Periodic Trend Notes c4 Honors re: 9/11 JG Periodic Trends Notes
advertisement

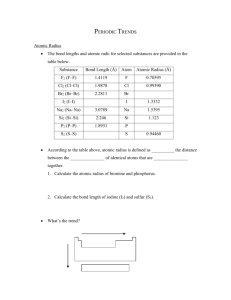
Periodic Trend Notes c4 Honors re: 9/11 JG Periodic Trends Notes from 9/21 WHAT IS A PERIODIC TREND? -a predictable change that repeats ex: seasons, months, days of the week, school day ATOMIC RADIUS: one-half of the distance from the nucleus of two like atoms. TREND ACROSS a period (left to right): DECREASES EXPLANATION: electrons enter the SAME energy level, as protons and electrons are added the force between the protons and electrons increase.The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus making the atom smaller. TREND DOWN a family: INCREASES EXPLANATION: as electrons are added to more energy levels,the inner layers shield the outer electrons from the pull of the nucleus. The added electrons have less attraction to the nucleus due to this shielding effect, increasing the atom’s size IONIZATION ENERGY: the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a specific atom TREND ACROSS a period(left to right): INCREASES EXPLANATION: the atom’s radius decreases, the electrons are held tighter by the nucleus, so it will take more energy to remove an electron. TREND DOWN a family: DECREASES EXPLANATION: the atom’s radius increases, the electrons are held less tightly by the nucleus, so it will take less energy to remove an electron. Electronegativity: the attraction of an atom for an additional electron. TREND ACROSS a period(left to right): INCREASES EXPLANATION: the atom’s radius decreases,the nucleus has a stronger pull on an extra electron TREND DOWN a family: DECREASES EXPLANATION: the atom’s radius increases, the nucleus has a weaker hold onan extra electron Ionic Radius: positive ions become smaller and negative ions become bigger than their neutral atom. Other Notes: valence electrons: number of electrons in the outermost energy level isoelectronic: same number of electrons These were not the only notes given in class you must check with a friend the make other additions to these basic notes!