CH: 22 ocean water and its circulation
advertisement

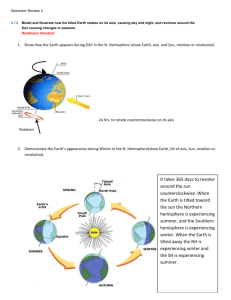
CH: 22 OCEAN WATER AND ITS CIRCULATION Answer the following in one or two sentences: 1. What do you understand by waves? Waves are the periodic rise and fall of water on the surface of the ocean caused by winds. When winds blow over the surface of the ocean, they tend to push the water up and down by friction in the direction they blow. 2. What causes tides? Tides are caused due to the gravitational pull exerted on the surface of the earth by the sun and the moon. Moon being closer, its gravitational pull affects the ocean more than that of the sun. 3. How are earthquakes and tsunamis connected? Severe earthquakes on the ocean floor causes disturbance which results in the formation of very high and powerful waves on the surface. These waves are known as tsunamis, which, on reaching the coast, cause massive destruction. 4. Define an ocean current. These are movements of large bodies of water on the surface of the oceans in a fixed path. 5. What is a tsunami? A tsunami is a massive tidal wave that is triggered by an earthquake on the ocean floor. Tsunamis cause massive destruction on reaching the coast. Answer the following in four or five sentences: 6. What do you understand by tides? Tides are periodic vertical rise and fall of ocean water resulting in a horizontal flow on the coast. These are caused due to gravitational pull exerted on the surface of the earth by the sun and the moon. Since the moon is closer, its gravitational pull affects the ocean more than that of the sun. The rise is called high tide (or flow of tide) while the fall is called low tide (or ebb of tide). 7. Distinguish between spring and neap tides. Spring tides occur during the New Moon and Full Moon phases, when the sun, earth and moon are in one line, the combined gravitational force of the sun and the moon is stronger and the tides are highest (and lowest) during this time. Neap tides occur during the First Quarter and the Last Quarter phases, i.e., when the sun, earth and moon form a right angle. The gravitational force of the moon is therefore offset by the gravitation force of the sun and the tides are not so high (and low) as spring tides. These tides are called neap tides. 3. Explain the usefulness of tides. Tides are useful in many ways. They are now being used to produce electricity called tidal energy. Ships are able to enter shallow ports only during high tides. Tides bring in large amount of fi sh during high tide, which are netted when the tide ebbs. Tides clear silt deposits from the mouth of rivers keeping them free for shipping movement. 4. Explain the difference between warm and cold currents. Ocean currents that flow from warm equatorial regions towards the Polar Regions are classified as warm currents. Those currents that flow from cold Polar Regions towards the equatorial regions are classified as cold currents. Gulf Stream and Brazilian Current are examples of warm ocean currents. The Labrador and Benguela Currents are cold currents. 5. How are ocean currents useful? Disturbance caused by an earthquake on the sea floor results in the formation of very high and powerful waves on the surface. These waves are known as tsunamis. These waves cause widespread destruction on reaching the coast. The tsunami that hit Japan in March 2011 left thousands dead and many more homeless.