How to build a Planck constant apparatus using LEDs
advertisement
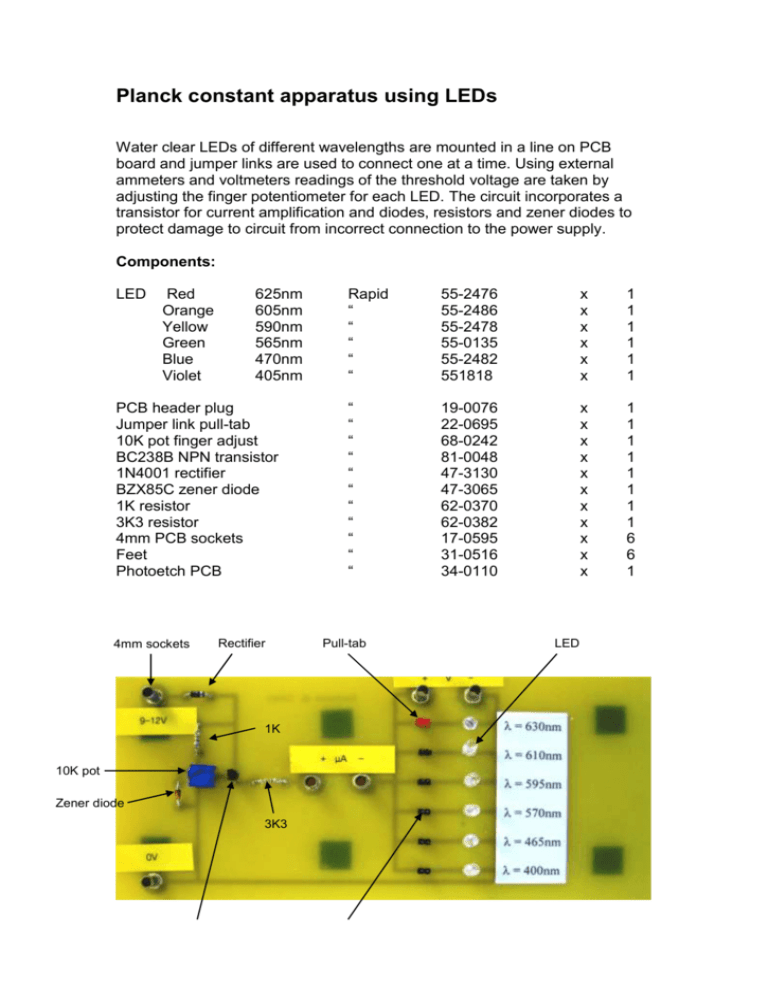
Planck constant apparatus using LEDs Water clear LEDs of different wavelengths are mounted in a line on PCB board and jumper links are used to connect one at a time. Using external ammeters and voltmeters readings of the threshold voltage are taken by adjusting the finger potentiometer for each LED. The circuit incorporates a transistor for current amplification and diodes, resistors and zener diodes to protect damage to circuit from incorrect connection to the power supply. Components: LED Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet 625nm 605nm 590nm 565nm 470nm 405nm PCB header plug Jumper link pull-tab 10K pot finger adjust BC238B NPN transistor 1N4001 rectifier BZX85C zener diode 1K resistor 3K3 resistor 4mm PCB sockets Feet Photoetch PCB 4mm sockets Rectifier 1K 10K pot Zener diode 3K3 Rapid “ “ “ “ “ 55-2476 55-2486 55-2478 55-0135 55-2482 551818 x x x x x x 1 1 1 1 1 1 “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ 19-0076 22-0695 68-0242 81-0048 47-3130 47-3065 62-0370 62-0382 17-0595 31-0516 34-0110 x x x x x x x x x x x 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 6 1 Pull-tab LED NPN transistor PCB Header PCB used (actual size) The design We decided to build new equipment for this experiment as the previous set up had loose LEDs which got mixed up, lost and broken legs due to bending. The new design has made the labelling wavelength of the LEDs clear. The equipment is easy to store and put out as everything is attached to one board. When physics students have worked with LEDs in the past we have come across the misconception that the colour of the light emitted was due to the filtering action of the coloured plastic. When choosing LEDs for this apparatus we chose LEDs with clear plastic casings so that it is clear to the students that it is coloured light that is being produced by the electrons moving across the junction. We also thought that labelling the LEDs just with their wavelength made the students draw a stronger link between colour and wavelength and made them practice converting wavelength in nm to frequency in Hz. We have built in some protection against damage by misuse: A diode to stop problems with reverse polarity connection to the power. A zener diode, resistor and transistor to limit the voltage and prevent damage by too high a supply voltage A resistor to limit the current so that the intensity of light from the LEDs does not damage the eyes We spent some time choosing the LEDs to get a fairly good straight line. The problem with the experiment is that not all of the LEDs are made from the same substance so there are different work functions for different colours. By being pragmatic in our choice of LEDs we have avoided some difficult explanations of anomalies which would obscure the main teaching point for most students. If you decide to select your own LEDs it is worth buying a range of devices and experimenting to get a good spread of points which produce a fairly good straight line – you may even decide to use uncertainty of the wavelength in the specification to aid the production of a straight line.