Review stations part 2 – key
advertisement
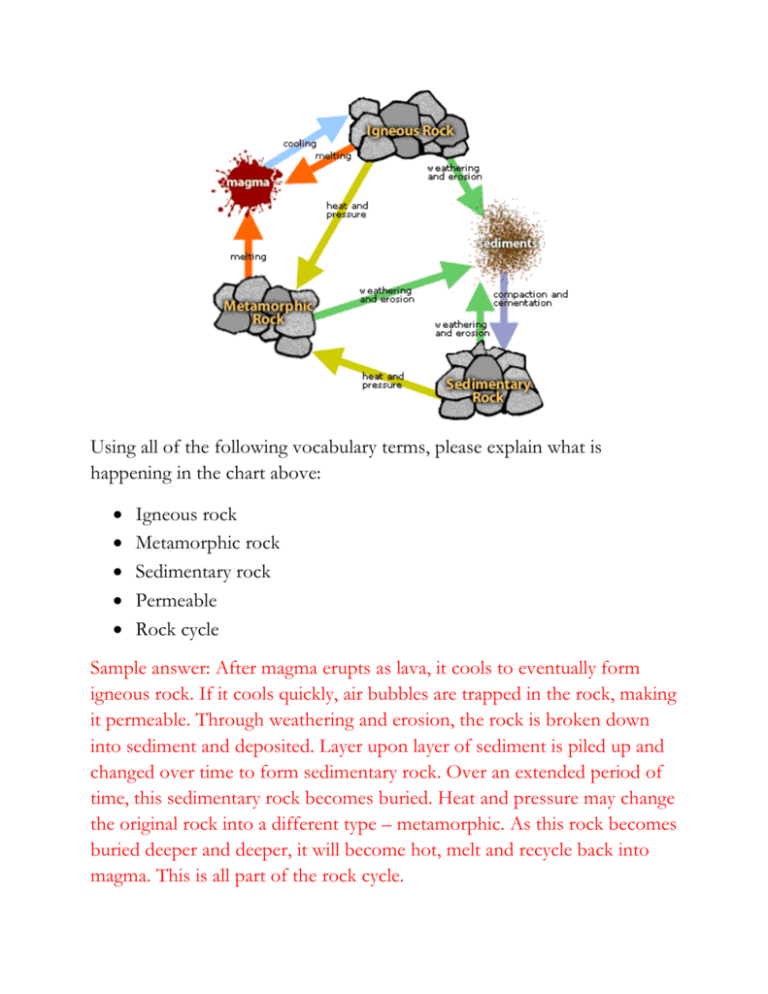
Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what is happening in the chart above: Igneous rock Metamorphic rock Sedimentary rock Permeable Rock cycle Sample answer: After magma erupts as lava, it cools to eventually form igneous rock. If it cools quickly, air bubbles are trapped in the rock, making it permeable. Through weathering and erosion, the rock is broken down into sediment and deposited. Layer upon layer of sediment is piled up and changed over time to form sedimentary rock. Over an extended period of time, this sedimentary rock becomes buried. Heat and pressure may change the original rock into a different type – metamorphic. As this rock becomes buried deeper and deeper, it will become hot, melt and recycle back into magma. This is all part of the rock cycle. If you were to use the worksheet above to identify a mineral, how would you find each of the properties listed? Describe what you would do to find each, using all of the following vocabulary terms: Hardness: Scratch the mineral with a series of items based on the Moh’s scale to determine the hardness. Streak: You can observe the streak by rubbing a mineral against a piece of unglazed porcelain tile to observe the color of its powder. Luster: Observe the mineral to see how it reflects light. Color: Observe the mineral to see its color. Specific gravity: Determine the density by dividing mass by volume. Cleavage: Determine of the mineral splits easily along flat surfaces. Fracture: Determine how the mineral looks when it breaks apart in an irregular way. Special properties: Determine if a mineral is magnetized, glows, or reacts to acid. Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what is happening in the diagram above: Epicenter Seismic waves Energy Convection currents During an earthquake, seismic waves race out from the epicenter in all directions, carrying energy with them. Seismic waves move away from the focus, through the Earth’s interior, and across the surface, often causing destruction in their path. Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what is happening in the chart above: Plate tectonics Convergent boundaries Transform boundaries Divergent boundaries Subduction The theory of plate tectonics states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in slow, constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. This explains the formation, movement and subduction of Earth’s plates. As the plates move, they collide (at convergent boundaries), pull apart (at divergent boundaries), or grind past each other (at transform boundaries) causing spectacular changes in Earth’s surface. Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what is happening in the diagram above: Sedimentary rock Fossil Location Age Deposition Fossils are remains of plants or animals that have been buried deep in sediment to create a mold. As the sedimentary rock forms, an outline of the plant or animal is permanently left in the rock – this is known as a fossil. Through deposition, layers of sedimentary rock exist on top of one another. The age of the fossil can be determined based on the location at which it is found in the sedimentary rock. This diagram shows that fossils can help to document how old the rock is. Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what the diagram above represents, even if some of the parts are not labeled: Crust Mantle Core, inner and outer Crustal plates Lithosphere Asthenosphere The three main layers of the Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. These layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pressure. The crust is a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor. The lithosphere is where the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust meet. This is where crustal plates exist. Crustal plates float on the asthenosphere, which is the soft layer just below the lithosphere. The mantle is made up of rock that is very hot, but solid. The outer core is a layer of molten material that surrounds the solid metal inner core. Using all of the following vocabulary terms, please explain what the diagram above represents, even if some of the parts are not labeled: Convection currents Plate tectonics Continental drift Unequal heating Pangaea Plate Tectonics is the theory that Earth’s surface is broken into many different parts called plates. These plates are pushed and pulled across Earth’s surface by convection currents in the mantle. Convection currents are set into motion because of the unequal heating of the asthenosphere. This theory, which was called Continental Drift, was first developed by Alfred Wegener when he noticed that the Earth’s continents fit together like pieces of a puzzle. He concluded that the continents started together as one giant supercontinent that he named Pangaea. Over time this continent broke apart and drifted to their present day positions.