combustion reactions - Riverside Rebel Science
advertisement
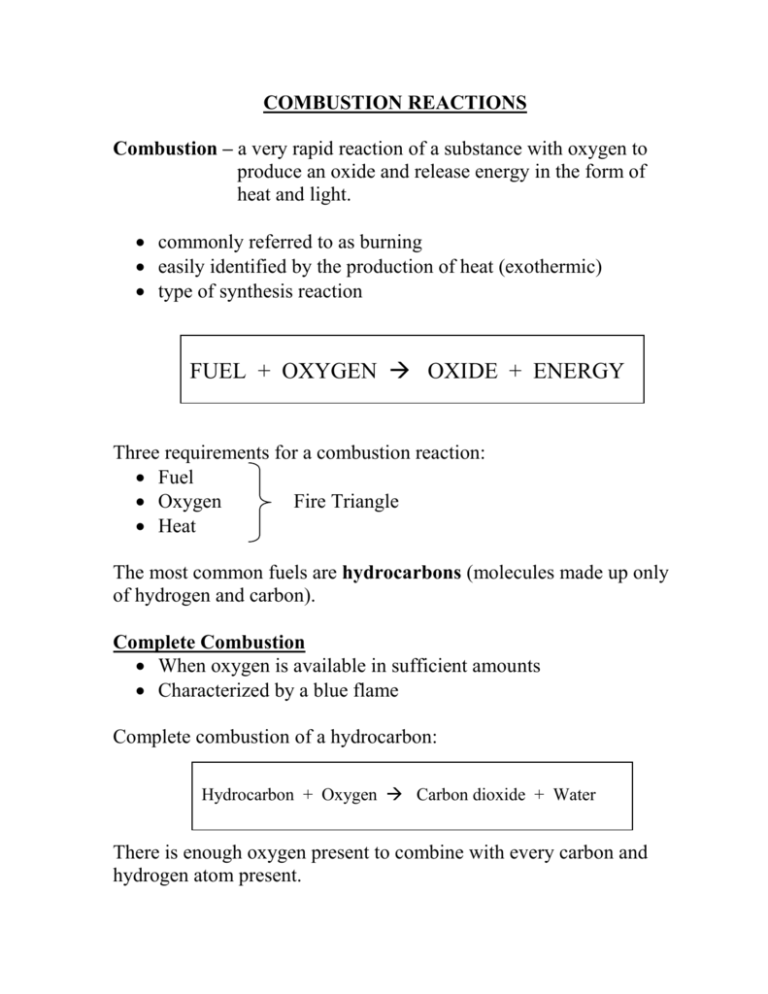
COMBUSTION REACTIONS Combustion – a very rapid reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce an oxide and release energy in the form of heat and light. commonly referred to as burning easily identified by the production of heat (exothermic) type of synthesis reaction FUEL + OXYGEN OXIDE + ENERGY Three requirements for a combustion reaction: Fuel Oxygen Fire Triangle Heat The most common fuels are hydrocarbons (molecules made up only of hydrogen and carbon). Complete Combustion When oxygen is available in sufficient amounts Characterized by a blue flame Complete combustion of a hydrocarbon: Hydrocarbon + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water There is enough oxygen present to combine with every carbon and hydrogen atom present. Incomplete Combustion If not enough oxygen is present, incomplete combustion occurs Characterized by an orange “dirty” flame Incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon: Hydrocarbon + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Carbon + Carbon + Water Monoxide An incomplete combustion reaction may produce any combination of the carbon containing products, however it MUST include water. Incomplete combustion can be characterized by the presence of black “soot” which indicates the presence of solid carbon. Carbon monoxide is a clear, colourless gas which is highly poisonous. Due to its similar size to diatomic oxygen, the hemoglobin in the blood bind to the carbon monoxide depriving the brain of oxygen. Examples: Complete combustion of pentane (C5H12) C5H12 + 8 O2 5 CO2 + 6 H2O Incomplete combustion of octane (C8H18) C5H12 + 7 O2 C5H12 + 5 O2 Or 4 CO2 + C + 6 H2O 4 CO + C + 6 H2O








