, time) if the project cannot complete as schedule Solution: Use standard estimation for this specific industry Page 8