C1_4_crude_oil_&_fuels_crossword_-_answers
advertisement

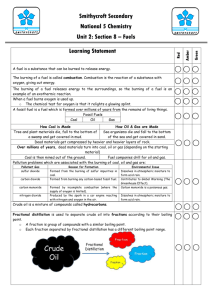
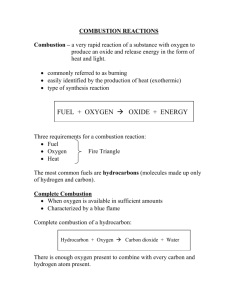
C1 4 Crude oil & fuels - answers Across 6. Gaseous pollutants given off from motor vehicles, a cause of acid rain. Nitrogen oxides 8. A way to distil liquids from a mixture of liquids by boiling off the substances at different temperatures, then condensing and collecting the liquids. fractional 12. The reflection of sunlight by tiny solid particles in the air. Global dimming 16. Easily ignited and capable of burning rapidly. flammable 17. A saturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2. alkane 18. When some elements or compounds are mixed together and intermingle but do not react together (i.e. no new substance is made). mixture 21. A toxic gas whose formula is CO. Carbon monoxide Down 1. Fitted to exhausts of vehicles to reduce pollutants released. Catalytic converter 2. A toxic gas whose formula is SO2. It causes acid rain. Sulphur dioxide 3. Small solid particle given off from motor vehicles as a result of incomplete combustion of its fuel. particulate 4. A compound containing only hydrogen and carbon. hydrocarbon 5. Hydrocarbons with similar boiling points separated from crude oil. fraction 7. Combustion when a fuel burns in insufficient oxygen, producing carbon monoxide as a toxic product. incomplete 9. A reaction where oxygen is added to a substance (or when electrons are lost from a substance). oxidised 10. The process of burning. combustion 11. Separation of a liquid from a mixture by evaporation followed by condensation. distillation 13. Fuel made from animal or plant products. biofuel 14. The increasing of the average temperature of the Earth. Global warming 15. Describes a hydrocarbon that contains as many hydrogen molecules as possible in each molecule. saturated 19. The resistance of a liquid to flowing or the ‘thickness’ or resistance of a liquid to pouring. viscosity 20. Fuels for cars made from plant oils. biodiesel Dr Barker 2011