Classification of Matter KEY
advertisement

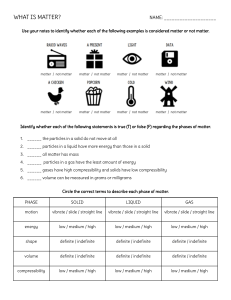
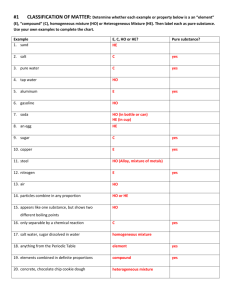
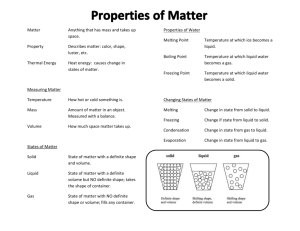
Name ______________________________________________ Kaspriskie CP Chemistry 2015-16 Classification of Matter Log in to EDpuzzle.com and watch the videos assigned to your class (CP Chemistry Period 6) Define Matter Anything that has mass and volume Give three examples of “not matter” light electricity and heat The universe is made up of energy and matter . What three categories are chemists interested in when they study matter? Properties, Structure (the form or shape of a substance), and Composition (parts that make up a substance) Define Properties Features of a substance; properties describe how matter interacts with other matter. Define Extensive properties depend on the amount of a substance Examplesof extensive properties Mass and volume Define Intensive properties depend on the identiy of a substance Examplesof intensive properties Malleability, magnetization, melting point, boiling point, freezing point condensation point, density Name and describe the Physical Properties that are mentioned. One can observe and measure physical properties without changing the identity Ex: mass, color, texture, scent, volume, hardness What does Physical Change do to a substance? Physical changes do not change the identity of a substance Ex: changes in states of matter Chemical changes are chemical reactions that change the identity of matter. States of Matter Name the three classical states of matter: Solid Gas Liquid Melting, Freezing Vaporizing, Condensing Use the following chart to complare the three classical states of matter. State of Matter Volume Shape Using solid colored circle draw a model of a substance in each State of Matter Solid definite definite definite Liquid Gas Indefinite(expands to fill space) Indefinite (takes shape of the container) Indefinite (takes shape of the container) Desctibe the Arrangement of Particles and the Attraction between the particles Fixed pattern Strong attraction close together, random pattern enough attraction to keep together Far apart, random motion Very weak attraction Categories of Matter Recreate the flow chart he draws in the video. Feel free to add examples, definitions, or pictures to help you learn this material. Matter Pure Substance Elements (Periodic Table) Compounds (Elements chemically combined, bonded) Mixture Homogeneous Heterogeneous Uniform throughout the substance When taking a sample from a substance, each sample is different Often called a solution Ex: Chocolate chip cookie each cookie (sample of the batter) is different