1. Draw a pie chart to show the gases that make up our atmosphere
advertisement

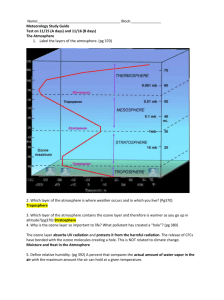
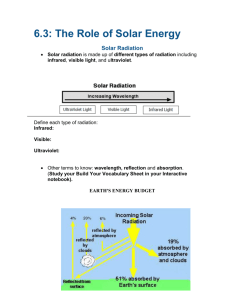
1. Draw a pie chart to show the gases that make up our atmosphere. Which gas can range from 04%? Why is this gas important? 78% nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, 0.93% argon, remainder is other gases Water vapor- causes weather, also is a greenhouse gas 2. Complete the blanks _warm_________ air rises and is less dense. __cool__________ air sinks and is more dense. (cool, warm) ___Cool_____________ air has high pressure. _____Warm_____________ air has low pressure. (cool, warm) Air pressure ____decreases_______________ with increasing altitude. (increases, decreases) 3. Label the following diagram with the layers of the atmosphere. Write how the temperature changes with altitude. Give the approximate location of the ozone layer and ionosphere. Thermosphere temp increases, part of the ionosphere Mesosphere temp decreases, part of the ionosphere Stratosphere temp increases, ozone layer Troposphere temp decreases 4. How many atoms of oxygen make up one molecule of ozone? 3 Why is ozone in the stratosphere good? Absorbs UV radiation from the sun Why is ozone in the troposphere bad? Is an air pollutant and contributes to smog 5. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. 1. What type(s) of energy is emitted from the SUN? All forms of electromagnetic radiation except gamma rays. Most of what reaches the Earth’s surface is visible light 2. What type of energy is emitted from the EARTH? Infrared radiation 3. What are four common greenhouse gases? . Carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrous oxide, methane 4. What would the Earth be like without greenhouse gases? Would be significantly colder because infrared radiation that is re-radiated from the Earth’s surface would be lost to space 6. Heat flows from objects with ____high________ temperature to _______low______ temperature. (low, high) 7. Define and give an example for each of the methods of heat transfer: -conduction- heat transfer in which molecules come in contact with one another Exp. A pan becomes hot when placed on the hot coils of the stovetop. The air in the lower atmosphere is warmed by coming in contact with the surface of the Earth. -convection- method of heat transfer in which heat flows through a moving fluid (air and water). Convection currents in our atmosphere transfer heat through rising and falling warm and cool air. Example- Convection ovens. Convection currents in the atmosphere and in the ocean. -radiation- method of heat transfer that travels in the form of waves of electromagnetic radiation (can travel through empty space) Exp. Microwave oven, solar radiation 8. What are the 2 main reasons for global winds? (Hint: Think about pressure and rotation of Earth) 1. differences in air pressure caused by difference in temperature. Warm air has low density and rises, creating regions of low pressure. Cold air has higher density and sinks, creating regions of high pressure. Wind will move from regions of high to low pressure. 2. The rotation of the Earth causes the Coriolis effect. Winds are deflected away from their intended target (the poles or the Equator) because the Earth rotates out from under them. Winds bend to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. 9. Complete the following diagram. Label: trade winds, polar easterlies, westerlies, doldrums, and horse latitudes. Show the direction of wind in each wind belt. 10. Draw and label a diagram for each: land breeze, sea breeze, valley breeze mountain breeze. Be sure to include the time of day, pressure conditions, where air is rising/falling, and which way the wind is blowing.

![wind [Repaired]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009822995_1-d740f770c04b871f35a8b5ad3684a975-300x300.png)