grade5-curriculum-sp2015 - This is the test page for HTML

Grade 5 Curriculum Planning for Practicum (Spring 2015)
Science and Writing Lesson 1 (Two Lessons - M 3/16 and W 3/18)
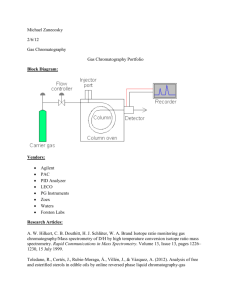
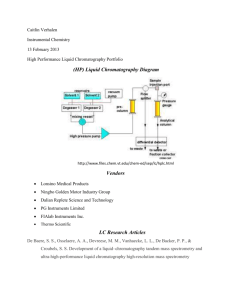
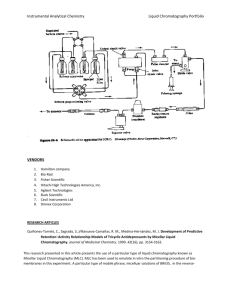
Science Lesson 1 Active Investigation Introduce the mystery and chromatography. Conduct a blank test.
Focus Question How can a test substance be separated?
Scientific Writing Informal observational notes; Use direction instruction to teach how to scientific illustration.
Writing Lesson 1 Use direction instruction to teach how to create a written observation.
Instructional Materials GEMS Crime Lab Chemistry http://lhsgems.org/GEM170.html
Science and Writing Lesson 2 (Two Lessons - M 3/25 and W 3/27)
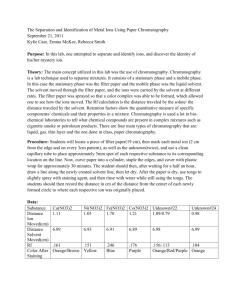
Science Lesson 2 Active Investigation Test the ransom note, introducing suspects, and testing the mystery pens
Writing Lesson 2
Focus Question What is chromatography? How can you identify a mystery substance using chromatography?
Scientific Writing Use direction instruction to teach how to create a data table.
Use direction instruction to teach how to write a basic conclusion.
Instructional Materials GEMS Crime Lab Chemistry
Science and Writing Lesson 3 (Two Lessons - M 4/6 and W 4/8
Science Lesson 3 Active Investigation Solving the Mystery
Focus Question How can you identify a mystery substance using chromatography?
Scientific Writing
Writing Lesson 4 Use direction instruction to teach how to write a basic conclusion.
Instructional Materials GEMS Crime Lab Chemistry http://lhsgems.org/GEM170.html
Science and Writing Lesson 4 (Two Lessons - M 4/13 and W 4/15)
Science Lesson Active Investigation Change a variable for a controlled experiment.
Focus Question How does changing the medium or solvent affect the separation of a test substance?
Scientific Writing Informal observational notes; Use direction instruction to teach how to create a scientific illustration.
Writing Lesson Use direction instruction to teach how to write a basic conclusion.
Instructional Materials GEMS Crime Lab Chemistry http://lhsgems.org/GEM170.html
THREE KEY ELEMENTS
Science Content
Big Ideas:
1.
All living and nonliving things are composed of matter.
2.
Matter has characteristic properties that distinguish one substance from another (independent of size or amount of substance).
3.
Chromatography is a technique that separates substances and mixtures.
4.
Capillary action is the tendency of a liquid to move upwards in paper (medium). The movement is a result of the molecules interacting with each other in liquids (solvent) and solids (medium, test substance).
Key Science Terms: matter, solid, liquid, molecules, force, capillary action, gravity, cohesion, adhesion, properties, chromatography, test substance, medium, solvent, system
Scientific Thinking: observing, comparing, classifying, predicting, reasoning, making claims and supporting with evidence, formulating conclusions, planning and conducting a controlled experiment.
Science Skills: using a hand lens; using a hand lens; how to create a scientific illustration, written observation, box and T chart, basic conclusion
CONTENT STANDARDS FOR STUDENTS
Alignment with NGSS http://www.nextgenscience.org/5spm-structures-properties-matter
5.Structure and Properties of Matter
5-PS1-3. Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
Alignment with RIGSEs in Science (Click on “Science” on right side).
Domain: Physical Science
Statement of Enduring Knowledge: PS1 - All living and nonliving things are composed of matter having characteristic properties that distinguish one substance from another (independent of size or amount of substance).
Assessment Target Criteria: PS1 (K-4) INQ –1
Collect and organize data about physical properties in order to classify objects or draw conclusions about objects and their characteristic properties (e.g., temperature, color, size, shape, weight, texture, flexibility)
Grade Span Expectation: PS1 (3-4)–1
Students demonstrate an understanding of characteristic properties of matter by …
1a identifying, comparing, and sorting objects by similar or different physical properties (e.g., size, shape, color, texture, smell, weight, temperature, flexibility).