Ecosystems & Conservation Biology Vocabulary Worksheet
advertisement

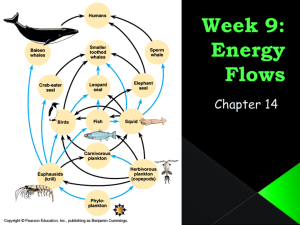
Chapter 36: Ecosystems and Conservation Biology 1. producer: organism that makes its own food (autotroph) and produces organic molecules that serve as food for other organisms in its 2. consumer: organism that obtains food by eating producers (autotrophs) or other consumers 3. decomposer: organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms 4. trophic level: feeding level in an ecosystem 5. food chain: pathway of food transfer from one trophic level to another 6. herbivore: consumer that eats only producers 7. carnivore: consumer that eats only other consumers 8. omnivore: consumer that eats both producers and consumers 9. primary consumer: consumer that feeds directly on producers 10. secondary consumer: consumer that eats primary consumers 11. tertiary consumer: consumer that eats secondary consumers 12. detritus: wastes and remains of dead organisms 13. food web: pattern of feeding in an ecosystem consisting of interconnected and branching food chains 14. biomass: organic material manufactured by producers 15. primary productivity: rate at which producers in an ecosystem build biomass 16. energy pyramid: diagram representing energy loss from one trophic level to the next 17. biomass pyramid: diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem 18. pyramid of numbers: representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem 19. nitrogen fixation: process by which certain bacteria convert nitrogen gas to ammonia 20. nitrification: process by which certain bacteria convert ammonium to nitrates 21. transpiration: evaporation of water from a plant's leaves 22. deforestation: clearing of forests for agriculture, lumber, or other uses 23. greenhouse effect: process by which atmospheric gases trap heat close to Earth's surface and prevent it from escaping into space 24. global warming: rise in Earth's average temperature 25. eutrophication: rapid growth of algae in bodies of water, due to high levels of nitrogen and often phosphate 26. acid rain: precipitation that contains nitric and/or sulfuric acids 27. pollution: addition of substances to the environment that result in a negative effect 28. biological magnification: process by which pollutants become more concentrated in successive trophic levels of a food web 29. ozone: atmospheric gas (O3) that absorbs ultraviolet radiation, shielding organisms from its damaging effects 30. biodiversity: variety of life on Earth 31. overexploitation: practice of harvesting or hunting to such a degree that remaining individuals may not be able to replenish the population 32. conservation biology: application of biology to counter the loss of biodiversity 33. zoned reserve: area of land that is relatively undisturbed by humans and is surrounded by buffer zones that are minimally impacted by humans 34. buffer zone: area of a reserve that is minimally impacted by humans 35. sustainable development: use of natural resources in a way that allows them to renew themselves and be available for the future Chapter 36: Ecosystems and Conservation Biology Name: _____________________________ Chapter 36: Ecosystems and Conservation Biology Vocabulary producer: consumer: decomposer: trophic level: food chain: herbivore: carnivore: omnivore: primary consumer: secondary consumer: tertiary consumer: detritus: food web: biomass: primary productivity: energy pyramid: biomass pyramid: pyramid of numbers: nitrogen fixation: nitrification: Chapter 36: Ecosystems and Conservation Biology transpiration: deforestation: greenhouse effect: global warming: eutrophication: acid rain: biological magnification: ozone: biodiversity: overexploitation: conservation biology: zoned reserve: buffer zone: sustainable development: