Electrons as Waves
advertisement

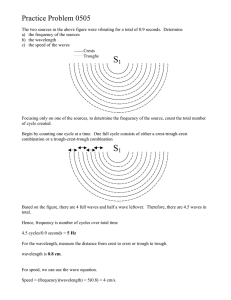
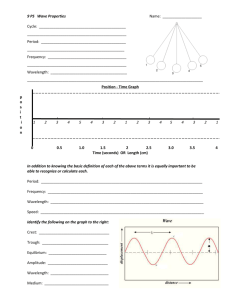
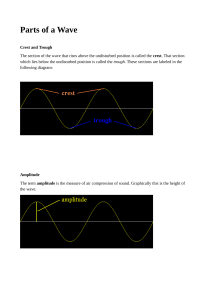
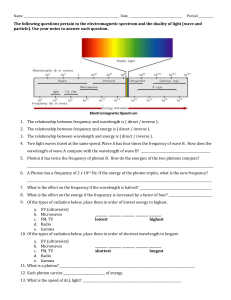
Wavelength ◦ The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave; either crest to crest or trough to trough ◦ Measured in m Frequency ◦ the number of waves that pass a given point per second; one hertz (Hz) equals one wave per second Amplitude ◦ The wave's height from the origin to crest or origin to trough ◦ Measured in m As shown in the formula, if wavelength increases, frequency decreases. As wavelength decreases, frequency increases. speed c =λυ = speed of light = 3.00 x 108 m/s If a gamma ray traveling at the speed of light has a frequency of 2.88 x 1021Hz, what is its wavelength? speed = λ υ 3.00 x 108 m/s = λ (2.88 x 1021 Hz) Answer: λ = 1.04 x 10-13 m Energy will increase as frequency increases E=hυ ◦ h is a constant = 6.626 x 10-34 Js A photon has an energy of 2.93 x 10 -25J. What is its frequency? E=hυ 2.93 x 10-25 J = (6.626x10-34 Js) υ Answer: υ = 4.42 x 105 Hz or 442,000 Hz What is the energy of an ultraviolet photon that has a wavelength of 1.18 x 10-8m? ◦E=hυ But wait? Do we have frequency? No? So…Find it! ◦ Speed = c = λ υ 3.00 x 108m/s = (1.18 x 10-8m) υ υ = 2.54 x 1016 ◦ Now solve for the energy E = (6.626 x 10-34 Js) (2.54 x 1016) E = 1.68 x 10-17 J