Ch 36.2 Student Notes CD

BIOLOGY
Chapter 36: Ecosystems and Conservation Biology
Name:________________________
Section Goal: The student will relate ecosystem productivity to biomass and describe the information provided by the three types of ecological pyramids.
Vocabulary:
1.
Biomass-
2.
Primary productivity-
3.
Energy pyramid-
4.
Biomass pyramid-
5.
Pyramid of numbers-
Concept 36.2 Energy flows through ecosystems.
I. Productivity of Ecosystems
A. Available energy or energy budget is limited in an ecosystem.
B. For most ecosystems, the amount of sunlight that enters the ecosystem determines the budget.
C. Earth’s producers make billions of kilograms of organic material, or biomass, each year.
D. The rate at which producers build biomass is called primary productivity.
E. Primary productivity determines the maximum amount of energy available to all the higher trophic levels in an ecosystem.
F. Productivity is different for different ecosystems:
1. Tropical rainforests have the highest productivity. Why? Their warm moist climate supports year-round growing.
2. Productivity is low in typically dry & cold Tundra.
3. Conditions are more moderate for producers in grasslands
G. Exception – organisms living in deep dark ocean do not get their energy from the sun; prokaryotic producers can extract energy from sulfur compounds released by hydrothermal vents to make organic compounds.
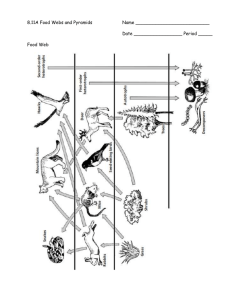
II. Ecological Pyramids
A. Energy is “spent” at each step of the food web.
B. As each consumer feeds, some energy is transferred from the lower trophic level to the higher trophic level.
C. An average of 10% of the available energy at a trophic level is converted to biomass in the next higher trophic level.
D. The rest of the energy (about 90%) is lost as heat.
E. The amount of energy available to top-level consumers is tiny compared to that available to primary consumers.
F. It takes a lot of vegetation to support higher trophic levels.
G. Most food chains are limited to three or four levels because there is not enough energy at the top of the energy pyramid to support another trophic level.
H. Ecological pyramids are diagrams used to depict information about energy, biomass, and numbers of organisms at different trophic levels. (see Figures 36-7 & 36-8)
Lesson Reflection:
Complete the Ecological Pyramid handout.
Lesson Assessment:
1. What does primary productivity measure? What does it tell you about an ecosystem?
2. What point does each type of ecological pyramid emphasize?
3. What does the shape of the energy pyramid indicate?
Summary of Key concepts:
Complete the Summary of Key Concepts for36.2 and turn into the box.
Technology/Application/Connection to real-world:
Popcorn Energy Flow LAB
Root Beer Activity