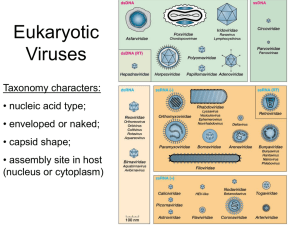
Parts of a Virus
advertisement
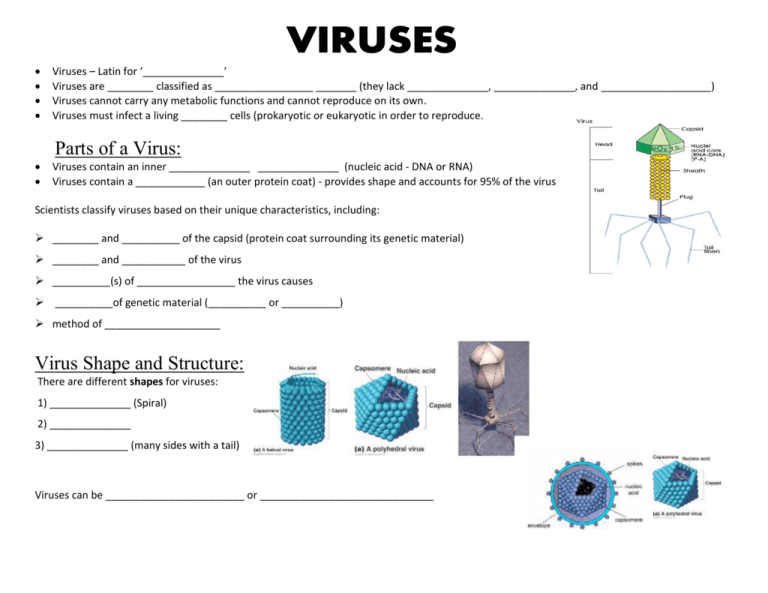
Viruses – Latin for ‘______________’ Viruses are ________ classified as _________________ _______ (they lack ______________, ______________, and ___________________) Viruses cannot carry any metabolic functions and cannot reproduce on its own. Viruses must infect a living ________ cells (prokaryotic or eukaryotic in order to reproduce. Parts of a Virus: Viruses contain an inner ______________ ______________ (nucleic acid - DNA or RNA) Viruses contain a ____________ (an outer protein coat) - provides shape and accounts for 95% of the virus Scientists classify viruses based on their unique characteristics, including: ________ and __________ of the capsid (protein coat surrounding its genetic material) ________ and ___________ of the virus __________(s) of _________________ the virus causes __________of genetic material (__________ or __________) method of ____________________ Virus Shape and Structure: There are different shapes for viruses: 1) ______________ (Spiral) 2) ______________ 3) ______________ (many sides with a tail) Viruses can be ________________________ or ______________________________ Looking In: Methods of Reproduction: _____________________________ = the time it takes between when the virus _____________ a cell and when symptoms _______________ (when the virus ruptures the cell). There are _________ types of reproduction/replication: The __________________ Cycle and The __________________________ Cycle Lytic Cycle: ____________________ & _____________: - Proteins on the surface of the virus bind to protein receptors on the surface of the host cell’s membrane; The virus injects its genetic material (DNA or RNA) into the host cell) ___________________: - The host cell replicates the parts of the virus (synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids). ___________________: - New viruses are assembled in the host cell. ___________________: - The host cell bursts open (lysis) and releases the new viruses – they go on to invade other cells Note: 25-45 min. production of 100s of viruses Lysogenic Cycle: ____________________ & _____________: - The virus attaches to/invades host cell and injects its genetic material (nucleic acid - DNA or RNA) into the host cell. _______________________: - The viral DNA (genetic material) is inserted into the host cell’s DNA and is referred to as a _________________. _______________________: - The provirus (viral DNA) remains ________________ (inactive) for a period of time while replication of the host cell occurs without any harm to it. - A “trigger” or “stimulus” activates the provirus, and it separates from the host DNA. The trigger stimulates the lytic cycle to begin, and the infection/death of the host cell. ___________________: - The host cell replicates the parts of the virus (synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids). ___________________: - New viruses are assembled in the host cell. ___________________: - The host cell bursts open (lysis) and releases the new viruses – they go on to invade other cells Humans and Viruses Many common human diseases are caused by viruses Viruses attack cells as it reproduce The destruction of the cells causes the symptoms of disease Routes of Transmission: