Practice key
advertisement
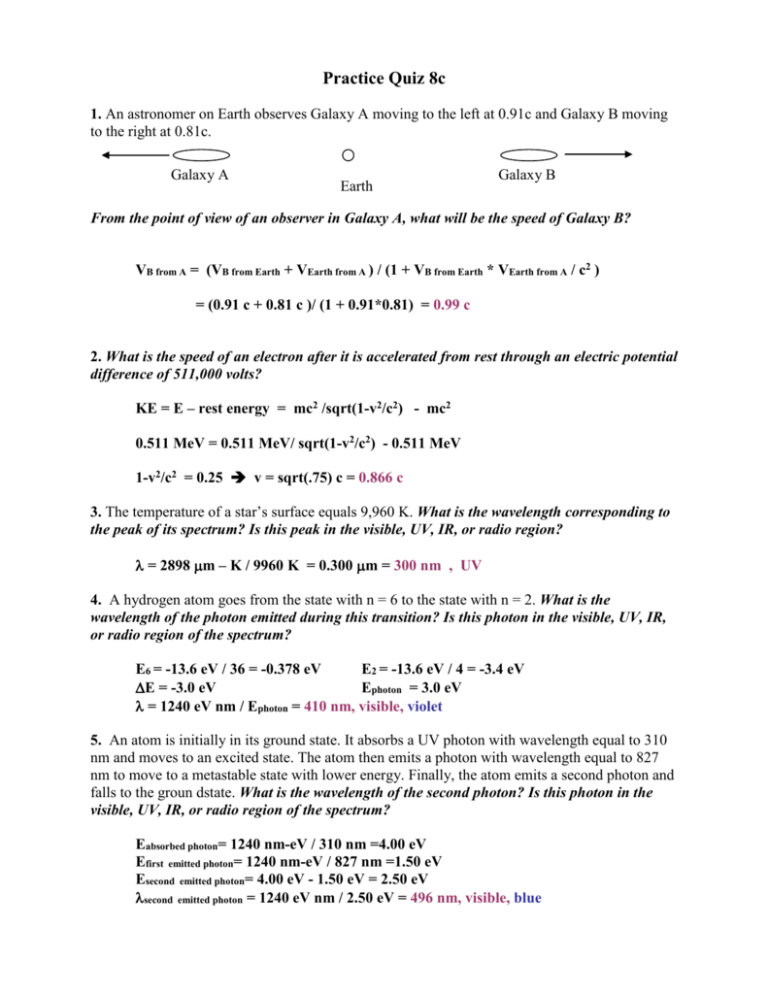
Practice Quiz 8c 1. An astronomer on Earth observes Galaxy A moving to the left at 0.91c and Galaxy B moving to the right at 0.81c. Galaxy A Earth Galaxy B From the point of view of an observer in Galaxy A, what will be the speed of Galaxy B? VB from A = (VB from Earth + VEarth from A ) / (1 + VB from Earth * VEarth from A / c2 ) = (0.91 c + 0.81 c )/ (1 + 0.91*0.81) = 0.99 c 2. What is the speed of an electron after it is accelerated from rest through an electric potential difference of 511,000 volts? KE = E – rest energy = mc2 /sqrt(1-v2/c2) - mc2 0.511 MeV = 0.511 MeV/ sqrt(1-v2/c2) - 0.511 MeV 1-v2/c2 = 0.25 v = sqrt(.75) c = 0.866 c 3. The temperature of a star’s surface equals 9,960 K. What is the wavelength corresponding to the peak of its spectrum? Is this peak in the visible, UV, IR, or radio region? = 2898 m – K / 9960 K = 0.300 m = 300 nm , UV 4. A hydrogen atom goes from the state with n = 6 to the state with n = 2. What is the wavelength of the photon emitted during this transition? Is this photon in the visible, UV, IR, or radio region of the spectrum? E6 = -13.6 eV / 36 = -0.378 eV E2 = -13.6 eV / 4 = -3.4 eV E = -3.0 eV Ephoton = 3.0 eV = 1240 eV nm / Ephoton = 410 nm, visible, violet 5. An atom is initially in its ground state. It absorbs a UV photon with wavelength equal to 310 nm and moves to an excited state. The atom then emits a photon with wavelength equal to 827 nm to move to a metastable state with lower energy. Finally, the atom emits a second photon and falls to the groun dstate. What is the wavelength of the second photon? Is this photon in the visible, UV, IR, or radio region of the spectrum? Eabsorbed photon= 1240 nm-eV / 310 nm =4.00 eV Efirst emitted photon= 1240 nm-eV / 827 nm =1.50 eV Esecond emitted photon= 4.00 eV - 1.50 eV = 2.50 eV second emitted photon= 1240 eV nm / 2.50 eV = 496 nm, visible, blue