II. True of False (15 points)
advertisement

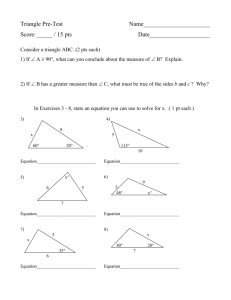
Chem 220 –EXAM IV – SPRING 2012 Name Date Points Earned I. Multiple Choice (15 points) #1 #2 #3 SHOW ALL WORK!!!!!! - Remember to RELAX #4 #5 II. True of False (15 points) #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 III. Solve (12 points) #1 #2 IV. Short Answer (40 points) *Do 5 of the 8 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 V. Spectra (18 points) #1 #2 BONUS (8 points) Total Points I. Multiple Choice (15 pts) 1. FRET stands for a. Fluorescence Recovery Electron Transfer b. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer c. Fluorescence Recovery Energy Transfer 2. Fluorescence involves the excitation and emission of light based on the theory that a. the emission wavelength and excitation wavelength are the same b. the emission wavelength is shorter than the excitation wavelength c. the emission wavelength is longer than the excitation wavelength 3. The following relationship is correct a. wavelength of Π to Π* transition > wavelength of σ to σ* b. wavelength of σ to σ* transition > wavelength of Π to Π* 4. If you want your molecule’s fluorescence to be quenched then you should a. decrease temperature b. increase temperature c. turn off the lights O 5. The functional group, R-C-R is a. Aldehyde b. Ketone c. Carboxylic acid II. True or False (If False, Explain why (15 pts total) 1. A solution of red Kool-Aid transmits light at a wavelength range of 650 – 700 nm. 2. Phosphorescence is a luminescence process that can occur if there is an internal conversion from an excited Singlet to an excited Triplet state. 3. Absorption of visible radiation is a lower energy transition than absorption of ultraviolet radiation. 4. Energy is directly proportional to wavenumber. 5. A solution of hexane will absorb UV light. III. Solve (21 pts TOTAL) 1. a. (7 pts) Beryllium(II) forms a complex with acetylacetone (166.2 g/mol). Calculate the % transmittance when measured in a 1 cm cell at 295 nm if the molar absorptivity of a 1.34 ppm solution of the complex is 3.15 x 104 M-1cm-1. b. (4 pts) Calculate the energy in Joules that is required to excite this complex? c. (1 pt) What functional group is prevalent in this complex? IV. Short Answer (40 pts TOTAL) Do 5 of the following 8 * do 1 extra for BONUS – Mark as BONUS 1. (6 pts) Use the theory of molecular orbitals along with figures to explain why the electrons in π bonds made from p orbitals are easier to excite than the electrons in σ bonds made from p orbitals. 2. You are on Spring Break and you are bragging to some new friends how you are pre-med and that you study chemistry, physics, and biology. They are really impressed and one of them asks you, “Hey, smarty, how does sunblock work?” You look at the back of the bottle and notice that one of the main components is oxybenzone. What do you tell your new friend? 3. Explain using Molecular Orbital Theory and an energy level diagram why benzene absorbs at a lower wavelength than diethylether (CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3). 4. Draw benzene. How many absorption maxima would you expect to see in the UV/Vis spectrum of benzene? b. What orbital transitions would the absorptions that you mentioned above correspond to? c. Would you expect another absorption if you added an NH2 group to the benzene molecule? If so, what would this orbital transition be? 5. Would the following molecules be IR active, Raman active, or both? Why? Draw the Lewis Structures for each. a. benzene b. NH3 c. CO2 6. Label the following energy transitions a. E2 E1 E0 b. V2 v1 a. Fluorescence V2 v1 V2 v1 d. c. 7. Explain in detail why FRET is often referred to as a “molecular ruler”. 8. Explain how FRAP can be used to measure of the diffusion of molecules? V. Spectra (18 pts TOTAL) 1. (8 pts TOTAL)You find a bottle in your kitchen cupboard you have no idea of what it is. You take it to the lab in HT and put it in the hood. You carefully take some of it out and decide to analyze it which results in the IR spectrum below. You also do mas spec and determine that the molecular weight of this molecule is 60 g/mol. You also notice that it has a peculiar yet familiar smell. What is this chemical???? a. What are the main functional groups in this molecule? (6 pts) b. Draw the Lewis structure for this molecule? (1 pt) b. What is the name of this molecule? (1 pts) 2. (10 pts TOTAL) a. (4 pts) What allows the molecules below to be able to absorb UV light? Be specific by mentioning orbital transitions. b. (2 pt) Do you predict a difference in the ability of the two to absorb UV light? If so, why? c. (3 pts) What allows the molecules below to absorb IR light? Be specific. d. (1 pt) How specifically would you tell the difference between the two when looking at the IR spectra? OH OH Cl Cl Molecule A Molecule B