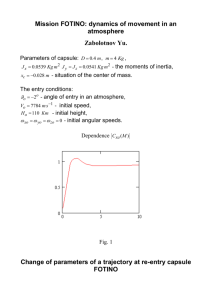
pH dependence of kinetic isotope effects support/provide
advertisement

On line supplementary material The pH dependence of kinetic isotope effects in monoamine oxidase A indicates stabilisation of the neutral amine in the enzyme-substrate complex. Rachel V. Dunn, Ker Marshall, Andrew W. Munro, Nigel S. Scrutton Faculty of Life Sciences, Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, University of Manchester, 131 Princess Street, Manchester, M1 7DN, UK. 0.16 0.14 A 0.12 -1 kcat (s ) 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.00 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 pH 1.8 B 1.6 -1 -1 kcat/Km (s mM ) 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 pH Fig S1. pH dependence of the steady-state kinetic parameters of MAO A-catalysed oxidation of benzylamine at 20 oC. (A) Plot of kcat versus pH. (B) Plot of kcat/Km versus pH. 0.10 0.09 A 0.08 0.07 -1 kred (s ) 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.00 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 8.5 9.0 9.5 pH 3.0 B 2.0 -1 kred/Ks (s mM ) 2.5 -1 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 pH Fig. S2. pH dependence of the reductive half-reaction of MAO A-catalysed oxidation of benzylamine at 20 oC. (A) Plot of kred versus pH. (B) Plot of kred/Ks versus pH. 0.09 0.085 Relative absorbance 0.08 0.075 0.07 0.065 0.06 0.055 0.05 0.045 0.04 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Time (s) Fig. S3. Reaction transient for MAO A-catalysed oxidation of 0.5 mM PEA at pH 9.0, 20 oC. The data (black line) were fit to an equation for a double exponential decay with offset (grey line). 0.07 0.065 Relative absorbance 0.06 0.055 0.05 0.045 0.04 0.035 0.03 0.025 0.02 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Time (s) Fig. S4. Reaction transient for MAO A-catalysed oxidation of 0.4 mM benzylamine at pH 8.5, 20 oC. The data (black line) were fit to an equation for a double exponential decay with offset (grey line). 3.5 3.0 2.5 -1 k (s ) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 PEA (mM) Fig. S5. Substrate dependence of the reductive half-reaction of MAO A-catalysed oxidation of PEA at pH 8.5, 20 oC. The rate at each concentration is the average of at least three replicates, and the error is the standard deviation. The data were fit to the equation y = (kcat*x)/(Ks+x); the errors in the limiting rate of flavin reduction and the substrate binding constant are those determined from curve fitting.