Biology
advertisement

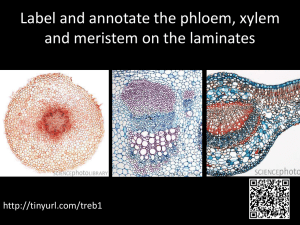
Teacher: Izabela Wierzbowska Year Group: IB1 Subject: Biology SL/HL Term: Winter SL – standard level, HL – higher level, AHL – additional higher level, IA – internal assessment Week 1 2 3 Aim/Objectives 2.2. Water: SL and HL The students should: - describe water molecule - state that substances can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic - compare thermal properties of water with those of methane - describe use of water as a coolant in sweat AHL: 9 Plant biology, 9.1 transport in the xylem of plants: the students should understand that transpiration is the consequence of gas exchange in the leaf, plants transport water from the roots to the leaves to replace losses from transpiration 2.4. Proteins SL and HL The students should: - understand that amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides - understand that the amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. - understand that every individual has a unique proteome IA: Jagiellonian University – organic chemistry part1: chromatography, atomic absorption spectrometry, and colorimetry Proteins cont. SL and HL The students should: - state that rubisco, insulin, immunoglobulins, rhodopsin, collagen and spider silk are examples of the range of protein functions IA: Jagiellonian University – organic chemistry part 1: chromatography, atomic absorption spectrometry, and colorimetry Activities Class work with text book and given handouts Class work with text book and given handouts, individual work: IA report Whole class work: power point presentation to the class on health problems on obesity, dietary energy deficiency, kwashiorkor, anorexia nervosa and coronary heart disease IA: class and individual work, writing reports 4 5 6 7 2.1 Molecules to metabolism, IA: laboratory work SL and HL: food tests, denaturation of proteins by heat or by deviation of pH from the optimum Obligatory experimental work 2.5 Enzymes SL and HL Students should: - understand that enzymes have an active site to which specific substrates bind. - state that enzyme catalysis involves molecular motion and the collision of substrates with the active site. AHL: Transport in the xylem of plants cont., students should: understand that cohesive property of water and the structure of xylem vessels allow transport under tension, the adhesive property of water and evaporation generate tension forces in leaf cell wall Enzymes cont. SL and HL Students should: - understand that temperature, pH and substrate concentration affect the rate of activity of enzymes - describe methods of production of lactose-free milk and its advantages AHL: transport in the xylem of plants cont., students should: state that active uptake of mineral ions in the roots causes absorption of water by osmosis - describe adaptations of plants in deserts and in saline soils for water conservation Enzymes cont. Students should - understand that enzymes can be denatured. - state that immobilized enzymes are widely used in industry. AHL: transport in the xylem of plants cont., students should draw the structure of primary xylem vessels in sections of stems based on microscopic images, design an IA: class and individual work, writing reports Revision of the material : 2.1 – 2.4 molecules to metabolism, water, carbohydrates and lipids, Class work with text book and given handouts Class work with text book and given handouts Class work with text book and given handouts 8 9 10 experiment to test hypothesis about the effect of temperature or humidity on transpiration rates Enzymes cont. SL and HL IA: Experimental investigation of a factor affecting enzyme activity. 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA SL and HL Students should: - state that the nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides - state that DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose. - - understand that DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. AHL: 9.2 Transport in the phloem of plants., students should state that plants transport organic compounds from sources to sinks; incompressibility of water allows transport along hydrostatic pressure gradients 2.6 DNA and RNA cont. SL and HL Students should: - draw simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and bases. - understand Crick and Watson’s elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making AHL: 9.2 Transport in the phloem of plants cont., students should describe active transport of organic compounds in phloem tubes; identify of xylem and phloem in microscope images of stem and root Laboratory work, writing report Revision of the material: 2,5-2,6: proteins and enzymes Class work with text book and given handouts Class work with text book and given handouts