PAP Biology Virus Cornell Notes Answer guided question here
advertisement

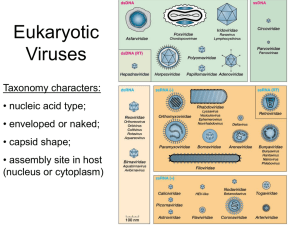
PAP Biology Virus Cornell Notes Answer guided question here. Answer guided question here. Answer guided question here. Explain why a virus is considered to be non-living. Viruses - Biological particles that are NOT made of cells. – Viral particles are extremely small in size. – Don’t eat, respire or respond to their environment. (No metabolism.) – Parasitic: they require a host. Host is an organism that shelters and nourishes something. – Host provides the virus with all the materials needed to make copies of itself can NOT reproduce on its own. – Therefore, viruses are considered to be nonliving. Describe the Structure of a Virus. Capsid: protective coat made of protein DNA orRNA: nucleic acids – Influenza virus has DNA – Retrovirus has RNA Envelope: outer lipid layer and an inner protein layer surrounding the capsid Projections: spike projections on the envelope that helps recognize and attach to a host cell What makes a retrovirus different from all other organisms we study? A retrovirus is a virus that contains an RNA core as it’s genetic material that replicates by transcribing it’s RNA into DNA. The DNA is then incorporated into the host’s genome. – Retro means reverse order or backwards. – Retroviruses have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase which makes RNA transcribe DNA. PAP Biology Virus Cornell Notes Draw 4 virus shapes: Answer guided question here. Answer guided question here. Shape (draw each in column to left) – Polyhedral virus: geometric shapes (colds) – Binal virus: 2 parts – polyhedral capsid and helical tail – Helical virus: helical with nucleic acid coil (influenza) – Filovirus: threadlike or looped at the end (Ebola) Compare and contrast how viruses reproduce. Lytic cycle ex. Chicken pox (Page 481) – rapid cycle – 1 Virus invades the cell by attaching and injecting it’s genetic material – replication occurs with genetic material incorporated into host’s genome. – many new viruses are made – cell lyses (dies/breaks apart) – many viruses are released to invade new cells Lysenogenic cycle ex. Cold sores – delayed symptoms – Does NOT kill cell immediately – Viral DNA segment attaches to the cell’s chromosome prophage – Some prophage remains in the lysogenic cycle indefinitely – Environmental stimulus causes the prophage to separate into lytic cycle How are viral diseases different from those caused by other factors? Viruses are pathenogenic meaning they cause disease. Diseases caused by viruses: – animal viruses (rabies, feline leukemia, mad cow) PAP Biology Virus Cornell Notes plant viruses (tobacco mosaic, turnip yellow mosaic) – bacterial viruses - bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacterial cells. – Can also cause disease in humans (flu, measles, HIV, herpes, warts) – Viral diseases can NOT be treated using antibiotics. They must run their course or be prevented by vaccination. VIRUS SUMMARY: