Chapter 13 Gases
advertisement

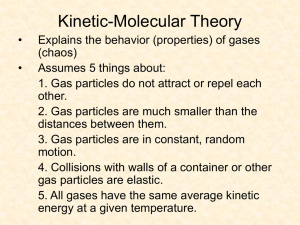
Gases Laws Notes Pressure Pressure- force per unit area caused by particles hitting the walls of a container Barometer- Measures atmospheric pressure Atmospheric Pressure- Results from the weight of the air- mass of air being pulled toward the center of the earth by gravity. Manometer- Measures pressure of a gas in a container Two types – Open and Closed Units for pressure: mm Hg, torr, Pascal (Pa), Kilopascal (kPa), atmospheres (atm), pounds square inch (psi) 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = 101325 Pa = 101.3 kPa = 14.69 psi Ex: You have 28 psi. How many atm? Torr? Pascals? Learning Check: How many mmHg are 8.92atm? Boyle’s Law Relationship between pressure and volume (constant temp.) Inverse proportion P V P1V1= P2V2 Ex: Consider a 1.5 L sample of CCl2F2 at a pressure of 56 torr. If pressure is changed to 150 torr at constant temperature, what is the new volume? Learning Check Boyle’s Law variables: Is Boyle’s Law an inverse or direct relationship? Boyle’s Law constants: Boyle’s Law formula: Charles’ Law Relationship between volume and temperature (constant pressure) Inverse proportion V T oC + 273 = ____ K Temperature in Kelvin V1 = V2 T1 T2 Ex: A 2.0 L sample of air is collected at 298 K and cooled to 278 K, the pressure is held constant. What is the volume? Learning Check Charles’ Law variables: Is Charles’ Law an inverse or direct relationship? Charles’ Law constants: Charles’ Law formula: Gay-Lussac’s Law Relationship between pressure and temperature (constant volume) Inverse proportion P T oC + 273 = ____ K Temperature in Kelvin P1 = P2 T1 T2 Ex A mylar balloon is filled with helium gas to a pressure of 107 kPa when the temperature is 22 °C. If the temperature changes to is 45 °C, what will be the pressure of helium in the balloon? Learning Check Gay-Lussac’s Law variables: Is Gay-Lussac’s Law an inverse or direct relationship? Gay-Lussac’s Law constants: Gay-Lussac’s Law formula: Avogardo’s Law Relationship between volume and moles (constant temp. and pressure) Inverse proportion V n n = #moles V1 = V2 n1 n2 Ex: 12.2L sample contains 0.50 moles O2. If O2 is converted to O3, what will the volume be? 3O22O3 Learning Check Avogadro’s Law variables: Is Avogadro’s Law an inverse or direct relationship? Avogadro’s Law constants: Avogadro’s Law formula: Combined Gas Law Combination of Boyle’s law, Charles’ law and Gay-Lussac’s Law P1 V1 = P2 V2 T1 T2 Ex: A 3.5 L sample of Argon exerts a pressure of 6.32 atm at 27 °C. When the volume is increased to 4.7 L and the pressure is decreased to 4.15 atm, what is the final temperature? Learning Check Combined Gas Law variables: Combined Gas Law constants: Combined Gas Law formula: A gas is heated from 263.0 K to 298.0 K and the volume is increased from 24.0 liters to 35.0 liters by moving a large piston within a cylinder. If the original pressure was 1.00 atm, what would the final pressure be? Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT R = 0.08206 L* atm mol * K Ex: H2 has a volume of 8.56 L at 0oC and 1.5 atm. Calculate the moles of H2 present. P= pressure (atm) V= volume (L) n= Mole Gas (mol) T=temperature (K) R= universal gas constant Learning Check: How many moles of gas are contained in a 2.00L flask at 98.8 kPa and 25.0°C? Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures Partial Pressure – pressure that a gas would exert if it alone in the container. Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3… Ex: A container holds three gases: oxygen, carbon dioxide, and helium. The partial pressures of the three gases are 2.00 atm, 3.00 atm, and 4.00 atm, respectively. What is the total pressure inside the container? A common method of collecting gas samples in the laboratory is to bubble the gas into a bottle filled with water and allow it to displace the water. When this technique is used, however, the gas collected in the bottle contains a small but significant amount of water vapor. As a result, the pressure of the gas that has displaced the liquid water is the sum of the pressure of the gas plus the vapor pressure of water at that temperature. The vapor pressures of water at various temperatures are given in Table. PTotal - Pvapor = PGas Learning Check What does it mean to collect gas over water? A sample of oxygen gas is collected over water. The total pressure is 98.56 kPa. The partial pressure of the dry oxygen calculated to be 95.70 kPa. What is the vapor pressure of water? Gas Stoichiometry STP = Standard Temperature and Pressure Standard Temperature = 0oC Standard Pressure = 1 atm Molar Volume 1.00 molgas = 22.4 Lgas Ex 1: A sample of N2 has a volume of 1.75 L at STP. How many moles of N2 are present? Ex 3: Calculate the volume of CO2 produced at STP from 152g of CaCO3. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 Ex 2: Calculate the volume of O2 produced at 1.00 atm and 25 oC by the decomposition of 10.5g KClO3. 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 Challenge: What would the value of the Gas Constant, R, be with the following units? kPa*L atm*L mol*K kmol*K