Carbonate & Bicarbonate Mixture Analysis: Titration Lab Report
advertisement

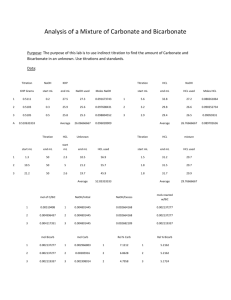
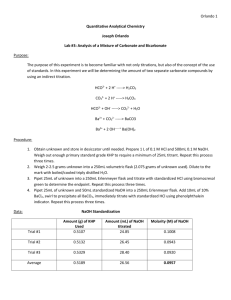
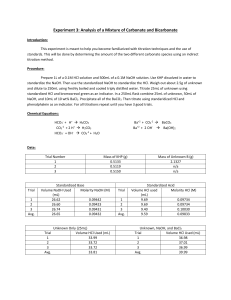
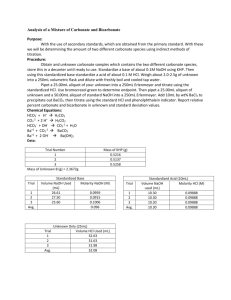
Experiment 3: Analysis of a Mixture of Carbonate and Bicarbonate Objective: In this lab we will learn about titrating and standards, along with a method to determine two different carbonate compounds. Background: Titrations are a process by which an unknown concentrated solution is measured with a solution with a known titration called a titrant. This process is done until the reaction is complete. Acid/base titrations involve an acid or base titrant that is being reacted in an acidic or basic solution until the equivalence point has been reached. At this point there will be a color change to indicate that the equivalence point has been reached. Procedures: 1.) Obtain one unknown containing a mixture solution of sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate – store in desiccator until needed. Prepare 1 liter of 0.1 M HCl and 500.0 mL of 0.1 M NaOH 2.) Use primary standard grade KHP (in oven drying) weigh enough to require at least 25 mL of titrant. Standardize 0.1 M NaOH. Repeat until 3 good trials are obtained. 3.) Standardize the base, use this to standardize the 0.1 M HCl. Repeat until 3 good trials are obtained 4.) Weigh 2.0 – 2.5 g of unknown into 250 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to the mark with freshly boiled and cooled triply distilled water 5.) Pipet 25.00 mL aliquot of known into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, titrate with standardized HCl using bromocresol green determine the endpoint. Repeat until 3 good trials are obtained. 6.) Pipet 25.00 mL aliquot of unknown and 50.00 mL aliquot of standardized NaOH into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10 mL of 10 wt% BaCl2, swirl to precipitate all BaCl2. Immediately titrate with standardized HCl using phenolphthalein indicator. Repeat until 3 good trials are obtained. Data: Unknown B Standardize HCl w/ H2O NaOH Trial mL HCl Added 1 28.2 2 25.5 3 24.5 Average 26.07 Standardize NaOH (base) Trial mL NaOH 1 26.4 2 24.9 3 26.0 Average 25.77 Mass of KHP: 1. 0.5098 g 2. 0.5109 g 3. 0.05098 g 0.5098𝑔 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟒𝟗𝟕 𝒎𝒐𝒍 204.2𝑔 0.5109𝑔 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟓𝟎𝟐 𝒎𝒐𝒍 204.2 𝑔 0.5098𝑔 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟒𝟗𝟕 𝒎𝒐𝒍 204.2𝑔 mL HCl to unknown Trial 1 2 3 Average mL 31.5 30.4 29.7 30.53 Trials 1 2 3 mL 36.6 36.3 37.5 Calculations: Molarity NaOH 0.002497𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟔𝟗 𝑴 0.02577 𝐿 0.002502𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟕𝟏 𝑴 0.02577𝐿 0.002497𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟔𝟗 𝑴 0.02577𝐿 Average: 0.097 M Molarity HCl 0.002497𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟓𝟕𝟖𝑴 0.02607𝐿 0.002502𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟓𝟗𝟕 𝑴 0.02607𝐿 0.002497𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟗𝟓𝟕𝟖 𝑴 0.02607𝐿 Moles carbonate 𝑀𝐻𝐶𝑙 ∗ 𝑉𝐻𝐶𝑙 Trial 1 0.0969 ∗ 0.0566 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟑𝟓𝟓 Trial 2 0.0971 ∗ 0.0363 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟑𝟓𝟐 Trial 3 0.0969 ∗ 0.0375 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟑𝟔𝟑 Moles Bicarbonate 𝑀𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 ∗ 𝑉𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 Trial 1 0.00355 − 0.00256 = 𝟗. 𝟗𝒙𝟏𝟎^ − 𝟒 Trial 2 0.00352 − 0.00242 = 𝟕. 𝟖𝒙𝟏𝟎^ − 𝟒 Trial 3 0.0363 − 0.00252 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟏𝟏𝟏 Moles NaOH 𝑀 ∗ 0.0500 𝐿 0.097 ∗ 0.0500 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟒𝟖𝟓 Moles NaOH reacting with HCl 𝑀 ∗ 𝑉𝐻𝐶𝑙 Trial 1 0.097 ∗ 0.0264 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟓𝟔 Trial 2 0.097 ∗ 0.0294 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟒𝟐 Trial 3 0.097 ∗ 0.0260 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟐𝟓𝟐 Moles Carbonate 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑐𝑎𝑟𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 − 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑏𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑟𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 Trial 1 0.00355 − 9.9𝑥10−4 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟓𝟔 Trial 2 0.00352 − 7.8𝑥10−4 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟕𝟒 Trial 3 0.00363 − 0.00111 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟐𝟓𝟐 Mass % Bicarbonate 𝑚𝑜𝑙 ∗ 𝑀𝑊 ∗ 100 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 9.9𝑥10−4 ∗61.01069 0.20988 7.8𝑥10−4 ∗61.01069 0.20988 0.0011∗61.01069 0.20988 ∗ 100 = 𝟐𝟖. 𝟕𝟖 ∗ 100 = 𝟐𝟐. 𝟔𝟕 ∗ 100 = 𝟑𝟐. 𝟐𝟕 Mass % of Carbonate 𝑚𝑜𝑙 ∗ 𝑀𝑊 ∗ 100 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 0.0056∗60.008 2.0988 ∗ 100 = 𝟏𝟔. 𝟎𝟕 0.00274∗60.00∗ 2.0988 ∗ 100 = 𝟕. 𝟖𝟑 0.00252−60.008 2.0988 ∗ 100 = 𝟕. 𝟐𝟏 Conclusion: The NaOH and HCl were standardized to calculate the molarity of the NaOH and the HCl and KHP used. Then it was used to titrate an unknown. Indirect titration allowed for bicarbonate to be brought out of solution, allowed us to determine its concentration. Discussion: 1.) Primary standard is at least 99.9% pure, weighed and used directly. KHP was ours 2.) 2° standard is prepared in the lab and standardized against 1° standard. NaOH was ours. 3.) Indirect titration / back titration: reagent added to analyte to determine concentration of unknown analyte. Bicarbonate and carbonate were indirectly tirated with NaOH 4.) Titrant is a substance of known concentration used in a titration to determine the unknown concentration.