AGAA Unit 2 Plan (Geometric and Algebraic Connections)

Accelerated Geometry B/ Advanced Algebra
Unit 2: Geometric and Algebraic Connections Name ________________________________
Essential Question: How do I apply what I have learned about coordinate geometry to a real-world situation?
DAY STANDARD TOPIC LESSON ASSIGNMENT CREDIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.1
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.1
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.5
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.6
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.7
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.4
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.4
All Unit 2 Standards
All Unit 2 Standards
Equations of Circles
Solving Systems of Parabolas and Lines;
Solving Systems of Circles and Lines
Slopes: Parallel and Perpendicular
QUIZ on Circles, Systems, and Slopes
Perimeter/Area and Partitions
Coordinate Proofs
More Coordinate Proofs
Review Unit 2
UNIT 2 TEST
5-2
4-4 & 5-2
+
+
5-1 +
5-1 +
+ Not in our text book (see provided worksheets, etc.)
Standards for the Unit:
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.1
Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.4
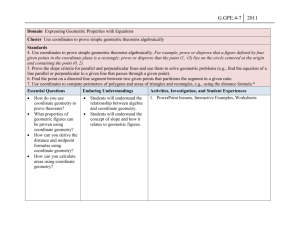
Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0,2). (Focus on quadrilaterals, right triangles, and circles.)
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.5
Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point).
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.6
Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio.
MGSE9-12.G.GPE.7
Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula.