File
advertisement

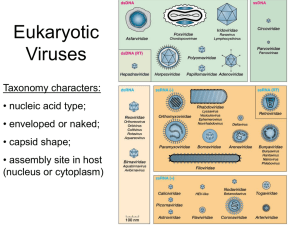
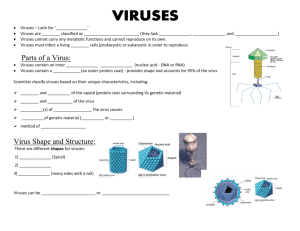
Chapter 2.5 Viruses & Bacteria Review - KEY 1. Define antibiotics? Why do antibiotics work against bacteria and not viruses? Chemical substance derivable from a mold or bacterium that kill microorganisms and cures infections 2. The protein capsid of a protein surrounds the genetic information (DNA/RNA) in a virus. 3. Bacteria that make their own food by obtaining their energy from inorganic molecules to make food, rather than obtaining energy from the sun are called chemoautotrophs. 4. Know the difference between the following (describe each one below): a. Photoautotrophs: make own food using sunlight b. Chemoautotrophs: make own food using chemicals c. Heterotrophs: can’t make own food & must “eat chemicals” or organic matter d. Decomposers: perform photosynthesis and eat organic matter or chemicals 5. Know the difference between the following (describe each below): a. Obligate Aerobes: must have oxygen to live b. Obligate Anaerobes: must not have oxygen (may die in presence of oxygen) c. Facultative Anaerobes: can live with or without oxygen 6. The lytic cycle is a cycle of viral infection, replication, and cell destruction. For the following, please identify if the statement is true or false and explain why you think so. 7. T or F “Viruses are considered living because they are capable of reproduction.” 8. T or F “Viruses consist of DNA or RNA surrounded by a coat of protein.” 9. T or F “The host cell is destroyed during the lysogenic cycle.” 10. T or F “A pathogen is harmful to living organisms because it causes disease.” 11. T or F “Antibiotics interfere with metabolic processes in bacteria that viruses do not have.” 12. T or F “Viruses can only produce in living cells.” 13. T or F “Viruses are considered cellular organisms.” 14. T or F “Viruses have nuclei and organelles.” 15. T or F “Viruses contain genetic information (DNA or RNA).” 16. T or F “Viruses can reproduce independently (without a host cell).” 17. T or F “Viruses perform metabolism and homeostasis.” 18. T or F “Prokaryotes that break down dead organisms and wastes are called decomposers.” 19. The protective outer coat of a virus is called a protein capsid. 20. Antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not viruses. 21. Tell some reasons why viruses are NOT considered LIVING. a. b. c. d. Do not reproduce Do not pass genetic traits to offspring Do not metabolize Need a host cell in order to survive 22. Match the diagram letters with the best statement: B C E A D A Virus’ genetic information is injected into host cell. The virus’ genetic information is copied. The host cell explodes, releasing more viruses. C The virus attaches itself to the host cell. Cell reproduces more viruses. B D E 23. A typical virus consists of a protein coat and a genetic information ( DNA/RNA). 24. E. coli is a bacterium with short, thin, hair-like projections called pili. These can help it stick to other cells or transfer genetic material. 25. Viruses are surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. 26. Conjugation is the process through which bacterial cells such as E. coli transfer pieces of genetic material using pili. 27. What is the first line of defense for the body against foreign invaders? What is the second line of defense? What do you do when all lines of defense fail? 1. Physical and chemical barriers that are always ready and prepared to defend the body from infection (skin, tears, mucus, cilia, stomach acid) 2. Immune response, group of cells, tissues and organs that work together to protect the body, the immune system 3. Treatment (antibiotics) 28. Identify either Bacteria and Virus 29. Virus Virus Bacteria 30. Vaccination is the process by which a dead or disabled pathogen (or proteins from that pathogen) is introduced into the body so that an immune response results without an actual infection. 31. Do viruses have organelles? Why? No. They have free-floating genetic material (DNA or RNA). They are non-living and cannot reproduce without a living host. 32. When a virus finds a host cell what does it do? What is this process called? Viruses attach themselves to a living host cell via the lock and key model. They then insert their genetic material into the host and replicate their viral genetic material. 33. What is a vaccine? Dead or weakened pathogen that helps the immune system produce antibodies against the pathogen (aka: acquired immunity). 34. Sketch each bacteria shape below: Rod (Bacilli) Round (Coccus) Spiral bacteria (Spirilla) 35. Label the following picture using the terms: tail sheath, tail fibers, protein capsid. 36. Label the following picture using the terms: DNA, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, flagella.