ALGEBRA 1 MATHEMATICS STANDARDS
advertisement
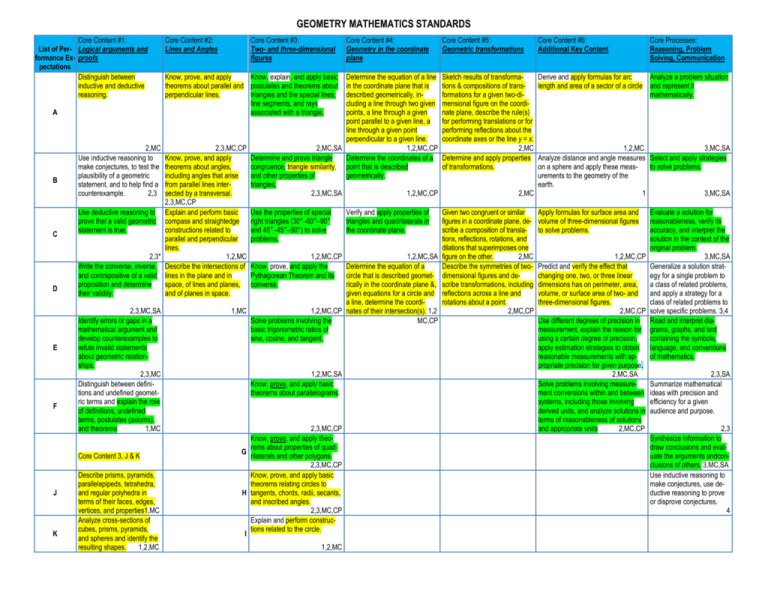
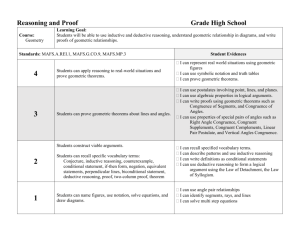
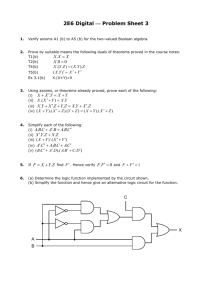
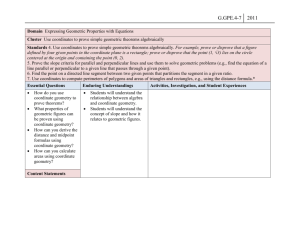
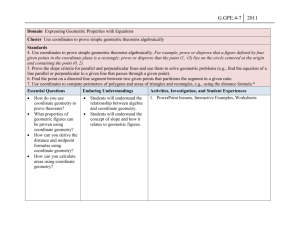
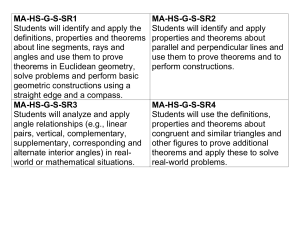
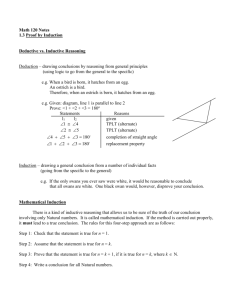
GEOMETRY MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Core Content #1: List of Per- Logical arguments and formance Ex- proofs pectations Distinguish between inductive and deductive reasoning. A B C D E F 2,MC Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures, to test the plausibility of a geometric statement, and to help find a counterexample. 2,3 Use deductive reasoning to prove that a valid geometric statement is true. 2,3* Write the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of a valid proposition and determine their validity. 2,3,MC,SA Identify errors or gaps in a mathematical argument and develop counterexamples to refute invalid statements about geometric relationships. 2,3,MC Distinguish between definitions and undefined geometric terms and explain the role of definitions, undefined terms, postulates (axioms), and theorems 1,MC Core Content 3, J & K J K Describe prisms, pyramids, parallelepipeds, tetrahedra, and regular polyhedra in terms of their faces, edges, vertices, and properties1,MC Analyze cross-sections of cubes, prisms, pyramids, and spheres and identify the resulting shapes. 1,2,MC Core Content #2: Lines and Angles Core Content #3: Two- and three-dimensional figures Know, prove, and apply Know, explain, and apply basic theorems about parallel and postulates and theorems about perpendicular lines. triangles and the special lines, line segments, and rays associated with a triangle. Core Content #4: Geometry in the coordinate plane Determine the equation of a line in the coordinate plane that is described geometrically, including a line through two given points, a line through a given point parallel to a given line, a line through a given point perpendicular to a given line. 2,3,MC,CP 2,MC,SA 1,2,MC,CP Know, prove, and apply Determine and prove triangle Determine the coordinates of a theorems about angles, congruence, triangle similarity, point that is described including angles that arise and other properties of geometrically. from parallel lines intertriangles. sected by a transversal. 2,3,MC,SA 1,2,MC,CP 2,3,MC,CP Explain and perform basic Use the properties of special Verify and apply properties of compass and straightedge right triangles (30°–60°–90° triangles and quadrilaterals in constructions related to and 45°–45°–90°) to solve the coordinate plane. parallel and perpendicular problems. lines. 1,2,MC 1,2,MC,CP 1,2,MC,SA Describe the intersections of Know, prove, and apply the Determine the equation of a lines in the plane and in Pythagorean Theorem and its circle that is described geometspace, of lines and planes, converse. rically in the coordinate plane &, and of planes in space. given equations for a circle and a line, determine the coordi1,MC 1,2,MC,CP nates of their intersection(s). 1,2 Solve problems involving the MC,CP basic trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine, and tangent. 1,2,MC,SA Know, prove, and apply basic theorems about parallelograms. 2,3,MC,CP Know, prove, and apply theorems about properties of quadG rilaterals and other polygons. 2,3,MC,CP Know, prove, and apply basic theorems relating circles to H tangents, chords, radii, secants, and inscribed angles. 2,3,MC,CP Explain and perform constructions related to the circle. I 1,2,MC Core Content #5: Geometric transformations Core Content #6: Additional Key Content Core Processes: Reasoning, Problem Solving, Communication Sketch results of transformations & compositions of transformations for a given two-dimensional figure on the coordinate plane, describe the rule(s) for performing translations or for performing reflections about the coordinate axes or the line y = x. 2,MC Determine and apply properties of transformations. Derive and apply formulas for arc Analyze a problem situation length and area of a sector of a circle and represent it mathematically. Given two congruent or similar figures in a coordinate plane, describe a composition of translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations that superimposes one figure on the other. 2,MC Describe the symmetries of twodimensional figures and describe transformations, including reflections across a line and rotations about a point. 2,MC,CP Apply formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional figures to solve problems. 1,2,MC. 3,MC,SA Analyze distance and angle measures Select and apply strategies on a sphere and apply these measto solve problems. urements to the geometry of the earth. 2,MC 1 3,MC,SA Evaluate a solution for reasonableness, verify its accuracy, and interpret the solution in the context of the original problem. 1,2,MC,CP 3,MC,SA Predict and verify the effect that Generalize a solution stratchanging one, two, or three linear egy for a single problem to dimensions has on perimeter, area, a class of related problems, volume, or surface area of two- and and apply a strategy for a three-dimensional figures. class of related problems to 2,MC,CP solve specific problems. 3,4 Use different degrees of precision in Read and interpret diameasurement, explain the reason for grams, graphs, and text using a certain degree of precision, containing the symbols, apply estimation strategies to obtain language, and conventions reasonable measurements with apof mathematics. propriate precision for given purpose. 2,MC,SA 2,3,SA Solve problems involving measureSummarize mathematical ment conversions within and between ideas with precision and systems, including those involving efficiency for a given derived units, and analyze solutions in audience and purpose. terms of reasonableness of solutions and appropriate units 2,MC,CP 2,3 Synthesize information to draw conclusions and evaluate the arguments andconclusions of others. 3,MC,SA Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures, use deductive reasoning to prove or disprove conjectures. 4