Cheickna Touré Presentation - Ministerial Leadership Initiative for
advertisement
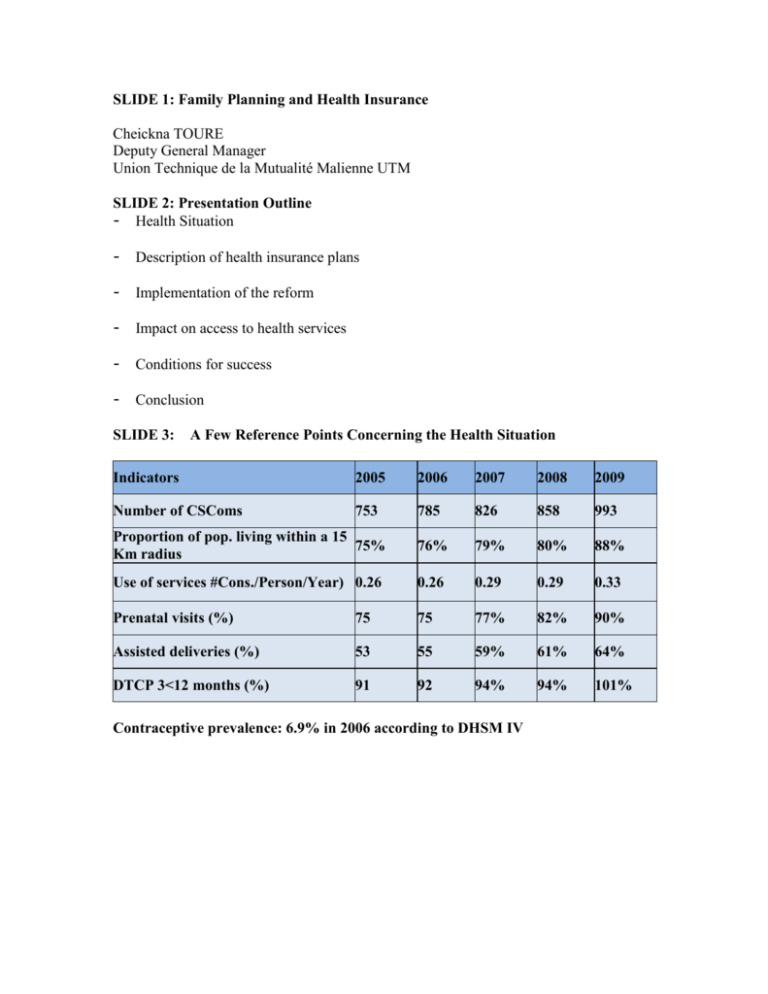
SLIDE 1: Family Planning and Health Insurance Cheickna TOURE Deputy General Manager Union Technique de la Mutualité Malienne UTM SLIDE 2: Presentation Outline - Health Situation - Description of health insurance plans - Implementation of the reform - Impact on access to health services - Conditions for success - Conclusion SLIDE 3: A Few Reference Points Concerning the Health Situation Indicators 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Number of CSComs 753 785 826 858 993 Proportion of pop. living within a 15 75% Km radius 76% 79% 80% 88% Use of services #Cons./Person/Year) 0.26 0.26 0.29 0.29 0.33 Prenatal visits (%) 75 75 77% 82% 90% Assisted deliveries (%) 53 55 59% 61% 64% DTCP 3<12 months (%) 91 92 94% 94% 101% Contraceptive prevalence: 6.9% in 2006 according to DHSM IV SLIDE 4: A Few Reference Points Concerning the Health Situation Reste du Monde 14% Etat 22% Autres privés 4% Ménages 51% Collectivités décentralisées 9% Autres privés = Other Private Reste du Monde = Rest of the World Etat = Central Government Collectivités décentralisées = Local Governments Ménages = Households SLIDE 5: A Few Reference Points Concerning the Health Situation - A major share of health care expenditures is financed by households - In the breakdown of household-financed health care expenditures, the proportion of money spent on drugs is comparatively higher for poorer households - Half of the money spent on health care is received by the private sector SLIDE 6: Health Insurance Plans Eliminating the financial barriers restricting access to health care services in Mali 2 contributory schemes and 1 non-contributory scheme - Compulsory health insurance - Target: Government workers, recipients of subsidized benefits, employees, members of parliament, retirees, and recipients of pensions - Financing: Contributions by employers and employees - Medical assistance programs - Target: The poor - Financing: Subsidies by the central government and local governments - Mutual/community health organizations - Target: informal and agricultural sectors - Financing: Subsidies by the central government and contributions from members SLIDE 7: Health Insurance Plans Distribution of the Target Population among the Various Health Insurance Plans Mutual/community health organizations 78% Compulsory medical insurance 17% Medical assistance programs 5% SLIDE 8: Implementation of the Reform - For compulsory medical insurance and medical assistance programs - Creation of a legal framework and development of organizational structures to enable a launch in 2010 Mutual/community health organizations - A legal framework for mutual/community health organizations in existence since 1996 has even inspired policies developed at the community level - Absence of an organizational framework conducive to their expansion - Incentives for restructuring the community health movement, among other things through the principle of complementary financing of the mutual/community health organizations in addition to members’ contributions - Desire to promote equity in terms of access to health care SLIDE 9: Implementation of the Reform - Setting up of a minimum package of benefits for the entire population corresponding to those offered by the compulsory medical insurance and medical assistance programs Typical basic Benefit Packages (CSCOM) Outpatient Services · Primary care visits · Dental diagnostic visits · Dressings, shots, transfusions · Immunization card · Minor outpatient surgery · Dental care · Ultrasounds · Medical tests/Labs · Branded or specialty drugs · Generic drugs Transportation · Ambulances Inpatient services (case follow-up) · Hospital stay package (user fee: perfusion) · Ultrasounds · Medical tests/Labs · Branded or specialty drugs · Generic drugs · Medical consumables Maternity · Prenatal visit+ cost of materials · · · · · · · · Postnatal visit Family Planning Delivery without complications Inpatient stay Ultrasounds Medical tests/Labs Branded or specialty drugs Generic drugs Extended Benefit Package (Hospitals) Outpatient care · Primary care visit · Dental diagnostic visit · Ophthalmology visit · Consultations with other medical specialists · Dressings, shots, transfusions · Minor outpatient surgery · Dental care · X-rays/Scans/Ultrasounds · Medical tests/Labs · Branded or specialty drugs · Generic drugs Transportation · Ambulance Inpatient services · Hospital stay package · X-rays/Scans/Ultrasounds · Medical tests/Labs · Branded or specialty drugs · Generic drugs · Medical consumables · Surgery Maternity · Gynecology visit · Delivery with complications · C-section (free) · Inpatient stay · X-rays/Scans/Ultrasounds · Medical tests/Labs · Branded or specialty drugs · Generic drugs SLIDE 10: Implementation of the Reform Why and how should family planning be included in the health insurance benefit package? - prevention - control of health expenditures. which includes controlling the cost of services - appropriate rate structure for contributions - making health insurance services more appealing - top-down approach to health care expenditures SLIDE 11: Impact on Access to Health Services - Offering health insurance to 50% of the population of Mali within 5 years Anticipation of Population Coverage by Mutual/Community Health Insurance Organizations Proportion of the population covered by a mutual/community health insurance organization - Raising to .47 the utilization index of health care services - Increasing to 50% the share of mutual/community health insurance organizations in the total income of all health centers SLIDE 12: Conditions for Success - Having a systematic vision of health care that eliminates the fracture between supply and demand for health services - Accepting the necessity to change the paradigm for the health financing model - Requiring a real commitment - not just a promise - from decision-makers to support a system whose results will be visible mostly in the long run - Insisting on performance, but also being patient