the oceans
advertisement

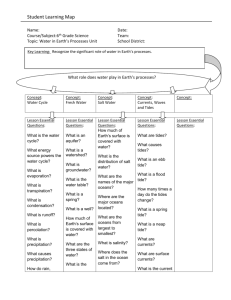
Name____________________ Test Date____________ Parent Signature____________________________ Study Guide Unit 10 Oceanography This unit addresses the movement of water through the crust, ocean, and atmosphere #1 Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. Explain that a large portion of the Earth’s surface is water, consisting of oceans, rivers, lakes, underground water, and ice. Relate various atmospheric conditions to stages of the water cycle. Describe the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world’s oceans. Explain the causes of waves, currents, and tides. #2 Students will describe various sources of energy and with their uses and conservation. Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy. Questions – students will be asked to answers these questions throughout the unit. #1 How does the location of water on Earth's surface and the conditions of the atmosphere affect its path through stages of the water cycle? #2 How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor? THE OCEANS 1. Locate and name the five major oceans. A) _________________________ B) _________________________ C) _________________________ D) _______________________ E) _______________________ 2. The earth's oceans are _________________________ 3. Almost ____________ of the earth's surface is covered by water. 4. The majority of Earth's surface is _________________________________________________ 5. Underneath the ocean, the earth has _________________________, _________________________, and _________________________ which are often _________________________ than those on dry land. 6. Draw and label the following ocean floor features: coast, continental shelf, continental slope, continental rise, ocean. 7. Draw and label the following ocean floor features: Mid Ocean Ridge, Volcanic Island , Seamount, Abyssal Plain, Trench 8. Salinity is the ___________________________________________ in a solution. 9. Name three things that can affect ocean salinity. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 10. Where would the salinity of the ocean probably be the lowest? ___________________________ 11. What happens to the temperature of ocean water as you go deeper? ___________________________ 12. Since the _______________________ of Earth is covered in water, most ___________________________ falls on Earth’s ___________________________. CURRENTS 13. Ocean currents can be caused by factors such as _______________________, ______________________, ______________________, _________________________, and ___________________________________. 14. Ocean currents flow in ___________________________________________________ around the earth. 15. Differences in ___________________________ and ___________________________ causes currents. 16. Surface currents are the currents on the ___________________________ of the water (within ___________________________ of surface) 17. Surface currents are formed by ___________________, _______________________________________ of surface of Earth, and the ___________________________ (spinning) of the Earth. 18. List three factors that control surface current. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 19. Surface currents alter an area’s __________________. The ____________________________________ transfers to the adjoining ____________________________________ 20. Deep currents are water moving ____________________________________ of the surface. 21. Deep currents are formed by ________________________ in water __________________. 22. Deep Currents - An increase in __________________ increases __________________ and causes water to __________________. 23. Deep Currents - Colder water at the poles increases ____________________________________ causing water to __________________. 24. Deep Currents - Warmer water at the equator ____________________________________ and this creates the ______________________________. 25. _________________________ is the movement of water from the surface to greater depths 26. _____________________ is the vertical movement of deep water up to the surface. 27. The Gulfstream is the ____________________________________ flowing from the Equator along the __________________of the United States (__________________,__________________South Carolina, New York) to England. 28. What is the Coriolis Effect? ______________________________________________________ 29. How is the Coriolis Effect formed? ____________________________________ 30. The Coriolis Effect deflects moving objects to the __________________________________________ ______________________________ Hemisphere and to the ____________________________________ _____________________________ Hemisphere. 31. Coriolis Effect is important in the formation of ____________________________________ like hurricane and cyclones. 32. Ocean water often _____________________________ when it meets a land mass. This is called ____________________________________ 33. El Nino is __________________flowing from the ___________________________towards ________________________and then continental deflection forces the warm water to flow north along the coast of Mexico and the __________________ 34. El Nino causes ____________________________________ on the western coast of South and North America. TIDES 35. The _________________________________ and the __________________ (spinning) of the earth cause ocean water to bulge, producing __________________. 36. List the three things that cause high and low tides to form. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 37. Tides cycle as the Moon __________________________________ and as the position of the Sun changes. Throughout the day the sea level is_________________ rising or falling. 38. The __________________________________ is the difference in sea level between _________________ and _____________________. The tidal range will vary in ______________________________ depending on the location of the Sun and the Moon as well as the topography of the ______________________________. 39. Draw a diagram showing the following: tidal range, high tide, low tide 40. High tide is the point in the ___________________________ where the sea level is at its ____________. 41. Low tide is the point in the ___________________________ where the sea level is at its _____________. 42. A Spring Tide is an _____________________________ tide and _______________________________ tide formed when the sun, moon and Earth are lined in a __________________________________. 43. Spring Tides occur at the _______________________ and _______________________ phases of the moon. 44. Draw TWO pictures of the sun, moon, and Earth during a spring tide. 45. A Neap Tide is _________________ high tide and low tide formed when the sun and moon form a __________________________________ with the Earth. 46. Neap Tides occurs at the ___________________________ and ____________________________ phases of the moon. 47. Neap tides have high tides that are __________________________________ and the low tides are ___________________________________________________ 48. Spring Tides are _________________ high and low tides while Neap Tides are _________________ high and low tides. 49. Draw TWO pictures of the sun, moon, and Earth during a neap tide. SPECIAL WAVES 50. A wave is a long __________________________________ curling into an arched form and breaking on the shore. 51. A Tsunami is a ________________________________ that is formed by _________________________. 52. A rip current is a _________________, narrow ___________________________________ flowing outward from a shore that results from the return flow of waves and wind-driven water. 53. Draw a rip current 54. Undertow is the water ______________________to the ocean after a wave crashes at shore. Undertow may be strong enough to _____________________________________________________________________ 55. A long shore current is an ocean current that travels ___________________________________ 56. Draw a long-shore current 57. A storm surge occurs when ___________________ pushes a large ________________________ ___________ to shore during a hurricane. Vocabulary wave, current, tides, energy, salinity, density, down welling, upwelling, Gulfstream, Coriolis Effect, El Nino