Compliance Guideline for the Hazard Communication Standard
advertisement

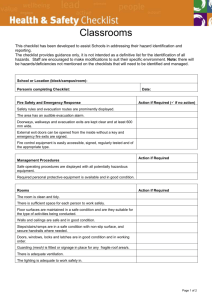
Compliance Guideline for the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) This is the most frequently cited OSHA standard. The purpose of the regulation is to ensure that employees who are, or may be exposed to hazardous substances understand the physical and health hazards associated with these substances so that appropriate steps may be taken to protect themselves. Unlike other chemical regulations, there is no minimum quantity exemption for this regulation. Even a small bottle of a "hazardous substance" on an employee's desk is sufficient to require an employer to develop a hazard communication standard program. The standard can be divided into five elements. You must comply with all of the elements to avoid citations. The elements are: 1. Develop a written program which documents the steps for compliance. 2. Prepare a list of all hazardous substances used in the workplace. Keep this list up-to-date. 3. Compile Material Safety Data Sheets on the hazardous substances used in the workplace and make them available to all employees. 4. Ensure that all hazardous substance containers are properly labeled. 5. Conduct training classes for all affected employees. Many sheet metal contractors handle substances that contain a mixture of chemicals, for example, cleaners, adhesives, etc. According to this OSHA standard, if the mixture contains 1% or more of a listed "hazardous substance," the mixture itself is considered a hazardous substance. If the mixture includes 0.1% or more of a cancer causing agent, the mixture would be considered a hazardous substance. If you are not sure whether the product is a hazardous substance, it is suggested that you assume that it is unless you are notified otherwise by the manufacturer or supplier. You should perform the following actions to comply with the OSHA standard. 1. Prepare a written Hazard Communication compliance program. The written program should be concise, accurate, and contain the following information: a. an explanation of how you will meet the requirements of labeling, b. collecting and maintaining Material Safety Data Sheets, and c. providing employee training and information. 2. Conduct an inventory to determine whether you have any hazardous substances at your shop or on your worksites. The list should include the product name, manufacturer name and the address and location where the product is being used in your facility. 3. Review the Company's Material Safety Data Sheets. If, based upon the results of the hazardous substance inventory, there are missing Material Safety Data Sheets; send a written request for a copy of the document to the manufacturer, importer or distributor of the product. Keep a copy of the request letter. 4. Ensure all products are properly labeled. Generally, the manufacturer or distributor assumes this responsibility. However, it is your responsibility to ensure completeness of the label. If you are buying products in bulk and transfer product in smaller containers, it is your responsibility to label these secondary containers. 5. Conduct Employee training. You should conduct training sessions with all affected employees to explain: a. the elements of the regulation, b. how chemicals affect the body, c. how to read a Material Safety Data Sheet and label, and d. what steps to take for additional information. Training should always be well-documented. At a minimum, have a sign-in sheet and an outline of the topics covered. Be sure to give employees an opportunity to ask questions during the training. EXHIBIT B - HAZCOM CHEMICAL INVENTORY LIST For SMACNA MEMBER COMPANY NAME METALS: WELDING ROD: GASES: Prepainted Galvanized Steel ER 316LP Welding Rod 100% Nitrogen Galvanized Iron Steel ER70S-6 Wire 95% Argon, 5% Oxygen Aluminum Aluminum ER4043 100% Oxygen Galvanized Electrolitic E 8018W2 Welding Rod 100% Argon Type 316, 304 Stainless Steel Stainless Steel ER316L Wire 100% Acetylene Mild Steel (Hot/Cold Rolled) Aluminum ER5356 75% Argon, 25% Carbon Dioxid Copper E-7018 Welding Rod 35% Hydrogen, 65% Nitrogen Lead E-6011 Welding Rod 100% Carbon Dioxide Silicon Bronze A5.7/ER Cusi-A 98% Argon, 2% Oxygen ACIDS: Flux Cored Steel E71T-GS Mig Wire E 100 All Sol Flux 50/50 Tin Lead Solder Alloy 90% Helium, 7.5% Argon, 2.5% Carbon Dioxide Propane La-Co Regular Flux Paint Sal Ammoniac CHEMICALS: SEALERS & GLUES Solder Paste Delo 400 30W Motor Oil 999A Silicone Glazing Compound Muratic Acid AW ISO 150 Machine Oil Vulcum 921 Metal Etch Kerosene Putty Hardener 0200 Surfuric Acid Isopropyl Alcohol Sikaflex Automatic Transmission Oil 795 Plastic Adhesive PLASTICS: Lubricating Oil Foster Fos-Stik 85-45 Polyproplyne Gasoline Ductmate 795 Caulking Plexiglass Acetone Vulkem 116 Visqueen Aluminum Putty Aluminum Gutterseal Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Goof-Off Remover United Duct Sealer 3174 Anti-Seize Compound Bitumastic 300M A&B PAINTS: Petrofer Spiral Pipe Mach. Oil Spray Adhesive Spray Paint Penetrant/Lubricant Glas Grip 925/901/658 Spray Primer Diesel 7000 Neoprene Mineral Thinner Loctite EPDM Adhesive Metal Primer CRC 3-36 Lacquer Thinner Tap Magic Cutting Fluid Synthetic Reducer CRC Zinc Re Nu Carboline 134 Part A & B 795 Building Sealant Rain Patch Roofing Cement FIBERGLASS: United Duct Sealer 3438 Ductboard Waterproofing Membrane Rock Wool 732 Multi Purpose Sealant Sound Attenuation Richard’s APEX