Effect of spin injection on the superconducting properties in La0
advertisement
Effect of injected spins with different polarized orientations on the
superconductivity of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3/La1.85Sr0.15CuO4 thin films
M. J. Zhang1, Y. W. Yin1,a), T. S. Su1, M. L. Teng1, D. L. Zhang1, X. G. Li1,b), L. J. Zou2
1
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, Department of Physics,
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, P. R. China
2
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Institute of Solid State Physics, Chinese Academy of
Sciences, Hefei 230031, P. R. China
Supplementary information
S1. Magnetization loops with the magnetic field applied parallel and perpendicular to
the film plane:
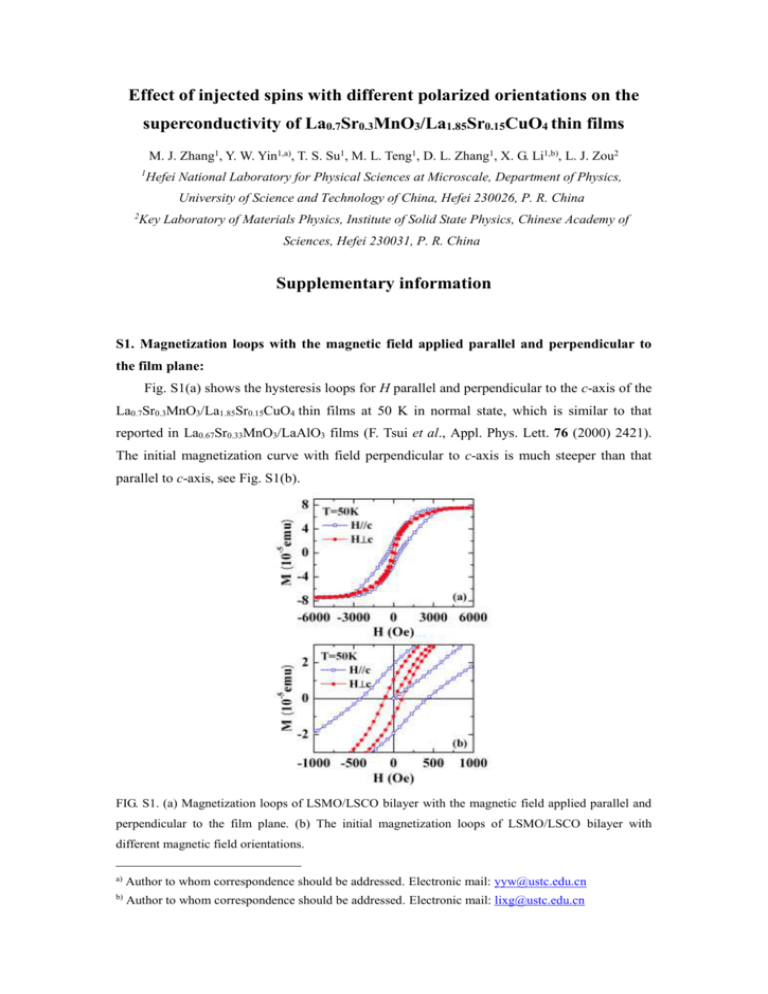
Fig. S1(a) shows the hysteresis loops for H parallel and perpendicular to the c-axis of the
La0.7Sr0.3MnO3/La1.85Sr0.15CuO4 thin films at 50 K in normal state, which is similar to that
reported in La0.67Sr0.33MnO3/LaAlO3 films (F. Tsui et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 76 (2000) 2421).
The initial magnetization curve with field perpendicular to c-axis is much steeper than that
parallel to c-axis, see Fig. S1(b).
FIG. S1. (a) Magnetization loops of LSMO/LSCO bilayer with the magnetic field applied parallel and
perpendicular to the film plane. (b) The initial magnetization loops of LSMO/LSCO bilayer with
different magnetic field orientations.
a)
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Electronic mail: yyw@ustc.edu.cn
b)
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Electronic mail: lixg@ustc.edu.cn
S2. Determination of the flux pinning potential U for flux motion:
The flux pinning potential for flux motion, U0(H), is determined by fitting the resistive
transition broadening curves according to Arrhenius law (T ) 0 exp{U 0 ( H )(1 t ) n / k BT } ,
see Fig. S2. All these resistive transition broadening data can be well described by the
Arrhenius dependence, which is a characteristic of thermally-activated flux flow (TAFF).
FIG. S2. Semilogarithmic ρ-1/T polts for sample with various magnetic fields perpendicular and
parallel to c-axis. The red solid lines are the fittings to the data in the TAFF region.
S3. The atomic force microscopy (AFM) image of single LSCO layer surface:
Fig. S3 shows the AFM image obtained on a 45 nm single LSCO film. The LSCO
surface exhibits a step-and-terrace morphology, with a step height of 0.4 nm. The films are
atomically flat with a root-mean-square (RMS) roughness of 0.3 nm, determined over the
scan area 5×5 m2. The high morphological quality of the LSCO film confirms the epitaxial
growth of LSMO layer and promises the excellent interface contact of the bilayer.
FIG. S3. AFM image of 45 nm-thick single LSCO film surface with an RMS roughness of 0.3 nm.
![Photoinduced Magnetization in RbCo[Fe(CN)6]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/005886955_1-3379688f2eabadadc881fdb997e719b1-300x300.png)