Study Guide for Weather Test :(gases, air pressure, layers of
advertisement

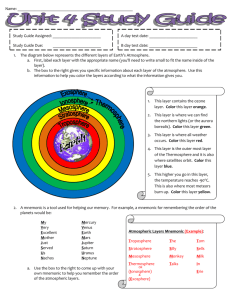
7.E.1 Study Guide for Weather Test :(gases, air pressure, layers of atmosphere, pollution) Terms: Know how to use the vocabulary words. Look at each word on the list. If you would be stumped by it, ask! Weather: conditions in troposphere at a particular place and time Weather is driven by SUN, WATER, GRAVITY. Climate is the average of weather conditions for a place over a period of many years. Normal greenhouse effect is good—a natural process. Keeps Earth warm. Exaggerated greenhouse effect caused by humans is BAD; see pollution section at bottom of page. Gases: Nitrogen 78 % Oxygen 21% Trace gases 1% (includes carbon dioxide—important!) What is Ozone (O3) and what does it do? (good and bad)—See pollution section below. Water vapor varies from 0%- 5% ( 0%= desert, 5%= rainforest). Other gases don’t vary, but their percentages adjust accordingly. What other things are found in the atmosphere (particulates--dust particles, smoke, and salt—some of them important for starting condensation of water vapor) What holds the atmosphere to Earth? GRAVITY!!! What do carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases do to the atmosphere? (Hold Earth’s heat like a blanket. It does not take much! Human activity has added much carbon dioxide. See Pollution section below.) Air Pressure: weight of column of air pushing on an area (from all directions) What is a barometer? (instrument that measures air pressure) pressure up=good weather, pressure down= bad weather (REMEMBER the trick?: air pressure thumbs up= good,/thumbs down = bad) Mercury barometer (open container, liquid mercury, poisonous, not portable, unit=inches of mercury) Aneroid barometer (closed container, air chamber, not poisonous, portable, unit=millibars) What properties does air have? (density, mass, weight and pressure) Why is it hard to breath at high altitudes? (less dense, oxygen molecules too spread out) Know the following: B Pressure high low Altitude low high Density high low Hot air rises (molecules spread out) and cold air sinks (molecules close together) Layers of the Atmosphere: Tropical snakes make tea (with Iono and Exo). Another mnemonic device for layers of atmosphere: Trodden Snakes Must Think I’m Evil! What factor determines a NEW LAYER in the atmosphere? TEMPERATURE SHIFT! 4 main layers of the atmosphere (troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere) Thermosphere*: (Gets HOT, 53-outer space, has northern lights and satellites) Mesosphere: (Gets COLD, 30-53 miles, has shooting stars, burns up incoming rocks) Stratosphere: (Gets HOT, 7-30 miles, has airplanes and ozone) Troposphere: (Gets COLD, ends at 7 miles, has weather, animals, mountains) *Thermosphere is divided into 2 parts: ionosphere (with northern lights) and exosphere (with satellites) Pollution: Acid rain is caused by sulfur and nitrogen oxides. Ozone bad: Odious Ozone leads to photochemical smog (in troposphere). tropo ozone Ozone good: Oh, wonderful Ozone protects us from UV radiation (in stratosphere). strato ozone O= oxygen atom O2= oxygen gas O3= ozone What do CFC’s do to the atmosphere? (destroy stratospheric ozone) Burning lots of fossil fuels adds too much CO2 to air. What are the results? abnormally increased greenhouse effect, which can lead to global warming / climate change Need to add: Global winds, cloud types