Supporting information_Dec08
advertisement

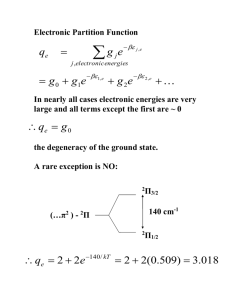
Supporting Information for Molecular Vibrations of Methane Molecules in the Structure I Clathrate Hydrate from Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Simulation Masaki Hiratsuka, Ryo Ohmura, Amadeu K. Sum, and Kenji Yasuoka* Vibrational modes of methane molecule There are nine vibrational modes (15 degrees of freedom – 3 translations – 3 rotations), which are classified into four kinds of vibrational types, such as three bending, two rocking, one symmetric stretching, and three asymmetric stretching vibrational types. The small scattered vibrational spectra in bending vibrations are possibly resulting from the three complex types of degenerated motions. The animated images and frequencies shown here to illustrate the type of vibrational mode were calculated in harmonic approximation using simulation package CPMD. (These schemes were not calculated from molecular dynamics simulations). The calculation was based on the Density Functional Theory. The basis set and treatment of the exchange correlation terms were the same as the computation of the clathrate hydrate in the article. Only one methane molecule was in the box and the lattice length was 11.83 Å. The actual vibrational frequencies and spectra for the clathrate hydrate in article were generated from the ab initio MD simulations. 1 Bending: three degenerated motions (1260 cm-1). Rocking: two degenerated motions (1502 cm-1). Symmetric stretching: no degenerated motion (2962 cm-1). Asymmetric stretching: three degenerated motion (3075 cm-1). 2 Autocorrelation functions The autocorrelation function CAA is calculated by following equation The physical value A is defined for five autocorrelation functions: velocity of hydrogen atoms, change in the C-H bond length, change in the H-C-H angle, change in the C-H vector direction, and center of mass velocity of the methane molecule. The mathematical expression and the computed autocorrelation functions for guest molecules in small and large cages are shown as following. The red and green lines show autocorrelation functions in the small and large cages, respectively. Velocity of hydrogen atoms 3 C-H bond length H-C-H angle: Angle made by two C-H bonds, bond1 and bond2 in following equation, in a methane molecule. 4 C-H direction Direction is defined as the angle between standard direction rCH(0) vector and rCH(t) vector. Velocity of center of molecule The values of i in the following equation are the atoms in the methane molecule: four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. 5 Animation of the methane molecule in the cages The animations of the methane molecule in the small and large cages are extracted from trajectory of the Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics simulation from 5 ps to 9 ps. 6