G.GPE.4-7.12.8.11
advertisement
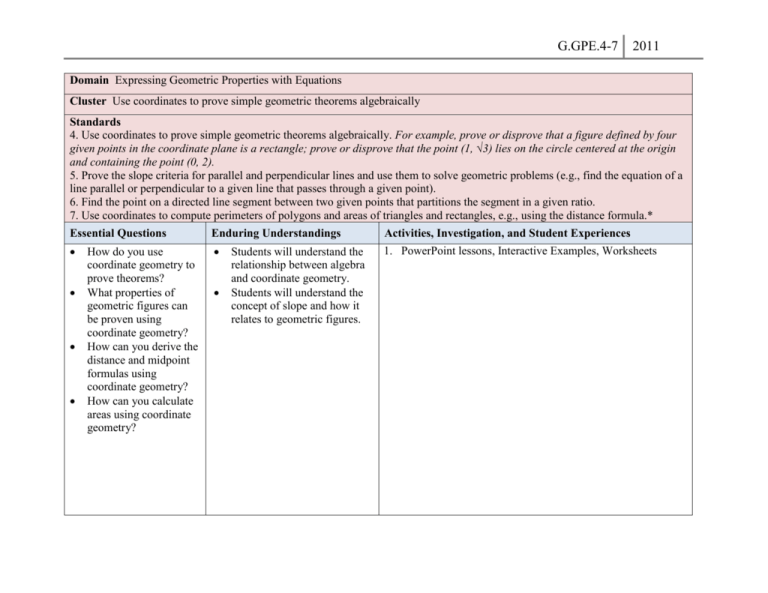
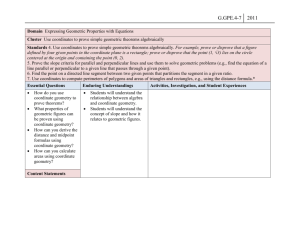
G.GPE.4-7 2011 Domain Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations Cluster Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically Standards 4. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). 5. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). 6. Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. 7. Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula.* Essential Questions Enduring Understandings How do you use coordinate geometry to prove theorems? What properties of geometric figures can be proven using coordinate geometry? How can you derive the distance and midpoint formulas using coordinate geometry? How can you calculate areas using coordinate geometry? Students will understand the relationship between algebra and coordinate geometry. Students will understand the concept of slope and how it relates to geometric figures. Activities, Investigation, and Student Experiences 1. PowerPoint lessons, Interactive Examples, Worksheets G.GPE.4-7 Content Statements Students will be able to use coordinate geometry to prove geometric theorems algebraically. Students will be able to use slope to prove lines are parallel or perpendicular. Students will be able to find equations of lines based on certain slope criteria such as finding the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point. Students will be able to find a point on a line segment that divides the segment into a given ratio when given two points. Students will be able to use coordinate geometry and the distance formula to find the perimeters of polygons and the areas of triangles and 2011 G.GPE.4-7 2011 rectangles. Assessments Student Participation Questioning Quizzes (Teacher Given and Self Quizzes) Benchmark/Test Homework Equipment Needed: SMARTboard Projector Paper and pencil Calculator (Graphing and Scientific) Compass Protractor Ruler Straightedge Graph Paper Isometric Dot Paper Hands-on and virtual two- and three-dimensional manipulatives (i.e. prisms) Geo-boards Geometer’s Sketchpad Teacher Resources: 1. Math Warehouse Website: http://www.mathwarehouse.com/algebra/linear_equation/par allel-perpendicular-lines.php G.GPE.4-7 2011